How do you know if your body is fighting a virus

Viruses, microscopic invaders, stealthily attack our bodies, leaving us feeling unwell. Recognizing the body's valiant fight against these unwelcome guests is crucial for proactive healthcare. This article will delve into the telltale signs and symptoms that reveal your body is actively battling a viral infection. By understanding the body's defense mechanisms, we empower ourselves to seek timely medical attention and make informed decisions to support our recovery.
Recognizing the Signs: Is Your Body Fighting a Virus?
Your body is a complex system, and its response to a viral infection can manifest in many ways. Identifying these signs early can be crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. While some symptoms overlap with other illnesses, certain indicators strongly suggest your body is actively combating a virus. It's important to remember that self-diagnosis is unreliable, and if you're concerned about your health, you should always consult a medical professional.
1. Fever and Chills
A fever, often accompanied by chills, is a classic sign of a viral infection. Your body raises its temperature to inhibit viral replication. Chills are your body's attempt to generate heat. The severity of the fever varies depending on the virus and your individual response. A mild fever may resolve on its own, while a high fever may require medical attention. It's crucial to monitor your temperature and seek medical help if it's excessively high or persistent.
2. Fatigue and Weakness
Extreme fatigue and overall weakness are common symptoms. Your immune system is working overtime to fight the virus, leading to a significant energy drain. This feeling of exhaustion can persist even after other symptoms have subsided. Rest is crucial during this phase to allow your body to recover and rebuild its energy reserves.
3. Muscle Aches and Body Pains
Many viral infections cause muscle aches and body pains (myalgia). This is partly due to your body's inflammatory response to the virus. These aches can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the virus and individual susceptibility. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the discomfort.
4. Respiratory Symptoms
Respiratory symptoms, such as a cough, sore throat, runny nose, and congestion, are frequently associated with viral infections, particularly those affecting the respiratory system. These symptoms arise from the virus's impact on the mucous membranes lining your airways. The severity of these symptoms can vary widely.
5. Gastrointestinal Issues
Some viruses, particularly those causing gastroenteritis ("stomach flu"), can lead to gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms are caused by the virus infecting the cells lining your digestive tract. These symptoms can cause dehydration, so it's essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
| Symptom | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | Elevated body temperature | Mild to severe |
| Fatigue | Extreme tiredness and weakness | Mild to severe |
| Muscle Aches | Pain in muscles | Mild to severe |
| Cough | Airway irritation | Mild to severe |
| Sore Throat | Inflammation of the throat | Mild to severe |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Stomach upset | Mild to severe |
| Diarrhea | Loose, watery stools | Mild to severe |
https://youtube.com/watch?v=pf1dBxYlxPo%26pp%3DygUII2FzaW1tdW4%253D
How do you feel when your immune system is fighting a virus?
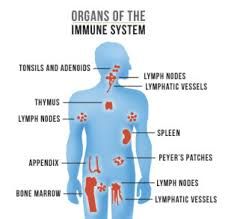
When your immune system is fighting a virus, you experience a range of symptoms, the severity of which depends on several factors, including the specific virus, your overall health, and the strength of your immune response. The body's reaction isn't a single, unified feeling, but rather a complex interplay of responses designed to eliminate the invader. You might feel perfectly fine if your immune system swiftly and efficiently neutralizes the virus before it can cause significant damage. However, if the virus manages to replicate and spread, you'll likely experience various symptoms related to your body's defense mechanisms and the virus's effects on your cells and tissues.
Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most common symptoms is fatigue, often profound and debilitating. This is your body's way of conserving energy to focus resources on fighting the infection. It’s not just simple tiredness; it's a deep-seated exhaustion that persists even after rest. This extreme tiredness is due to your body diverting energy away from non-essential functions to bolster the immune response. Weakness often accompanies fatigue, making even simple tasks feel challenging.
- Reduced energy levels: You might find yourself needing to rest frequently and having difficulty concentrating.
- Muscle aches: Muscle weakness and soreness are common due to the body's inflammatory response.
- General malaise: A feeling of overall unwellness and discomfort pervades your being.
Fever and Chills
Fever is a crucial part of your immune system's response. Your body increases its core temperature to inhibit viral replication and enhance immune cell activity. This rise in temperature is often accompanied by chills, a sensation of coldness despite a rising body temperature. This paradox reflects the body's attempt to generate heat to combat the infection.
- Elevated body temperature: A fever can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Shivering and shaking: Chills are your body's attempt to increase its internal temperature.
- Sweating: As your fever breaks, you may experience significant sweating.
