What vitamins are good for mouth ulcers

The discomfort and pain associated with mouth ulcers can be a significant annoyance. While they usually heal on their own within a few weeks, there are steps that can be taken to potentially speed up the healing process. One factor that may contribute to the development and severity of mouth ulcers is a deficiency in certain vitamins. In this article, we will delve into the specific vitamins that have been linked to oral ulceration and explore their role in supporting oral health.
Which Vitamins Can Help Heal Mouth Ulcers?
While no vitamin directly cures mouth ulcers (also known as aphthous ulcers), several vitamins and nutrients play a crucial role in supporting the body's natural healing processes and can help reduce the severity and duration of these painful sores. The key is to focus on a balanced diet rich in these nutrients rather than relying on supplements alone. Always consult a doctor or dentist if you have persistent or severe mouth ulcers.
Vitamin B12's Role in Mouth Ulcer Healing
Vitamin B12 is essential for cell growth and repair, making it vital for healing mouth ulcers. A deficiency in B12 can lead to various health problems, including oral lesions. While a deficiency is a direct cause of ulcers in some cases, supplementing with B12 alone might not always suffice. A balanced approach to addressing any underlying deficiency, along with good oral hygiene, is crucial for effective treatment.
The Importance of Vitamin B Complex for Oral Health
The B vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and B9 (folate), work synergistically to support the body's immune function and cell regeneration processes. A deficiency in any of these can compromise the body's ability to heal effectively, making it harder to fight off infections and heal mouth ulcers. Consuming a diet rich in foods containing these vitamins, or taking a B complex supplement under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may provide benefits.
Vitamin C's Antioxidant Properties and Ulcer Healing
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system and plays a critical role in collagen production. Collagen is a key structural protein in tissues, including the mouth lining. Adequate vitamin C levels help in wound healing, making it beneficial for faster recovery from mouth ulcers. However, consuming excessive amounts of vitamin C is not recommended.
Iron's Contribution to Mouth Ulcer Healing
Iron deficiency is a common cause of oral manifestations, including mouth ulcers. Iron is crucial for red blood cell production and oxygen transport, both essential for tissue repair. Addressing an iron deficiency, if present, is crucial for healing mouth ulcers and improving overall health. Always get an iron level test from your doctor before supplementing.
Zinc's Role in Immune Function and Ulcer Healing
Zinc is a vital mineral for immune function and wound healing. It plays a role in cell growth and repair, and deficiencies can impair the body's ability to fight off infections, making mouth ulcers worse and slower to heal. Ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation (after consulting a doctor) can be beneficial.
| Vitamin/Mineral | Role in Mouth Ulcer Healing | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | Supports cell growth and repair | Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy |
| B Complex Vitamins | Supports immune function and cell regeneration | Whole grains, legumes, leafy green vegetables |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, supports collagen production | Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers |
| Iron | Essential for red blood cell production and oxygen transport | Red meat, spinach, lentils |
| Zinc | Supports immune function and wound healing | Oysters, nuts, seeds, beans |
Which Vitamins Can Help Heal Mouth Ulcers?
While no vitamin directly cures mouth ulcers (also known as aphthous ulcers), several vitamins and nutrients play a crucial role in supporting the body's natural healing processes and can help reduce the severity and duration of these painful sores. The key is to focus on a balanced diet rich in these nutrients rather than relying on supplements alone. Always consult a doctor or dentist if you have persistent or severe mouth ulcers.
Vitamin B12's Role in Mouth Ulcer Healing
Vitamin B12 is essential for cell growth and repair, making it vital for healing mouth ulcers. A deficiency in B12 can lead to various health problems, including oral lesions. While a deficiency is a direct cause of ulcers in some cases, supplementing with B12 alone might not always suffice. A balanced approach to addressing any underlying deficiency, along with good oral hygiene, is crucial for effective treatment.
