What is the best treatment for allergy

Allergies are a common condition that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening anaphylaxis. The best treatment for allergies depends on the type of allergy, the severity of the symptoms, and the individual's overall health.
What is the Best Treatment for Allergies?
There's no single "best" treatment for allergies, as the ideal approach depends on several factors, including the type of allergen, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's overall health. Treatment aims to either prevent exposure to the allergen or to manage the allergic response. A combination of methods is often most effective.
Allergy Medications
A range of medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, available over-the-counter (OTC) or by prescription, block the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids, available as nasal sprays, are very effective at reducing inflammation in the nasal passages. Leukotriene modifiers are another option, often prescribed for persistent asthma and allergies. For severe allergic reactions, epinephrine (adrenaline) auto-injectors, like EpiPens, are crucial for immediate treatment. It's essential to consult a doctor to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for your specific needs.
Allergy Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
Allergy immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT), involves gradually exposing the body to increasing amounts of the allergen over time. This helps to desensitize the immune system, reducing the allergic response. While it requires commitment (often years of treatment), it can provide long-term relief and may even lead to a remission of symptoms. It's most effective for specific allergies like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, and should be administered under strict medical supervision.
Environmental Control Measures
Avoiding allergens as much as possible is a cornerstone of allergy management. This involves implementing environmental controls in your home and workplace. For dust mite allergies, this could include using dust mite-proof bedding, regularly washing bedding in hot water, and using air purifiers with HEPA filters. For pet allergies, minimizing contact with pets, regular cleaning, and using air purifiers can help. For pollen allergies, keeping windows closed during high pollen counts, showering after being outdoors, and using air conditioning can reduce exposure.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve allergy symptoms. Maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can strengthen the immune system and reduce its reactivity. Regular exercise can also improve overall health and potentially reduce allergy symptoms in some individuals. These measures may not eliminate symptoms entirely but can contribute to better overall allergy management.
When to See a Doctor
It's important to seek medical advice if your allergy symptoms are severe, interfering with your daily life, or if you experience symptoms of a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat. A doctor can diagnose your allergies, recommend appropriate treatments, and monitor your progress. Ignoring allergies can lead to the development of more severe reactions over time, hence early intervention is key.
| Treatment Type | Description | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Block histamine release | Good for mild to moderate symptoms | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Reduce nasal inflammation | Very effective for nasal congestion and itching | Nosebleeds (rare) |
| Allergy Immunotherapy | Desensitizes immune system | Long-term relief, may lead to remission | Injection site reactions, rare systemic reactions |
| Environmental Control | Reduces allergen exposure | Highly effective in reducing symptom severity | Requires effort and consistency |
What is the Best Treatment for Allergies?
There's no single "best" treatment for allergies, as the ideal approach depends on several factors, including the type of allergen, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's overall health. Treatment aims to either prevent exposure to the allergen or to manage the allergic response. A combination of methods is often most effective.
Allergy Medications
A range of medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, available over-the-counter (OTC) or by prescription, block the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids, available as nasal sprays, are very effective at reducing inflammation in the nasal passages. Leukotriene modifiers are another option, often prescribed for persistent asthma and allergies. For severe allergic reactions, epinephrine (adrenaline) auto-injectors, like EpiPens, are crucial for immediate treatment. It's essential to consult a doctor to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for your specific needs.
Allergy Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
Allergy immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT), involves gradually exposing the body to increasing amounts of the allergen over time. This helps to desensitize the immune system, reducing the allergic response. While it requires commitment (often years of treatment), it can provide long-term relief and may even lead to a remission of symptoms. It's most effective for specific allergies like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, and should be administered under strict medical supervision.
Environmental Control Measures
Avoiding allergens as much as possible is a cornerstone of allergy management. This involves implementing environmental controls in your home and workplace. For dust mite allergies, this could include using dust mite-proof bedding, regularly washing bedding in hot water, and using air purifiers with HEPA filters. For pet allergies, minimizing contact with pets, regular cleaning, and using air purifiers can help. For pollen allergies, keeping windows closed during high pollen counts, showering after being outdoors, and using air conditioning can reduce exposure.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve allergy symptoms. Maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can strengthen the immune system and reduce its reactivity. Regular exercise can also improve overall health and potentially reduce allergy symptoms in some individuals. These measures may not eliminate symptoms entirely but can contribute to better overall allergy management.