Headache and Body Aches
Headaches and body aches (myalgia) are also frequent companions of a viral infection. The inflammation and immune response can cause pain throughout the body. These aches are often described as generalized muscle pain rather than localized pain from a specific injury. The headache can result from inflammation, dehydration, or the body's overall stress from fighting the virus.
- Generalized pain: Pain can affect muscles, joints, and even bones.
- Headache intensity: The severity can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
- Sensitivity to light and sound: Some individuals experience photophobia and phonophobia.
Respiratory Symptoms
Many viruses target the respiratory system, leading to symptoms like cough, sore throat, and runny or stuffy nose. These symptoms arise because the virus is directly affecting the cells in your airways, causing inflammation and irritation. The body's attempt to clear the virus from the airways results in the production of mucus and coughing.
- Coughing: This is the body's attempt to expel mucus and irritants from the airways.
- Sore throat: Inflammation of the throat lining can cause pain and discomfort.
- Nasal congestion: Inflammation and mucus production can lead to a stuffy or runny nose.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Some viruses can affect the digestive system, causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This is less common than respiratory symptoms but can still be a significant part of the illness experience. These symptoms are likely due to the virus's direct effect on the gastrointestinal tract or an indirect effect through the body's inflammatory response.
- Nausea and vomiting: These can lead to dehydration if severe.
- Diarrhea: Frequent bowel movements can also lead to dehydration.
- Abdominal cramps: Pain and discomfort in the abdomen are also possible.
How do you know a virus is leaving your body?

Unfortunately, there's no single definitive sign that a virus is completely gone from your body. Viral infections are complex, and your body's immune response varies. While some symptoms might lessen or disappear, this doesn't guarantee the virus's complete eradication. Detection methods, such as PCR tests, can show the presence of viral genetic material, but even a negative test doesn't always guarantee complete clearance, as trace amounts might remain undetectable. The disappearance of symptoms is often the best indicator, but it's crucial to understand that this isn't a perfect measure. Your body is constantly working to clear the infection, and this process often takes time and may involve periods of symptom improvement and relapse, depending on the virus and your immune system.
Symptoms Gradually Subside
The most common sign that your body is fighting off a viral infection is the gradual reduction and eventual disappearance of symptoms. This is a result of your immune system successfully neutralizing the virus and reducing its replication. The timeline varies significantly, dependent on the virus's type and the strength of your immune response. Some people may experience a complete resolution of symptoms within a few days or weeks, while others might have lingering effects for a longer duration. It’s important to note that this gradual improvement doesn’t directly measure the viral load, only the symptoms.
- Fever subsides: A decreasing fever usually indicates the body's inflammatory response is waning.
- Cough and congestion lessen: Reduced respiratory symptoms usually signify improvement in lung function and viral clearance.
- Energy levels return: Feeling less fatigued indicates the immune system is no longer battling intensely.
Increased Energy and Improved Well-being
As your body recovers from a viral infection, you'll typically experience a gradual return to your normal energy levels and overall well-being. This doesn't necessarily mean the virus is completely gone, but it reflects your body's improved ability to function despite the infection. This restoration of energy and well-being is a positive sign of recovery, but is not a guarantee that the virus has been completely eradicated. The recovery time varies greatly among individuals.
- Improved sleep quality: Restful sleep is a sign of reduced inflammation and stress on the body.
- Increased appetite: A return to normal eating habits signals a decline in the overall impact of illness.
- Improved mood: Feeling less irritable or depressed indicates that your system is recovering.
Negative Viral Tests
While not always definitive, a negative viral test can suggest a reduced or absent viral load. Different tests have different sensitivities, meaning some might detect even small amounts of the virus while others might require a higher viral load to be detected. A negative PCR test, for example, means that the test couldn't detect any viral genetic material at the time of testing. However, this doesn't always mean the virus is entirely gone, as it might still be present at levels below the test's detection limit or in areas not sampled.
- PCR tests: Detect the presence of viral genetic material.
- Antigen tests: Detect viral proteins.
- Antibody tests: Detect the presence of antibodies produced in response to the virus, indicating a past infection, not necessarily current presence.
Medical Professional Assessment
Seeking advice from a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate assessment of your recovery. Doctors can assess your symptoms, consider your medical history, and potentially order further tests to help determine the extent of the infection and your recovery progress. They can offer guidance on when you can safely return to normal activities and provide treatment if necessary. Regular check-ups can be particularly valuable for individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Physical examination: A doctor can check for lingering symptoms.
- Medical history review: Helps determine the severity and duration of infection.