The Importance of Vitamin B Complex for Oral Health
The B vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and B9 (folate), work synergistically to support the body's immune function and cell regeneration processes. A deficiency in any of these can compromise the body's ability to heal effectively, making it harder to fight off infections and heal mouth ulcers. Consuming a diet rich in foods containing these vitamins, or taking a B complex supplement under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may provide benefits.
Vitamin C's Antioxidant Properties and Ulcer Healing
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system and plays a critical role in collagen production. Collagen is a key structural protein in tissues, including the mouth lining. Adequate vitamin C levels help in wound healing, making it beneficial for faster recovery from mouth ulcers. However, consuming excessive amounts of vitamin C is not recommended.
Iron's Contribution to Mouth Ulcer Healing
Iron deficiency is a common cause of oral manifestations, including mouth ulcers. Iron is crucial for red blood cell production and oxygen transport, both essential for tissue repair. Addressing an iron deficiency, if present, is crucial for healing mouth ulcers and improving overall health. Always get an iron level test from your doctor before supplementing.
Zinc's Role in Immune Function and Ulcer Healing
Zinc is a vital mineral for immune function and wound healing. It plays a role in cell growth and repair, and deficiencies can impair the body's ability to fight off infections, making mouth ulcers worse and slower to heal. Ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation (after consulting a doctor) can be beneficial.
| Vitamin/Mineral | Role in Mouth Ulcer Healing | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | Supports cell growth and repair | Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy |
| B Complex Vitamins | Supports immune function and cell regeneration | Whole grains, legumes, leafy green vegetables |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, supports collagen production | Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers |
| Iron | Essential for red blood cell production and oxygen transport | Red meat, spinach, lentils |
| Zinc | Supports immune function and wound healing | Oysters, nuts, seeds, beans |
What vitamin are you lacking when you get mouth ulcers?
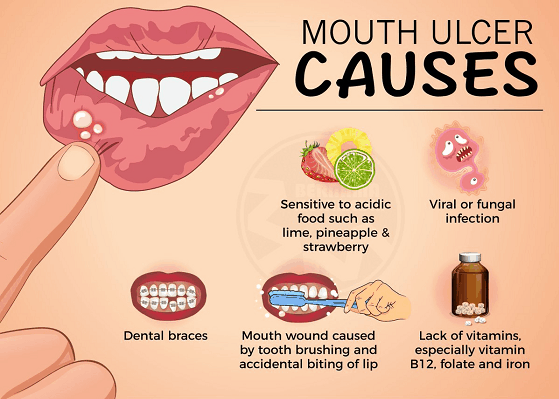
While mouth ulcers, also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores, can have various causes, a deficiency in certain vitamins, particularly vitamin B12, can be a contributing factor. Other B vitamins, such as B2 (riboflavin) and B9 (folic acid), also play a role in maintaining healthy oral mucosa. A deficiency in these vitamins can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to mouth ulcers. However, it's crucial to remember that mouth ulcers aren't solely caused by vitamin deficiencies; other factors like stress, injury, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions can also trigger them. It's always best to consult a doctor or dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B deficiencies that may manifest in the mouth?
Symptoms of vitamin B deficiencies, especially B12, can significantly impact oral health. Beyond mouth ulcers, you might experience other oral manifestations. These include glossitis (inflammation of the tongue), which may present as a swollen, smooth, or red tongue. Cheilitis (inflammation of the lips) might also occur, leading to cracked or sore lips. Furthermore, a burning sensation in the mouth or tongue can be another indication. Remember, these symptoms aren't exclusive to vitamin B deficiencies and could be indicative of other underlying health problems. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis.
- Glossitis: Inflammation of the tongue, causing swelling, redness, and a smooth appearance.
- Cheilitis: Inflammation of the lips, often resulting in cracking, soreness, and bleeding.
- Burning mouth syndrome: A persistent burning sensation in the mouth, even without visible sores.
How does vitamin B12 contribute to oral health?