When to See a Doctor
It's important to seek medical advice if your allergy symptoms are severe, interfering with your daily life, or if you experience symptoms of a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat. A doctor can diagnose your allergies, recommend appropriate treatments, and monitor your progress. Ignoring allergies can lead to the development of more severe reactions over time, hence early intervention is key.
| Treatment Type | Description | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Block histamine release | Good for mild to moderate symptoms | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Reduce nasal inflammation | Very effective for nasal congestion and itching | Nosebleeds (rare) |
| Allergy Immunotherapy | Desensitizes immune system | Long-term relief, may lead to remission | Injection site reactions, rare systemic reactions |
| Environmental Control | Reduces allergen exposure | Highly effective in reducing symptom severity | Requires effort and consistency |
What is the most effective allergy treatment?
There's no single "most effective" allergy treatment, as the best approach depends heavily on the individual, the severity of their allergies, and the specific allergen causing the reaction. Treatment strategies often involve a combination of approaches. For many, allergy medications, particularly antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids, provide significant relief. For others, allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy) may be the most effective long-term solution by modifying the immune system's response to allergens. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers, are crucial regardless of other treatments.
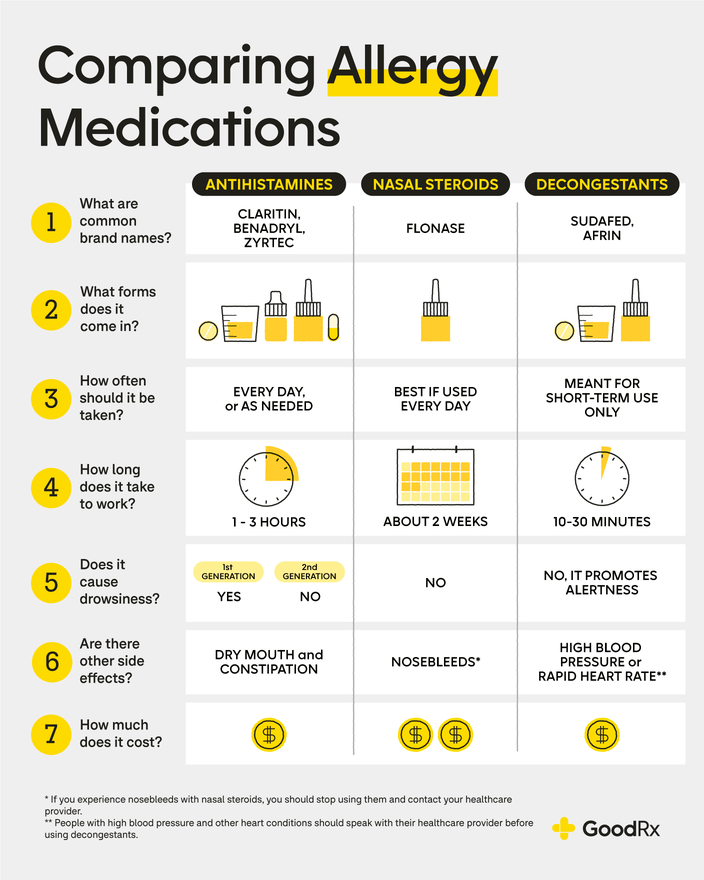
Allergy Medications: Antihistamines and Decongestants
Antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin) are highly effective at relieving allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction. Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion. However, overuse can lead to rebound congestion.
- Antihistamines are generally well-tolerated but can cause drowsiness in some individuals.
- Decongestants should be used cautiously and only for short periods.
- Combination medications containing both antihistamines and decongestants are available.
Nasal Corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase), mometasone (Nasonex), and budesonide (Rhinocort), are highly effective in reducing nasal inflammation and are often considered a first-line treatment for allergic rhinitis (hay fever). They are available over-the-counter and by prescription, offering longer-lasting relief than antihistamines alone. They work by reducing inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Reduce nasal inflammation more effectively than other treatments.
