How to boost your immune system to fight allergies

In the realm of health and wellness, our immune system stands as a formidable defender, shielding us from a myriad of microscopic invaders. For those plagued by allergies, a weakened immune response can leave them vulnerable to the relentless attacks of pollen, dust, and other allergens. The good news is that empowering our immune system can be a powerful weapon in the battle against allergy symptoms. Let's delve into the world of immunology and explore how we can harness its power to vanquish allergies and restore respiratory harmony.
Strengthening Your Immune System for Allergy Relief
Boosting your immune system is a crucial step in managing allergies. It's not about eliminating allergies entirely, but rather about reducing the severity of your reactions and improving your body's ability to tolerate allergens. A strong immune system can help regulate the inflammatory response that triggers allergic symptoms. This means less sneezing, less itching, and potentially fewer medication needs. However, it's crucial to understand that strengthening your immune system is a long-term strategy, not a quick fix. Consistency is key, and what works for one person may not work for another. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Prioritize Sleep and Manage Stress
Sleep deprivation and chronic stress significantly weaken the immune system. Adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night) allows your body to repair and rebuild, including your immune cells. Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can suppress immune function, making you more susceptible to allergies. Effective stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help regulate your body's response to allergens and improve overall well-being. Aim for regular relaxation practices to counteract the effects of stress on your immune system.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sufficient Sleep (7-9 hours) | Immune cell regeneration, reduced inflammation |
| Yoga/Meditation | Stress reduction, improved immune regulation |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Calming effect, reduced cortisol levels |
Maintain a Balanced and Nutritious Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides your body with the essential nutrients needed to support a strong immune system. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits, combat oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing allergic reactions. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in immune function. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats, as these can negatively impact immune health.
| Food Group | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables (especially berries and leafy greens) | High in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals |
| Whole Grains | Provide fiber and essential nutrients |
| Lean Proteins | Support immune cell production |
| Probiotic-rich foods (yogurt, kefir) | Promote gut health and immune function |
Stay Hydrated and Exercise Regularly
Hydration is essential for optimal immune function. Water helps flush out toxins and supports the transportation of immune cells throughout the body. Regular physical activity boosts circulation, improves lymphatic drainage (which helps remove waste and toxins), and reduces inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. However, avoid overexertion, as intense exercise can sometimes temporarily suppress immune function.
| Activity | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drinking plenty of water | Flushing out toxins, supporting immune cell function |
| Moderate-intensity exercise (30 minutes most days) | Improved circulation, reduced inflammation, lymphatic drainage |
Supplement Wisely (Consult a Doctor First!)
Some supplements, such as vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc, have been shown to support immune function. However, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as excessive intake can be harmful. They can assess your individual needs and recommend appropriate dosages. Self-treating with supplements without professional guidance can be risky and may not be effective for allergy management.
| Supplement | Potential Benefits (Consult a doctor before use) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Supports immune cell function |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant properties, immune support |