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and health of the oral mucosa, the lining of the mouth. It is crucial for cell growth and repair, including the cells that make up the lining of the mouth and the tissues that provide support and function. A deficiency in B12 can impair this process, making the mouth more vulnerable to injury and thus more susceptible to the formation of mouth ulcers. This is because a deficiency can weaken the immune response, making the body less efficient in repairing damaged tissues.
- Cell growth and repair: B12 is essential for the formation and maintenance of healthy oral tissues.
- Immune system support: Adequate B12 levels help ensure a healthy immune response, protecting against infection and promoting healing.
- Prevention of inflammation: Sufficient B12 contributes to reducing inflammation in the mouth, reducing the likelihood of ulcers.
What are other potential causes of mouth ulcers besides vitamin deficiencies?
While vitamin deficiencies are a factor, many other causes contribute to mouth ulcers. Stress is a common trigger, as it can weaken the immune system, making you more vulnerable. Minor injuries, like biting your cheek or accidentally scraping your mouth, can also cause ulcers. Hormonal changes, particularly during menstruation, can also be linked to their development. Furthermore, certain medical conditions such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, and Behçet's disease, can increase susceptibility to mouth ulcers. Lastly, certain medications and food sensitivities can be contributing factors.
- Stress: Weakening the immune system and making the body more susceptible to ulcers.
- Minor injuries: Accidental trauma to the mouth lining.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormone levels, particularly during menstruation.
How can I increase my intake of B vitamins?
Boosting your intake of B vitamins through diet is an excellent first step. Foods rich in B vitamins include meat (especially liver), poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and leafy green vegetables. Fortified foods like cereals and nutritional yeast can also be good sources. However, for individuals with suspected deficiencies, a healthcare professional can recommend specific B vitamin supplements to address any deficiencies. Always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Dietary changes: Incorporate B-vitamin-rich foods into your daily diet.
- Supplements: Consider B vitamin supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Fortified foods: Include fortified cereals or other foods in your diet.
When should I seek professional medical advice about mouth ulcers?
While many mouth ulcers resolve on their own within a week or two, you should consult a doctor or dentist if: your ulcers are painful, persistent, or unusually large; if you experience fever, swollen lymph nodes, or other systemic symptoms alongside the ulcers; or if you notice changes in the appearance of the ulcers over time (e.g., they become unusually deep or have irregular edges). These signs could suggest a more serious underlying medical condition, requiring prompt medical attention.
- Persistent or unusually large ulcers: Ulcers that don't heal or grow excessively large.
- Accompanying symptoms: Fever, swollen glands, or other signs of infection.
- Changes in ulcer appearance: Ulcers that become deeper, irregular in shape, or change color.
What heals mouth ulcers fast?
There's no single magic cure for mouth ulcers (also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores), and healing time varies depending on the size and severity of the ulcer. However, several treatments can significantly speed up the healing process and alleviate discomfort. Over-the-counter medications and home remedies often provide relief. It's important to note that if ulcers are persistent, recurrent, or unusually large, you should consult a dentist or doctor to rule out underlying medical conditions.
Oral Anesthetic Gels and Sprays
These provide temporary pain relief. Products containing benzocaine or lidocaine numb the affected area, making eating and drinking less painful. The numbing effect doesn't heal the ulcer itself, but it significantly improves comfort while the ulcer heals naturally. Remember to follow the product instructions carefully.
- Benzocaine: A common topical anesthetic that numbs the area.
- Lidocaine: Another effective topical anesthetic with a numbing effect.
- Apply as directed – avoid excessive use.
Anti-inflammatory Mouthwashes
Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. However, hydrogen peroxide can sometimes irritate the ulcer further, so it's best to use it cautiously and only as directed. Chlorhexidine is generally better tolerated. These mouthwashes should not be swallowed.
- Chlorhexidine: Effective in reducing inflammation and fighting bacteria.
- Hydrogen peroxide: Can help clean the ulcer but may sting.