- Further testing: Blood tests or imaging can be ordered to assess organ function.
How to tell if your body is fighting an infection?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-bacterial-infection-7705652_final-2f1b8b2429b2495c8333b584512d3afa.jpg)
Your body has a complex immune system designed to fight off infections. When an infection invades – whether it's a virus, bacteria, fungus, or parasite – your body initiates a defense mechanism, triggering various signs and symptoms. These responses vary in severity depending on the type and severity of the infection, your overall health, and your immune system's strength. Recognizing these signals is crucial for seeking timely medical attention if needed. Many symptoms overlap with other conditions, so it's vital to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Infection
Several common signs indicate your body is actively fighting an infection. These are often nonspecific, meaning they can manifest with various illnesses. Fever is a classic sign, representing your body's attempt to create an inhospitable environment for pathogens. Chills often accompany fever, resulting from your body trying to raise its temperature. Fatigue, or unusual tiredness, is another frequent symptom as your immune system works to combat the infection. Other signs include:
- Muscle aches and pains: These aches often indicate inflammation as your body's defense mechanisms are activated.
- Headache: An infection can trigger inflammation, resulting in headaches.
- Sore throat: This indicates inflammation in the throat, frequently linked to viral or bacterial infections.
Elevated Body Temperature (Fever)
A fever is a significant indicator of infection. Your body raises its core temperature to inhibit the growth of infectious agents. The severity of the fever can vary, but a temperature above 100.4°F (38°C) is generally considered a fever. It's crucial to monitor your temperature regularly, and if it remains high or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seek medical attention.
- Use a reliable thermometer: Ensure accurate measurement for proper assessment.
- Monitor temperature fluctuations: Note any significant increases or decreases.
- Consult a doctor: If your fever is high, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms.
Inflammation and Swelling
Inflammation is a key aspect of your body's immune response. It's characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain in the affected area. This response occurs as white blood cells rush to the site of infection to fight off pathogens. Inflammation is a natural part of the healing process, but excessive or persistent inflammation can indicate a severe infection.
- Observe the affected area: Look for signs of redness, swelling, and heat.
- Monitor for pain: Increased pain may signal a worsening infection.
- Seek medical attention: If inflammation is severe, widespread, or not improving.
Changes in Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small glands located throughout your body that are part of the lymphatic system, playing a critical role in fighting infections. When your body is battling an infection, these lymph nodes may become swollen and tender. This swelling indicates that your lymph nodes are working hard to filter out pathogens and produce immune cells to combat the infection.
- Check for swelling in the neck, armpits, or groin: These are common areas for lymph nodes.
- Feel for tenderness: Swollen lymph nodes are often painful to the touch.
- Consult a doctor if you notice significant or persistent swelling.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Infections can also affect the gastrointestinal tract, leading to various symptoms. These symptoms often manifest as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. These symptoms frequently result from viral or bacterial infections. Severe or persistent gastrointestinal issues can lead to dehydration, requiring prompt medical attention.
- Monitor frequency and severity of symptoms: Track the duration and intensity of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration.
- Seek medical attention: If symptoms are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other alarming signs.
How do you flush out a viral infection?

There's no single method to "flush out" a viral infection in the way you might flush out a contaminant. Viruses work by invading and replicating within your cells. Your body's immune system is the primary mechanism for combating viral infections. While you can't directly "flush" them out, you can support your immune system to fight the infection more effectively and hasten recovery. This involves focusing on rest, hydration, and overall good health practices.
Supporting Your Immune System
Your immune system is your body's defense against viruses. A strong immune system is crucial for effectively fighting off a viral infection. You can bolster your immune system by ensuring you're getting adequate rest, nutrition, and managing stress levels. This approach helps your body combat the infection naturally.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight off infections.
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods that provide your body with the vitamins and minerals it needs to function optimally.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can suppress the immune system, making you more susceptible to illness.
Hydration is Key
Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health and helps your body function optimally during an illness. Fluids help flush out toxins and keep your mucous membranes moist, aiding in the removal of viruses from your system. This doesn't directly kill viruses, but helps your body's natural processes.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider electrolyte drinks if you're experiencing significant fluid loss through vomiting or diarrhea (always consult a doctor first).
- Avoid sugary drinks which can dehydrate you further.
Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest is critical for your body to repair and fight off infection. When you're sick, your body needs energy to combat the virus, and sleep is crucial for this process. Pushing yourself too hard can prolong illness and hinder recovery.
- Get plenty of sleep each night.
- Avoid strenuous activities.
- Listen to your body and rest when you need to.