- Available as nasal sprays, making them easy to administer.
- May take several days to show full effects.
Allergy Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots or Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT))
Allergy immunotherapy involves gradually exposing the body to increasing doses of the allergen, building up tolerance over time. This can lead to long-term relief and even remission of allergy symptoms. Allergy shots are administered by injection, while sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) involves placing drops or tablets under the tongue. Both are effective, but SLIT offers a less invasive approach.
- Effective long-term solution for many allergy sufferers.
- Requires a commitment to a treatment regimen that can last several months or years.
- May not be suitable for everyone; individuals with severe asthma or other medical conditions may not be candidates.
Lifestyle Changes and Avoidance Strategies
Avoiding allergens is crucial for managing allergies. This involves identifying and minimizing exposure to triggers such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Strategies include using air purifiers, washing bedding frequently, and maintaining a clean home environment. Monitoring pollen counts and staying indoors during peak pollen seasons can also help.
- Identify and avoid triggers specific to your allergies.
- Maintain a clean living environment to minimize exposure to dust mites and other allergens.
- Use air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove allergens from the air.
Other Treatments and Considerations
Other treatments may be considered depending on the individual and the severity of their allergies. These may include leukotriene modifiers (like montelukast), which reduce inflammation; cromolyn sodium nasal spray, which helps prevent the release of histamine; and in severe cases, prescription-strength antihistamines or other medications. It's crucial to consult an allergist or doctor to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Leukotriene modifiers are helpful for individuals who don’t respond well to other medications.
- Cromolyn sodium can help prevent the onset of allergy symptoms.
- Severe allergy cases may require prescription medications and close medical supervision.
What is the fastest allergy relief?

There's no single "fastest" allergy relief that works for everyone, as the speed and effectiveness depend on individual factors like the allergen, the severity of the reaction, and the person's own body. However, some methods offer quicker relief than others. Generally, medications taken directly before or at the onset of symptoms tend to work the fastest. This includes certain over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. It's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, especially for severe allergies.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin), are readily available and can provide relatively quick relief from allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. However, they may take 30-60 minutes to start working fully. Nasal sprays containing antihistamines (like azelastine) offer faster local relief, working within minutes for nasal congestion and itching. Remember to follow the recommended dosage on the packaging.
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec): A non-drowsy option that provides 24-hour allergy relief. It's often preferred for daytime use.
- Fexofenadine (Allegra): Also a non-drowsy option, effective for relieving allergy symptoms without causing significant drowsiness.
- Loratadine (Claritin): Another non-drowsy antihistamine, often chosen for its long-lasting relief.
Prescription Medications
For more severe allergies or those that don't respond to OTC medications, prescription medications offer more potent relief. These might include stronger antihistamines, leukotriene modifiers (like montelukast), or nasal corticosteroids (like fluticasone). Leukotriene modifiers need to be taken regularly, but they work by preventing allergic reactions from occurring. Nasal corticosteroids, though not immediate-acting, reduce inflammation in the nasal passages over time, providing long-term relief from congestion and sneezing. Your doctor can determine which medication is best suited to your needs.
- Stronger Antihistamines: These are prescribed for more severe allergic reactions and provide more potent relief.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: These prevent inflammation and offer long-term allergy control, but may not provide immediate symptom relief.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: While not instant, they are highly effective at reducing nasal inflammation, leading to long-term relief.
Emergency Epinephrine
In cases of severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis (a life-threatening condition), epinephrine (adrenaline) is the fastest and most crucial treatment. Epinephrine is administered via an auto-injector (like an EpiPen) and works rapidly to counter the effects of the allergic reaction. It should be used immediately at the first sign of anaphylaxis and followed by immediate medical attention.
- Immediate Administration: Epinephrine must be injected immediately upon the onset of anaphylactic symptoms.
- Life-Saving Treatment: This is a life-saving medication for severe allergic reactions.