- Rinse gently and avoid swallowing.
Topical Steroid Medications
For recurrent or severe mouth ulcers, a doctor might prescribe a topical steroid medication. These potent anti-inflammatory agents can significantly reduce inflammation and pain, promoting faster healing. They are generally applied directly to the ulcer using a cotton swab or applicator. These should only be used under the guidance of a medical professional.
- Prescription required – not available over-the-counter.
- Reduces inflammation and pain quickly.
- Should only be used as directed by your doctor or dentist.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can provide relief and potentially hasten healing. These often involve gentle rinsing or application of soothing substances. While not scientifically proven to significantly speed healing, they often offer comfort. However, it’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene.
- Saltwater rinses: Help clean the area and reduce inflammation.
- Aloe vera gel: Soothes the ulcer and may promote healing.
- Avoid acidic or spicy foods and drinks which can irritate the ulcer.
Dietary Changes
Certain dietary changes can aid in healing and prevent further irritation. Avoiding acidic, spicy, or hard foods can significantly reduce pain and prevent further injury to the ulcer. Soft foods such as mashed potatoes, yogurt, and applesauce are generally easier to consume. Ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration during healing is essential.
- Soft foods are easier to eat without causing further pain.
- Avoid citrus fruits, spicy foods, and hard-to-chew items.
- Maintain a balanced diet to support healing.
What vitamin should I take for mouth sores?

There isn't one specific vitamin guaranteed to cure mouth sores. The cause of mouth sores (canker sores, cold sores, etc.) varies, and therefore the best treatment approach differs. While certain vitamins can support overall oral health and potentially aid in healing, they're not a standalone cure. A doctor or dentist should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment, especially if sores are persistent, painful, or show signs of infection.
What causes mouth sores?
Mouth sores, or ulcers, can stem from several factors. Stress is a common trigger, as are minor injuries to the mouth (like biting your cheek). Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can also contribute. Certain foods or ingredients, such as acidic fruits or nuts, might irritate the mouth and lead to sores. Finally, some individuals experience mouth sores related to underlying conditions like nutritional deficiencies or autoimmune diseases. It's crucial to understand the underlying cause to effectively treat the problem.
- Physical trauma: Accidental biting, brushing too hard, or dental work.
- Infections: Viral (like herpes simplex virus, causing cold sores), bacterial, or fungal.
- Systemic conditions: Autoimmune diseases like Behçet's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or nutritional deficiencies.
The role of B vitamins in oral health
B vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and B9 (folate), are essential for cell growth and repair, processes crucial for healing mouth sores. A deficiency in these vitamins can impair the body's ability to repair damaged tissues, potentially slowing the healing process. While supplementing with B vitamins mighthelp, it's crucial to address any underlying deficiency through a balanced diet or medical intervention rather than relying solely on supplements.
- B12: Supports nerve function and cell metabolism.
- B6: Involves in immune function and red blood cell formation.
- Folate (B9): Essential for cell division and DNA synthesis.
Vitamin C's impact on mouth sore healing
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, meaning it helps protect cells from damage. Since mouth sores represent damaged tissue, adequate vitamin C intake can theoretically promote faster healing. However, taking high doses of vitamin C won't magically cure a sore. A healthy diet rich in vitamin C-containing foods is generally sufficient, and excessive intake can lead to digestive issues.
- Antioxidant properties: Protects cells from free radical damage.
- Collagen synthesis: Supports tissue repair and wound healing.
- Immune system support: Helps the body fight off infections.
When to see a doctor or dentist about mouth sores
While minor mouth sores often heal on their own within a week or two, it's crucial to seek professional help if sores are persistent, excessively painful, bleeding excessively, or accompanied by fever, swollen lymph nodes, or other symptoms. A medical professional can accurately diagnose the underlying cause and recommend the appropriate treatment, which may include medication (like antiviral or antifungal drugs) or other interventions.
- Persistent sores: Lasting longer than two weeks.