| Zinc | Essential for immune cell function |
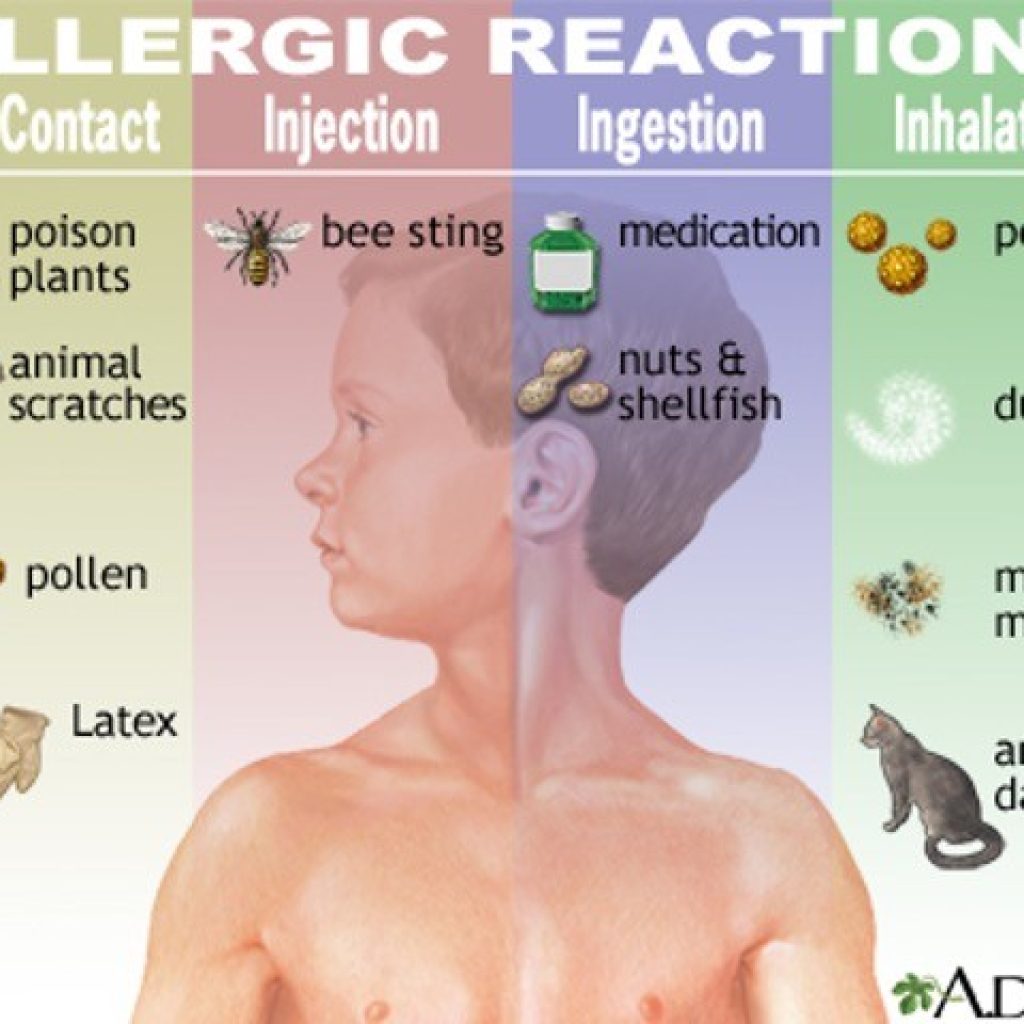
Avoid Allergens and Manage Exposure
While strengthening your immune system is important, minimizing exposure to known allergens is equally crucial. This includes identifying and avoiding trigger foods, using air purifiers, and practicing good hygiene to reduce exposure to dust mites, pollen, and pet dander. If you are unsure about your specific allergies, you should consult with an allergist for allergy testing and personalized advice to help manage your allergens effectively. Effective allergy management is a multifaceted approach that includes both strengthening the immune system and minimizing exposure to triggers. This strategy works together to improve allergy symptoms.
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Identify and Avoid Allergens | Minimize contact with substances causing allergic reactions. |
| Air Purifiers | Reduce airborne allergens in your home. |
| Good Hygiene | Reduce exposure to dust mites, pet dander, etc. |
| Allergy Testing | Identify specific allergens for targeted avoidance. |
Strengthening Your Immune System for Allergy Relief
Boosting your immune system is a crucial step in managing allergies. It's not about eliminating allergies entirely, but rather about reducing the severity of your reactions and improving your body's ability to tolerate allergens. A strong immune system can help regulate the inflammatory response that triggers allergic symptoms. This means less sneezing, less itching, and potentially fewer medication needs. However, it's crucial to understand that strengthening your immune system is a long-term strategy, not a quick fix. Consistency is key, and what works for one person may not work for another. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Prioritize Sleep and Manage Stress
Sleep deprivation and chronic stress significantly weaken the immune system. Adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night) allows your body to repair and rebuild, including your immune cells. Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can suppress immune function, making you more susceptible to allergies. Effective stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help regulate your body's response to allergens and improve overall well-being. Aim for regular relaxation practices to counteract the effects of stress on your immune system.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sufficient Sleep (7-9 hours) | Immune cell regeneration, reduced inflammation |
| Yoga/Meditation | Stress reduction, improved immune regulation |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Calming effect, reduced cortisol levels |
Maintain a Balanced and Nutritious Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides your body with the essential nutrients needed to support a strong immune system. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits, combat oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing allergic reactions. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in immune function. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats, as these can negatively impact immune health.
| Food Group | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables (especially berries and leafy greens) | High in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals |
| Whole Grains | Provide fiber and essential nutrients |
| Lean Proteins | Support immune cell production |
| Probiotic-rich foods (yogurt, kefir) | Promote gut health and immune function |
Stay Hydrated and Exercise Regularly
Hydration is essential for optimal immune function. Water helps flush out toxins and supports the transportation of immune cells throughout the body. Regular physical activity boosts circulation, improves lymphatic drainage (which helps remove waste and toxins), and reduces inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. However, avoid overexertion, as intense exercise can sometimes temporarily suppress immune function.
| Activity | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drinking plenty of water | Flushing out toxins, supporting immune cell function |
| Moderate-intensity exercise (30 minutes most days) | Improved circulation, reduced inflammation, lymphatic drainage |
Supplement Wisely (Consult a Doctor First!)