- Follow-Up Care: Even after administering epinephrine, it's critical to seek emergency medical care.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
While not providing instant relief, certain home remedies and lifestyle changes can help manage allergy symptoms over time and even reduce their severity. Avoiding known allergens is crucial. This might involve using air purifiers, keeping windows closed during high pollen counts, and frequently washing bedding. Rinsing nasal passages with a saline solution can help clear out irritants. These measures don't offer immediate relief but contribute to overall allergy control.
- Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding triggers is a cornerstone of allergy management.
- Saline Nasal Rinse: This can help clear out irritants and provide temporary relief.
- Consistent Lifestyle Changes: Regularly practicing these methods contributes to long-term allergy control.
Decongestants
Oral and nasal decongestants can offer quick relief from nasal congestion. Oral decongestants (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine) work by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages, reducing swelling. Nasal decongestant sprays (like oxymetazoline or phenylephrine) provide more localized and immediate relief. However, overuse can lead to rebound congestion, making it important to use them as directed. Additionally, these are not a solution for all allergy symptoms.
- Oral Decongestants: Provide systemic relief, affecting blood vessels throughout the body.
- Nasal Decongestant Sprays: Offer direct, localized relief to the nasal passages.
- Potential for Rebound Congestion: Overuse can lead to worsening congestion.
What is the fastest remedy for allergies?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural-allergy-remedies-89245_final-afc2c7d8000b4df183653b6b2af84f41.jpg)
There's no single "fastest" remedy for allergies, as the best approach depends on the specific allergen and the severity of the reaction. However, some treatments offer quicker relief than others. For mild symptoms, over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines are often the first line of defense, providing relatively rapid relief from symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. For more severe reactions or those involving breathing difficulties, immediate medical attention is crucial. Epinephrine auto-injectors (like EpiPens) are life-saving in cases of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction. Beyond immediate relief, allergy management involves identifying and avoiding triggers and potentially considering immunotherapy for long-term control.
Over-the-Counter Antihistamines for Quick Relief
Oral antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and cetirizine (Zyrtec) can provide relatively quick relief from allergy symptoms. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction. While they offer fast symptom relief, they can cause drowsiness, especially diphenhydramine. Choosing a non-drowsy formula like cetirizine or fexofenadine (Allegra) might be preferable if you need to remain alert.
- Benadryl (diphenhydramine): Fast-acting, but can cause significant drowsiness.
- Zyrtec (cetirizine): Less drowsy than Benadryl, effective for many allergy symptoms.
- Allegra (fexofenadine): Non-drowsy option, effective for seasonal allergies and hay fever.
Decongestants for Nasal Congestion
Nasal congestion is a common allergy symptom. Decongestants, available as nasal sprays or oral medications, can quickly relieve stuffiness. However, overuse of nasal sprays can lead to rebound congestion, making the problem worse in the long run. Oral decongestants like pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) can be effective but can also raise blood pressure. Always follow the instructions carefully and consult a doctor if you have underlying health conditions.
- Nasal sprays: Provide immediate relief but should be used for a limited time to avoid rebound congestion.
- Oral decongestants: Effective for congestion, but may raise blood pressure.
- Saline nasal sprays: A gentler option for nasal irrigation, can help clear nasal passages.
Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Itchy, watery eyes are typical allergy symptoms. Antihistamine eye drops can provide rapid relief from these symptoms. These drops work directly on the affected area, targeting the inflammation and itching. They are often more effective than oral antihistamines for eye-related allergy symptoms. Some eye drops also contain mast cell stabilizers which work by preventing the release of histamine.
- Antihistamine eye drops: Directly relieve itchiness and watering.
- Mast cell stabilizer eye drops: Prevent the release of histamine, offering longer-lasting relief.
- Combined antihistamine/mast cell stabilizer eye drops: Offer a combination of fast and long-term relief.
Epinephrine Auto-Injectors for Anaphylaxis
Epinephrine auto-injectors (like EpiPens) are crucial in treating anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction. These devices deliver a dose of epinephrine, a hormone that constricts blood vessels, opens airways, and counteracts the effects of histamine. It's essential to seek immediate medical attention even after administering epinephrine, as it only buys time until professional medical care can be given.