Over-the-Counter Medications
While over-the-counter medications won't directly "flush out" a virus, they can help manage symptoms. Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce fever and aches, while decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion. Always follow the instructions on the label and consult a doctor if you have concerns or underlying health conditions.
- Use pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to reduce fever and pain.
- Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion.
- Do not self-medicate – always consult a doctor or pharmacist before taking any medication, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many viral infections resolve on their own, it's important to seek medical attention if your symptoms are severe or worsen. This is especially true if you experience difficulty breathing, persistent high fever, severe dehydration, or other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can be crucial in managing complications.
- Seek medical attention if you have difficulty breathing.
- Consult a doctor if you have a persistent high fever (over 103°F or 39.4°C).
- If you are severely dehydrated or experience worsening symptoms, seek immediate medical care.
What are the common symptoms of a viral infection?
Many symptoms can indicate your body is fighting a virus. These symptoms often overlap with other illnesses, making diagnosis tricky without a medical professional's input. However, some common indicators include fever, often accompanied by chills and sweats. This is your body's immune system attempting to raise its temperature to inhibit viral replication. You might also experience fatigue, feeling unusually tired and lacking energy. This is partly due to your immune system working overtime and partly due to the virus itself weakening your body. Muscle aches and pains are also frequent, a sign of inflammation and your body’s response to the infection. A runny or stuffy nose, along with sore throat and cough, are typical respiratory symptoms. Headache is also common, potentially related to inflammation or the virus itself affecting the brain. Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can occur with some viral infections, particularly those affecting the stomach and intestines. Finally, some viral infections can cause a rash or skin changes. It's crucial to remember that the severity and combination of these symptoms can vary greatly depending on the specific virus and your individual health. If you experience severe symptoms or are concerned, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
How long does it typically take for symptoms to appear after viral exposure?
The incubation period – the time between exposure to a virus and the appearance of symptoms – varies significantly depending on the specific virus. Some viruses have very short incubation periods, with symptoms appearing within a day or two of exposure. Others have much longer incubation periods, lasting several days, weeks, or even longer. For example, the common cold often shows symptoms within one to three days, while the flu might take one to four days. On the other hand, viruses like HIV can have much longer incubation periods, sometimes remaining undetected for years. Several factors influence the incubation period, including the viral load (the amount of virus you were exposed to), your overall health (a weakened immune system might prolong the incubation period), and the specific strain of the virus itself. There is no single answer to how long it takes for symptoms to show after exposure. If you believe you may have been exposed to a virus, it is important to monitor yourself for symptoms and seek medical attention if you become seriously ill. The absence of symptoms during the incubation period doesn’t guarantee you haven't been infected.
Are there any specific tests to confirm a viral infection?
While many viral infections are diagnosed based on symptoms and a physical examination, there are also several specific tests that can confirm a viral infection. These tests can identify the specific virus causing the illness. One common method is a viral culture, where a sample (e.g., from your nose, throat, or blood) is grown in a lab to identify the virus. This process can take several days to yield results. Rapid antigen tests provide faster results, detecting viral proteins within minutes, but might not be as accurate as viral cultures. Molecular tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, are extremely sensitive and can detect even tiny amounts of viral genetic material, offering accurate results. These tests are commonly used for infections like influenza and COVID-19. Antibody tests detect the presence of antibodies your body has produced in response to a viral infection, indicating past exposure. These tests are useful for diagnosing past infections or determining immunity. The choice of test depends on the suspected virus, the urgency of diagnosis, and the resources available. A healthcare professional will determine the most appropriate test based on your symptoms and medical history. It’s important to consult a doctor for proper testing and diagnosis.
When should I seek professional medical attention for a suspected viral infection?
While many viral infections resolve on their own, it’s crucial to know when to seek professional medical advice. You should seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, persistent high fever, severe headache, stiff neck, confusion, or seizures. These symptoms can indicate a more serious complication or a secondary bacterial infection. If your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after a reasonable period (e.g., several days to a week for common viral infections), it's important to consult a doctor. Dehydration, due to vomiting or diarrhea, is another serious concern, requiring medical evaluation. Certain underlying medical conditions (like weakened immune systems) make individuals more vulnerable to complications from viral infections, necessitating prompt medical attention. Similarly, individuals belonging to high-risk groups (such as the elderly or pregnant women) should seek medical advice even for seemingly mild symptoms. Finally, if you are unsure whether your symptoms are due to a viral infection or something else, seeking medical evaluation is always the safest course of action. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent complications. A healthcare professional can provide accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and prevent any unnecessary delays in care.
Deja una respuesta