Some supplements, such as vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc, have been shown to support immune function. However, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as excessive intake can be harmful. They can assess your individual needs and recommend appropriate dosages. Self-treating with supplements without professional guidance can be risky and may not be effective for allergy management.
| Supplement | Potential Benefits (Consult a doctor before use) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Supports immune cell function |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant properties, immune support |
| Zinc | Essential for immune cell function |
Avoid Allergens and Manage Exposure
While strengthening your immune system is important, minimizing exposure to known allergens is equally crucial. This includes identifying and avoiding trigger foods, using air purifiers, and practicing good hygiene to reduce exposure to dust mites, pollen, and pet dander. If you are unsure about your specific allergies, you should consult with an allergist for allergy testing and personalized advice to help manage your allergens effectively. Effective allergy management is a multifaceted approach that includes both strengthening the immune system and minimizing exposure to triggers. This strategy works together to improve allergy symptoms.
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Identify and Avoid Allergens | Minimize contact with substances causing allergic reactions. |
| Air Purifiers | Reduce airborne allergens in your home. |
| Good Hygiene | Reduce exposure to dust mites, pet dander, etc. |
| Allergy Testing | Identify specific allergens for targeted avoidance. |
Can you build immunity to allergies?

Can You Build Immunity to Allergies?
No, you cannot build immunity to allergies in the same way you build immunity to infections like the flu or measles. Allergic reactions are caused by your immune system overreacting to a harmless substance (allergen), such as pollen, pet dander, or peanuts. This overreaction is mediated by IgE antibodies, which trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals leading to symptoms like sneezing, itching, rash or even life-threatening anaphylaxis. While your immune system doesn't develop a tolerance to these allergens in the way it does to pathogens, there are approaches that can help manage the severity of allergic reactions and sometimes reduce their frequency. These approaches focus on modifying the immune response rather than completely eliminating it.
What is an Allergy?
An allergy is a type of immune response where your body mistakenly identifies a harmless substance as a threat. This is different from an infection, where your immune system correctly responds to a dangerous pathogen. When you encounter an allergen, your immune system produces IgE antibodies that bind to mast cells. When exposed to the allergen again, the allergen binds to the IgE, triggering the release of histamine and other inflammatory molecules, leading to allergic symptoms.
- IgE antibodies are a key player in allergic reactions.
- Histamine causes many of the characteristic symptoms of allergies, such as swelling and itching.
- Allergens can vary widely, from pollen and dust mites to food and medications.
Can Immunotherapy Help?
Yes, immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT), can be effective for some allergies. These treatments involve gradually introducing increasing amounts of the allergen to your body over time. The goal is to desensitize your immune system, reducing its overreaction to the allergen. This doesn't eliminate the allergy, but it can significantly lessen the severity and frequency of symptoms. It's crucial to undergo immunotherapy under the supervision of an allergist.
- Allergy shots involve injections of gradually increasing doses of the allergen.
- Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) involves placing allergen extracts under the tongue.
- Immunotherapy is most effective for allergies to pollen, dust mites, and some types of pet dander.
Can you Outgrow Allergies?
While you can't build true immunity, some people do outgrow allergies, particularly those related to food allergies in childhood. This often happens because the immune system matures and becomes less reactive over time. However, it's not a guaranteed outcome, and some allergies persist throughout life. There's no way to predict who will outgrow an allergy and who will not.
- Food allergies are more likely to be outgrown than other types of allergies.
- Outgrowing an allergy is not a predictable process.
- Even if an allergy is outgrown, it's possible for the allergy to return.
Are There Other Management Strategies?
Besides immunotherapy, several other strategies can effectively manage allergic symptoms. These include allergen avoidance—minimizing exposure to known triggers—and medication such as antihistamines, decongestants, and corticosteroids. These medications help control symptoms but don't cure the allergy. In severe cases, emergency epinephrine might be necessary to treat anaphylaxis.
- Allergen avoidance is crucial in managing allergies.
- Antihistamines reduce the effects of histamine, relieving many allergic symptoms.
- Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications used for severe allergies.
What is the Role of Genetics in Allergies?
Genetic factors play a significant role in determining a person's susceptibility to allergies. Having a family history of allergies increases your risk of developing them yourself. This doesn't mean that having a family history guarantees you'll have allergies, but it highlights the importance of genetics in the development of allergic responses. Specific genes are associated with increased IgE production and other immune system characteristics that contribute to allergies.
- Family history is a strong predictor of allergy risk.
- Specific genes influence the production of IgE and other immune factors.
- Genetic predisposition doesn't guarantee the development of allergies, but it significantly increases the risk.
How to flush allergens out of your system?
How to Flush Allergens Out of Your System?
There's no single method to completely "flush" allergens out of your system. Allergens, once they've triggered a reaction, are processed by your body's immune system. However, you can take steps to reduce your body's allergen load and alleviate symptoms. These strategies focus on supporting your body's natural detoxification processes and minimizing further exposure. It's crucial to remember that these methods are supportive and should not replace medical advice. If you have severe allergic reactions, always consult a doctor or allergist.
Hydration is Key
Water is essential for your body's natural detoxification processes. Adequate hydration helps your kidneys and liver function efficiently, removing waste products, including some allergen byproducts, from your system. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Consider adding lemon to your water, as some believe it has cleansing properties, though scientific evidence is limited.
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Consider incorporating herbal teas known for their detoxifying properties, like dandelion or nettle tea (always check for allergies first).
- Avoid sugary drinks, which can dehydrate you.
Dietary Changes Can Help
Certain foods can support your body's detoxification efforts. Focus on a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, providing antioxidants that combat inflammation and support liver function. Probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, can also improve gut health, which plays a vital role in immunity. Minimizing processed foods, sugar, and alcohol is also crucial, as these can hinder your body's natural detoxification processes.
- Increase your intake of colorful fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants.
- Include foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Reduce or eliminate processed foods, sugar, and alcohol.
Support Your Liver and Kidneys
Your liver and kidneys are your body's primary detoxification organs. Providing them with support through diet and lifestyle can aid in the removal of waste products. Nutrients like vitamin C, glutathione, and choline are vital for liver function. Regular exercise also promotes efficient waste removal.
- Consume foods rich in Vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and berries.
- Include foods high in glutathione, like broccoli and avocados.
- Engage in regular physical activity to enhance circulation and waste removal.
Nasal Irrigation and Rinsing
If your allergies are affecting your sinuses, nasal irrigation or rinsing can help remove allergens trapped in your nasal passages. Saline nasal sprays or neti pots can be effective. However, always use sterile or distilled water to avoid infections.
- Use a saline nasal spray several times a day, as directed on the packaging.
- If using a neti pot, follow the instructions carefully and use distilled or sterile water.
- Ensure proper cleaning and storage of your neti pot to prevent bacterial growth.
Identify and Avoid Triggers
The most effective way to reduce allergen exposure is to identify and avoid your triggers. Keep a detailed allergy diary to track symptoms and potential triggers. This will help you pinpoint specific allergens to avoid and manage your symptoms more effectively. Working with an allergist can also help determine specific allergens through testing.
- Maintain a journal documenting your symptoms, meals, and environmental factors.
- Undergo allergy testing to identify specific triggers, if recommended by your doctor.
- Implement strategies to minimize exposure to identified allergens in your home and work environment.
What vitamin deficiency causes allergies?

There isn't one specific vitamin deficiency directly and definitively causingallergies. Allergies are complex immune system responses triggered by exposure to allergens (like pollen, pet dander, or food proteins). However, several vitamin deficiencies can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptibleto developing or experiencing more severe allergic reactions. It's not a cause-and-effect relationship, but rather a contributing factor to increased vulnerability.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Allergies
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune regulation. A deficiency can impair the function of immune cells, potentially leading to an overactive immune response and increased susceptibility to allergic reactions. Studies suggest a correlation between low vitamin D levels and a higher prevalence of allergies, particularly asthma and eczema. This doesn't mean low Vitamin D causesthese allergies, but that it may worsen them or make an individual more prone to developing them.
- Compromised immune response: Vitamin D deficiency weakens the immune system's ability to distinguish between harmless substances and true threats.
- Increased inflammation: Low Vitamin D levels are linked to increased inflammation throughout the body, exacerbating allergic symptoms.
- Altered immune cell function: Vitamin D helps regulate the production and activity of various immune cells, including T cells and B cells, which are vital in the allergic response.