- Immediate administration: Epinephrine is critical in anaphylaxis.
- Follow-up medical care: Even after administering epinephrine, seek immediate medical attention.
- Proper training: Learn how to use an EpiPen properly from a healthcare professional.
Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
Long-term allergy management often involves identifying and avoiding allergens. This is crucial to prevent allergic reactions. Keeping a detailed allergy diary, undergoing allergy testing, and taking steps to eliminate or minimize exposure to specific allergens can significantly reduce symptom frequency and severity. This preventative measure, while not providing immediate relief, is crucial for overall allergy control.
- Allergy testing: Determine specific allergens causing reactions.
- Allergy diary: Track symptoms and potential triggers.
- Environmental control: Minimize exposure to identified allergens.
What do doctors prescribe for really bad allergies?

For severe allergies, doctors typically prescribe a combination of treatments tailored to the specific allergen and the severity of the reaction. The goal is to control symptoms and prevent life-threatening anaphylaxis. Treatment often includes both short-term relief and long-term preventative measures. Short-term treatments focus on managing acute allergic reactions, while long-term management aims to reduce the frequency and severity of future reactions.
Medications for Immediate Relief
When experiencing a severe allergic reaction, immediate action is crucial. Doctors might prescribe epinephrine auto-injectors like EpiPen or Auvi-Q for immediate treatment of anaphylaxis. These deliver a dose of epinephrine to counteract the effects of the allergen. In addition to epinephrine, antihistamines and corticosteroids can be administered to reduce symptoms such as itching, swelling, and breathing difficulties. These are often given intravenously in emergency situations.
- Epinephrine auto-injectors (EpiPen, Auvi-Q): These are lifesavers in anaphylaxis, quickly reversing the potentially fatal effects of an allergic reaction.
- Intravenous (IV) antihistamines: These provide rapid relief from allergy symptoms like hives and itching.
- Intravenous corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and help manage severe symptoms such as swelling of the airways.
Long-Term Allergy Medications
To prevent future severe allergic reactions, doctors may prescribe various medications for long-term management. This often involves antihistamines, which are available in both oral and nasal spray forms. Leukotriene modifiers help reduce inflammation in the airways. For more severe cases, immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended to desensitize the body to the allergen over time. Immunotherapy is a long-term commitment but can be highly effective in reducing allergy symptoms.
- Oral antihistamines (Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine): These reduce allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
- Nasal corticosteroids (Fluticasone, Mometasone): These reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, relieving congestion and sneezing.
- Leukotriene modifiers (Montelukast, Zafirlukast): These help reduce inflammation in the airways and are often used for asthma and allergies.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): A long-term treatment that gradually desensitizes the body to allergens.
Specific Treatments for Different Allergens
The treatment strategy depends greatly on the specific allergen causing the reaction. For instance, someone with a severe peanut allergy might benefit from strict avoidance of peanuts and carrying an epinephrine auto-injector, along with perhaps oral antihistamines for milder reactions. Someone with seasonal allergies (hay fever) might be treated with nasal corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. Tailored treatment plans, based on the specific allergens and the patient's reaction history, are vital.
- Food allergies: Strict avoidance, epinephrine auto-injectors, and potentially antihistamines.
- Insect stings: Epinephrine auto-injectors, antihistamines, and potentially immunotherapy for repeated reactions.
- Environmental allergens (pollen, dust mites): Nasal corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and potentially immunotherapy.
Lifestyle Modifications and Avoidance Strategies
Beyond medication, managing severe allergies often involves significant lifestyle changes and avoidance strategies. This might involve removing allergens from the home environment (dust mite covers, air purifiers), adjusting diet to avoid specific foods, or avoiding certain activities during high pollen seasons. Proactive avoidance is a key part of preventing severe reactions.
- Environmental control: Removing allergens from the home (dust mite covers, HEPA filters).
- Dietary restrictions: Avoiding foods known to trigger allergic reactions.
- Avoiding triggers: Staying indoors during high pollen counts, using insect repellents.