- Severe pain: Interfering with eating, drinking, or speaking.
- Accompanying symptoms: Fever, fatigue, swollen glands.
Other factors affecting mouth sore healing
Beyond vitamins, other factors influence the healing of mouth sores. Good oral hygiene is vital – gentle brushing and rinsing with warm salt water can help keep the area clean and prevent infection. Avoiding irritating foods and maintaining adequate hydration are also important. Finally, managing stress levels can contribute to a faster recovery as stress is a common trigger for mouth sores.
- Oral hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing.
- Diet: Avoiding acidic or spicy foods.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water.
Does vitamin C get rid of mouth ulcers?

While vitamin C is essential for overall health and wound healing, there's no conclusive scientific evidence that it directly gets rid of mouth ulcers (also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores). While vitamin C plays a role in collagen production, a crucial component of tissue repair, its effect on mouth ulcers is not definitively proven to be curative. Many individuals report anecdotal relief from increased vitamin C intake, however, this is not supported by robust clinical trials. The healing process for mouth ulcers is complex and involves multiple factors beyond just vitamin C levels. Therefore, relying solely on vitamin C for treatment might not be effective for everyone.
The Role of Vitamin C in Wound Healing
Vitamin C is a crucial nutrient for collagen synthesis. Collagen is a vital protein that provides structural support to tissues, including those in the mouth. Therefore, adequate vitamin C levels are important for overall wound healing. However, this doesn't guarantee that increased vitamin C intake will specifically cure mouth ulcers. Other factors such as the immune response, the size and location of the ulcer, and overall health also significantly influence healing time.
- Collagen Production: Vitamin C is a cofactor for enzymes involved in collagen synthesis. Sufficient collagen is essential for tissue repair.
- Immune System Support: Vitamin C plays a role in immune function, bolstering the body's ability to combat infection. This indirect effect might aid healing, but doesn't directly target the ulcer.
- Antioxidant Properties: Vitamin C's antioxidant properties help protect cells from damage. This may contribute to a healthier environment for healing, but not as a primary treatment.
Other Factors Affecting Mouth Ulcer Healing
The healing of mouth ulcers is a multifaceted process influenced by several factors beyond vitamin C. Stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and minor injuries can all contribute to their development and healing process. Therefore, focusing solely on vitamin C intake may overlook these important aspects.
- Stress Levels: High stress levels can trigger or worsen mouth ulcers.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Women sometimes experience an increase in mouth ulcers during menstruation.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain autoimmune diseases and vitamin deficiencies can increase the frequency and severity of mouth ulcers.
Potential Benefits of Vitamin C Supplementation
While not a cure, adequate vitamin C intake through a balanced diet or supplements might support overall health and potentially contribute to faster healing, but the evidence is not definitive. However, it is vital to remember that excessive vitamin C intake can lead to digestive issues.
- Improved Immune Response: A strong immune system can help combat infections and promote faster wound healing.
- Enhanced Tissue Repair: Although not a direct cure for ulcers, adequate vitamin C supports the body's ability to repair tissues.
- General Health and Well-being: A healthy lifestyle with adequate vitamin C intake contributes to overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Mouth Ulcers
Several effective treatments exist for mouth ulcers, ranging from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications. Rinsing with a salt water solution, using topical anesthetic gels, and applying corticosteroids can significantly alleviate pain and accelerate healing. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially for recurrent or severe ulcers.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: These can help manage pain and discomfort.
- Topical treatments: These include gels or creams that can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Prescription medications: For severe or recurrent ulcers, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Rather than solely relying on vitamin C supplements, focusing on a balanced and nutritious diet rich in various vitamins and minerals is a more comprehensive approach to promoting good oral health and overall well-being. This approach addresses the various factors that might contribute to mouth ulcer formation and healing.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are excellent sources of vitamin C and other essential nutrients.
- Whole Grains: These provide fiber and other beneficial nutrients.