Vitamin A Deficiency and Allergies
Vitamin A is also essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. A deficiency can impair the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, which are the body's first line of defense against allergens. This weakened barrier can increase exposure to allergens, leading to a higher risk of allergic reactions. Furthermore, Vitamin A plays a role in regulating the immune response itself.
- Weakened skin barrier: Vitamin A is vital for maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes, which serve as a physical barrier against allergens.
- Impaired immune cell function: Similar to Vitamin D, Vitamin A influences the activity of several types of immune cells involved in the allergic response.
- Increased susceptibility to infections: A weakened immune system due to Vitamin A deficiency can increase vulnerability to infections, which can sometimes trigger or exacerbate allergic reactions.
Vitamin C Deficiency and Allergies
Although less directly linked to allergy development than Vitamins D and A, Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the body against oxidative stress, a factor potentially involved in allergic inflammation. While it doesn't directly prevent allergies, adequate Vitamin C intake may help reduce the severity of allergic symptoms by minimizing inflammation and supporting overall immune health.
- Antioxidant properties: Vitamin C combats free radicals, reducing inflammation associated with allergic reactions.
- Immune support: Vitamin C supports the overall function of the immune system.
- Reduced severity of symptoms: While not a cure, sufficient Vitamin C can potentially lessen the severity of allergic symptoms.
B Vitamins and Allergies
The B vitamins, particularly B6 and B12, are also important for immune function. Deficiencies can indirectly contribute to increased allergy risk by weakening the overall immune system response. B vitamins are involved in various metabolic processes that affect immune cell development and activity. A deficiency can lead to an imbalanced immune response.
- Immune cell production and function: B vitamins are necessary for the production and proper function of various immune cells.
- Reduction of inflammation: While not directly impacting the allergic response, deficiencies may contribute to heightened inflammation.
- Overall immune health: Adequate levels of B vitamins contribute to a strong and balanced immune system.
Zinc Deficiency and Allergies
Zinc plays a key role in immune cell development and function. Deficiency can lead to impaired immune responses, potentially increasing susceptibility to allergies. Similar to other vitamins, it does not directly cause allergies but can negatively impact the body's ability to manage allergic responses.
- Immune cell development: Zinc is crucial for the formation and maturation of immune cells.
- Immune regulation: It helps regulate immune cell activity, impacting both the innate and adaptive immune systems.
- Wound healing: Zinc's role in wound healing can indirectly affect allergic reactions associated with skin inflammation.
What drinks help with allergies?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tea-for-allergies-5197793_FINAL-d5f96a3f4f1440cf92b5718a88d1dbd8.jpg)
What Drinks Help with Allergies?
There's no single drink that magically cures allergies, but certain beverages can help manage symptoms or support your body's natural response. The effectiveness depends on the type of allergy and its severity. It's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if you experience severe allergic reactions.
Water: Staying Hydrated for Allergy Relief
Hydration is crucial during allergy season. Allergic reactions, particularly those involving congestion and runny nose, can lead to dehydration. Drinking plenty of water helps thin mucus, making it easier to clear from your sinuses. Sufficient hydration also supports overall immune function, which plays a role in managing allergy symptoms.
- Reduces mucus thickness: Water helps to thin the mucus, making it less difficult to expel.
- Supports immune function: Proper hydration is essential for optimal immune response.
- Prevents dehydration: Allergic reactions can lead to fluid loss through sneezing, coughing, and runny nose.
Herbal Teas: Soothing and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Certain herbal teas offer potential benefits for allergy symptoms. Chamomile tea, for example, possesses mild anti-inflammatory properties that may soothe irritated mucous membranes. Ginger tea can help alleviate nausea sometimes associated with allergy medications. Nettle tea is believed by some to have antihistamine-like effects, though more research is needed to confirm this. It's important to note that these effects are often mild and not a substitute for medical treatment.
- Chamomile: Soothes inflammation and may help with sleep disturbances caused by allergies.
- Ginger: Relieves nausea and digestive discomfort.
- Nettle: May have antihistamine-like properties (requires further research).
Broth-Based Soups: Electrolyte Balance and Comfort
Warm, broth-based soups are particularly beneficial during allergy season. They provide electrolytes lost through dehydration and offer a comforting warmth that can ease congestion symptoms. The sodium in broth can also help replenish electrolytes, especially if you've been experiencing excessive sweating or vomiting.
- Electrolyte replenishment: Replaces lost electrolytes from dehydration.