Emergency Preparedness and Action Plans
Individuals with severe allergies need a detailed emergency action plan, including knowing how and when to administer epinephrine, contacting emergency medical services, and having readily accessible medications. Regular review and updates to the action plan with a doctor are crucial. Having friends, family, and coworkers aware of the plan and trained in administering epinephrine can be life-saving.
- Epinephrine auto-injector training: Knowing how to use the device correctly and when to administer it.
- Emergency contact information: Keeping emergency numbers readily available.
- Medical alert bracelet or necklace: Clearly indicating allergies and necessary medications.
What is the best treatment for allergies?
There isn't a single "best" treatment for allergies, as the optimal approach depends heavily on the specific allergen causing the reaction, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's overall health. Treatment strategies are personalized and often involve a combination of methods. For mild allergic reactions, such as occasional sneezing or itchy eyes from pollen, over-the-counter (OTC) medications might suffice. These include antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), or loratadine (Claritin), which block histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic response. Nasal corticosteroids, like fluticasone (Flonase) or mometasone (Nasonex), can effectively reduce nasal inflammation. Eye drops containing antihistamines or mast cell stabilizers can alleviate itchy, watery eyes. However, for more severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening condition, immediate medical attention is crucial. Epinephrine (adrenaline) is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis, often administered via an auto-injector like an EpiPen. In such cases, allergists play a critical role in diagnosing the allergen and developing a comprehensive management plan. This might involve allergy shots (immunotherapy), which gradually desensitize the body to specific allergens over time, offering long-term relief. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding known allergens, using air purifiers, and regularly cleaning the home environment, can also contribute significantly to symptom management. Therefore, consulting an allergist or doctor is vital to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy based on your individual circumstances.
Can I treat my allergies at home?
For mild allergic reactions, some home treatments can provide relief. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications, such as antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine) and decongestants (e.g., pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine) can effectively manage symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. Nasal saline sprays can help rinse nasal passages, removing irritants and alleviating congestion. Cool compresses can soothe itchy eyes and skin. However, it's crucial to remember that home treatments are not suitable for all allergies or all severities of reactions. If your allergies are severe, interfere significantly with your daily life, or you experience symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives, you should seek immediate medical attention. Self-treating severe allergies can be dangerous. Furthermore, while OTC medications can provide temporary relief, they may not address the underlying cause of the allergy. If home remedies aren't providing sufficient relief or your symptoms worsen, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan, which might involve prescription medications or other therapies like allergy shots (immunotherapy).
What are allergy shots (immunotherapy)?
Allergy shots, also known as allergen immunotherapy, are a form of treatment that aims to desensitize your immune system to specific allergens. It involves a series of injections administered over a period of time, typically several months or years, containing gradually increasing doses of the allergen you are allergic to. The goal is to retrain your immune system to tolerate the allergen without triggering a significant allergic reaction. This therapy is often considered for individuals with moderate to severe allergies that are not adequately controlled by medication or other treatments. Common allergens targeted by immunotherapy include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and insect venom. While allergy shots can be very effective in reducing allergy symptoms and potentially leading to long-term remission, they are not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as severe asthma or autoimmune disorders, may not be candidates. The procedure involves regular visits to an allergist for the injections, and some individuals experience side effects such as mild injection site reactions or temporary worsening of symptoms. However, these side effects are typically manageable. Allergy shots are a long-term commitment, but they can offer significant benefits for those who qualify. A thorough evaluation by an allergist is crucial to determine the suitability and potential efficacy of this treatment option.
When should I see a doctor about my allergies?
You should see a doctor about your allergies if your symptoms are severe, interfering with your daily life, or worsening. This includes instances where you experience: Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or throat (signs of anaphylaxis), hives, severe itching, or persistent coughing or wheezing. If over-the-counter medications provide insufficient relief, or if your allergies seem to be getting worse over time, it’s important to seek professional medical advice. A doctor or allergist can perform allergy testing to accurately identify the specific allergens triggering your symptoms. Based on the test results and the severity of your reactions, they can recommend the most appropriate treatment plan, which may involve prescription medications, allergy shots, or lifestyle modifications. Don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your allergies. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure you receive the best possible care and management of your condition.
Deja una respuesta