- Lean Proteins: These contribute to tissue repair and immune function.
What vitamins are commonly associated with mouth ulcer healing?
Several vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining oral health and promoting the healing of mouth ulcers. Vitamin B12, for instance, is essential for cell growth and repair, making it vital in the healing process. Deficiencies in B12 can manifest as mouth ulcers, highlighting its importance. Similarly, vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that strengthens the immune system and aids in tissue repair. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to impaired wound healing, making it more difficult for mouth ulcers to heal. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is another key player; it's involved in energy production and cell function, processes crucial for healing. Folic acid (vitamin B9) is also important for cell growth and repair, working in tandem with B12. A deficiency in this vitamin can contribute to various health problems, including mouth ulcers. While these vitamins are crucial, it's important to note that simply taking high doses of supplements isn't a guaranteed solution. A balanced diet rich in these vitamins is the most effective approach. If you suspect a vitamin deficiency contributing to your mouth ulcers, consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized advice and testing.
Can taking vitamin supplements help heal mouth ulcers faster?
While a balanced diet rich in vitamins is beneficial for overall health and may aid in mouth ulcer healing, simply taking vitamin supplements isn't a guaranteed fix, and might not even speed up the healing process significantly. The effectiveness of vitamin supplements for mouth ulcers depends largely on the underlying cause of the ulcers. If the ulcers are caused by a vitamin deficiency, supplementing with the deficient vitamin may help. However, many mouth ulcers are triggered by factors other than nutritional deficiencies, such as trauma (e.g., biting your cheek), infections (e.g., herpes simplex virus), or certain medical conditions (e.g., autoimmune diseases). In these cases, vitamin supplements alone are unlikely to be effective. Moreover, excessive intake of certain vitamins can be harmful. Overdosing on certain vitamins can lead to adverse health effects. It's crucial to consult a doctor or registered dietitian before starting any vitamin supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. They can help determine if a vitamin deficiency is contributing to your mouth ulcers and advise on the appropriate dosage and type of supplements, if needed. Focusing on a healthy and balanced diet is often the most effective and safest approach to promoting healing.
Which foods are good sources of vitamins that help with mouth ulcers?
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is crucial for obtaining the vitamins that support mouth ulcer healing. Leafy green vegetables such as spinach and kale are excellent sources of folate (vitamin B9) and vitamin C. Citrus fruits like oranges and lemons are packed with vitamin C. Dairy products, particularly fortified milk and yogurt, can provide vitamin B12. Eggs are also a good source of riboflavin (vitamin B2). Lean meats and poultry can also offer vitamin B12. Legumes such as lentils and beans contain folate. A diverse and balanced diet incorporating these food groups is the most effective way to ensure you're getting the necessary vitamins for optimal oral health. Remember that cooking methods can affect vitamin content; steaming or lightly boiling vegetables helps retain more nutrients than frying or boiling for prolonged periods. Pay attention to food variety to ensure you receive a sufficient amount of all necessary vitamins, promoting not only better wound healing but also your overall well-being.
Are there any vitamins I should avoid taking if I have mouth ulcers?
Generally, there aren't specific vitamins you should actively avoid when you have mouth ulcers. However, excessive intake of certain vitamins can be harmful and may even exacerbate the problem. For example, taking extremely high doses of vitamin A can cause symptoms such as nausea, headaches, and liver damage. Similarly, excessive vitamin C intake can cause digestive upset. It's crucial to follow the recommended daily allowances (RDAs) for vitamins and not exceed them without medical supervision. Self-treating with high doses of vitamins is not recommended, and could potentially delay proper diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause of your mouth ulcers. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any vitamin supplementation, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. They can assess your individual needs and help determine if supplementation is necessary and, if so, recommend appropriate dosages to avoid potential adverse effects. Focus on a balanced diet to obtain the vitamins you need naturally, and seek professional advice if your mouth ulcers persist or are severe.
Deja una respuesta