- Soothing warmth: Helps relieve congestion symptoms.
- Comfort food: Provides a sense of well-being when feeling unwell.
Fruit Juices (with Caution): Vitamin C and Antioxidants
Some fruit juices, particularly those rich in Vitamin C, such as orange juice, are sources of antioxidants that may support immune function. However, it's important to consume these in moderation due to their sugar content. Excessive sugar can worsen inflammation in some individuals.
- Vitamin C boost: Supports immune function.
- Antioxidant properties: Helps protect cells from damage.
- Sugar content: Consume in moderation due to potential inflammatory effects.
Milk (or Alternatives): Calcium and Hydration
Milk, or dairy alternatives like almond or soy milk, can contribute to hydration and provide calcium, an essential nutrient for overall health and strong bones. However, dairy can be an allergen for some, so individuals with dairy allergies should avoid it and opt for suitable alternatives.
- Hydration: Contributes to fluid intake.
- Calcium source: Essential for bone health.
- Potential allergen: Individuals with dairy allergies should avoid dairy products.
What are the best ways to naturally boost my immune system to fight allergies?
Naturally boosting your immune system to better combat allergies involves a holistic approach focusing on lifestyle and diet. It's crucial to understand that there's no magic bullet, and what works for one person may not work for another. However, several strategies consistently demonstrate positive effects. Prioritizing sleep is paramount; aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep allows your body to repair and strengthen its defenses. Stress management is equally vital, as chronic stress weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to allergic reactions. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be incredibly beneficial. Furthermore, regular exercise, but not to the point of exhaustion, strengthens your immune system. Moderate-intensity activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are ideal. Finally, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential vitamins and minerals that support immune function. Focus on foods high in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and brightly colored vegetables. Probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, also contribute to gut health, which is intrinsically linked to a robust immune system. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Can supplements help boost my immune system for allergy relief?
While supplements can play a supporting role in boosting immunity and potentially alleviating allergy symptoms, they shouldn't be considered a standalone solution. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new supplements, especially if you are on other medications. Some supplements touted for immune support include Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Zinc, and probiotics. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that may reduce inflammation, a key factor in allergic reactions. Vitamin D plays a critical role in immune regulation, and deficiencies are linked to increased susceptibility to allergies. Zinc is essential for immune cell function, and adequate intake may help reduce the severity of allergic responses. Probiotics, beneficial bacteria for gut health, influence the immune system's response to allergens. However, the effectiveness of these supplements varies greatly depending on individual needs and underlying health conditions. It's essential to remember that supplements are not a replacement for a healthy lifestyle, including adequate sleep, stress management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet. Over-reliance on supplements without addressing these fundamental aspects of health can be counterproductive.
Are there any specific foods I should avoid or include to manage allergies better?
Dietary changes can significantly impact allergy symptoms. Identifying and eliminating trigger foods is crucial. Common food allergens include dairy, eggs, nuts, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. If you suspect a food allergy, it's essential to consult with an allergist for proper testing and diagnosis. Beyond avoiding triggers, focusing on anti-inflammatory foods can help manage allergy symptoms. This includes plenty of fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants, like berries, leafy greens, and broccoli. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, and chia seeds have anti-inflammatory properties. Conversely, reducing processed foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats is essential as these can exacerbate inflammation and worsen allergy symptoms. Hydration is also key, ensuring adequate water intake helps flush out toxins and supports immune function. Remember, individual reactions to food can vary, and what works for one person might not work for another. Maintaining a food diary to track potential triggers and their impact on your symptoms can be helpful in identifying specific dietary adjustments needed.
How long does it take to see results from boosting my immune system for allergy relief?
There's no single answer to how long it takes to see results from boosting your immune system for allergy relief. The timeframe depends on several factors, including the severity of your allergies, your overall health, the consistency of your efforts, and the specific strategies you're employing. Some individuals may notice improvements in their symptoms within a few weeks of implementing lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments. Others may require several months to see significant changes. Consistency is key; making lasting lifestyle changes rather than short-term efforts is crucial for long-term immune support. It's not a quick fix but rather a continuous process of nurturing your body's natural defenses. Regular check-ups with your doctor or allergist are recommended to monitor progress and make adjustments to your approach as needed. Be patient and persistent, and celebrate small victories along the way. Remember that a holistic approach encompassing sleep, stress management, exercise, and diet provides the most sustainable and effective path to enhancing your immune system and managing your allergies.
Deja una respuesta