Why is Claritin not working

If you're one of the millions of people who rely on Claritin to relieve your allergy symptoms, you may have been frustrated to find that it's not working as well as it used to. There are a number of reasons why Claritin may not be working for you, including:
Why Isn't Claritin Working for Me?
There are several reasons why Claritin (loratadine), a popular over-the-counter antihistamine, might not be effectively relieving your allergy symptoms. It's crucial to understand that Claritin works by blocking histamine, a chemical your body releases during an allergic reaction. However, its effectiveness depends on various factors, and it might not be the right medication for everyone or every situation.
Incorrect Dosage or Timing
Are you taking the correct dosage of Claritin? The recommended dose for adults is usually 10mg once daily. Taking less than the prescribed amount might not provide sufficient relief. Similarly, consistent timing is important. Taking it at the same time each day helps maintain consistent levels of the medication in your bloodstream for optimal effectiveness. If you're taking it inconsistently, you may experience fluctuations in symptom relief. Consider using a daily pill organizer to help you remember.
Underlying Conditions
Other underlying health conditions can affect the effectiveness of Claritin. For example, some people might have a different type of allergy that doesn't respond well to loratadine. Furthermore, certain pre-existing medical conditions or medications you're taking could interact with Claritin, reducing its efficacy. It's essential to consult your doctor to rule out any underlying health issues that may be interfering with treatment.
The Severity and Type of Allergy
Claritin is primarily effective for allergic rhinitis (hay fever) symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. However, it might not be as effective for other allergy symptoms, such as severe congestion or hives. If your allergies are severe or involve symptoms beyond what Claritin targets, you might need a different medication or a combination of treatments. The type of allergen also plays a role; Claritin's effectiveness might vary depending on whether you're allergic to pollen, pet dander, or other substances.
Medication Interactions
Certain medications can interact with Claritin, affecting its effectiveness or causing adverse side effects. For instance, interactions with other antihistamines or certain medications used to treat depression or anxiety are possible. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking. This will help them identify potential interactions and adjust your treatment accordingly.
Incorrect Diagnosis or Misidentification of Symptoms
It's essential to ensure that your symptoms are actually caused by allergies. Sometimes, symptoms that seem like allergies could be caused by other conditions, such as a common cold, sinus infection, or even a non-allergic rhinitis. If Claritin isn't working, a visit to your doctor is crucial to get an accurate diagnosis and rule out other possibilities. Accurate diagnosis is the first step to effective treatment.
| Possible Reason | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Dosage | Follow the instructions on the label carefully. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if unsure. |
| Underlying Medical Condition | Consult a doctor for a comprehensive evaluation. |
| Severity of Allergy | Discuss stronger allergy medications with your doctor. |
| Medication Interactions | Inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications taken. |
| Incorrect Diagnosis | Consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. |
Why Isn't Claritin Working for Me?
There are several reasons why Claritin (loratadine), a popular over-the-counter antihistamine, might not be effectively relieving your allergy symptoms. It's crucial to understand that Claritin works by blocking histamine, a chemical your body releases during an allergic reaction. However, its effectiveness depends on various factors, and it might not be the right medication for everyone or every situation.
Incorrect Dosage or Timing
Are you taking the correct dosage of Claritin? The recommended dose for adults is usually 10mg once daily. Taking less than the prescribed amount might not provide sufficient relief. Similarly, consistent timing is important. Taking it at the same time each day helps maintain consistent levels of the medication in your bloodstream for optimal effectiveness. If you're taking it inconsistently, you may experience fluctuations in symptom relief. Consider using a daily pill organizer to help you remember.
Underlying Conditions
Other underlying health conditions can affect the effectiveness of Claritin. For example, some people might have a different type of allergy that doesn't respond well to loratadine. Furthermore, certain pre-existing medical conditions or medications you're taking could interact with Claritin, reducing its efficacy. It's essential to consult your doctor to rule out any underlying health issues that may be interfering with treatment.
The Severity and Type of Allergy
Claritin is primarily effective for allergic rhinitis (hay fever) symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. However, it might not be as effective for other allergy symptoms, such as severe congestion or hives. If your allergies are severe or involve symptoms beyond what Claritin targets, you might need a different medication or a combination of treatments. The type of allergen also plays a role; Claritin's effectiveness might vary depending on whether you're allergic to pollen, pet dander, or other substances.
Medication Interactions
Certain medications can interact with Claritin, affecting its effectiveness or causing adverse side effects. For instance, interactions with other antihistamines or certain medications used to treat depression or anxiety are possible. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking. This will help them identify potential interactions and adjust your treatment accordingly.
Incorrect Diagnosis or Misidentification of Symptoms
It's essential to ensure that your symptoms are actually caused by allergies. Sometimes, symptoms that seem like allergies could be caused by other conditions, such as a common cold, sinus infection, or even a non-allergic rhinitis. If Claritin isn't working, a visit to your doctor is crucial to get an accurate diagnosis and rule out other possibilities. Accurate diagnosis is the first step to effective treatment.
| Possible Reason | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Dosage | Follow the instructions on the label carefully. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if unsure. |
| Underlying Medical Condition | Consult a doctor for a comprehensive evaluation. |
| Severity of Allergy | Discuss stronger allergy medications with your doctor. |
| Medication Interactions | Inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications taken. |
| Incorrect Diagnosis | Consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. |
What to do if Claritin is not working?

If Claritin (loratadine) isn't providing adequate relief from your allergy symptoms, several factors could be at play. The first step is to ensure you're using it correctly. This includes taking the correct dosage at the recommended intervals, as specified on the label or by your doctor. If you're still experiencing symptoms despite proper usage, it might be necessary to explore other options. Your symptoms might be caused by something other than allergies, or your body might not respond well to loratadine.
1. Determine the Cause of Your Symptoms
Before considering other medications, it's crucial to ascertain the exact cause of your symptoms. Are you truly experiencing an allergic reaction, or could something else be responsible? Keep a detailed allergy diary, noting down your symptoms, their severity, when they occur, and any potential triggers (pollen, pet dander, certain foods, etc.). This detailed information will be invaluable to your doctor in determining the best course of action. If your symptoms include things like a persistent cough, fever, or worsening congestion, it could point towards a different issue like a cold or the flu, rather than a typical allergic response.
- Consult a doctor to rule out other conditions.
- Keep a detailed diary of your symptoms and potential triggers.
- Consider conducting allergy tests to pinpoint specific allergens.
2. Consider Other Allergy Medications
If your symptoms are indeed allergy-related, your doctor might suggest switching to a different antihistamine. Cetirizine (Zyrtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra) are other popular choices that might be more effective for you. In some cases, a combination of medications, such as an antihistamine and a decongestant, could prove more beneficial. Remember to always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
- Discuss alternative antihistamines with your physician.
- Explore the possibility of combining medications under medical supervision.
- Understand the potential side effects of different medications.
3. Explore Other Treatment Options
Beyond medication, various other treatments can help manage allergy symptoms. Nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase) or mometasone (Nasonex), can effectively reduce nasal inflammation. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse away allergens and clear congestion. Immunotherapy (allergy shots) is a long-term treatment option that aims to desensitize you to specific allergens over time, potentially providing lasting relief. These options may require a consultation with an allergist or other healthcare professional.
- Consider using nasal corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Try saline nasal sprays to rinse allergens.
- Discuss immunotherapy as a long-term solution with your allergist.
4. Lifestyle Changes to Minimize Exposure
Making simple adjustments to your lifestyle can significantly reduce your exposure to allergens. This could involve avoiding known triggers like certain foods, pets, or pollen. Regularly cleaning your home to remove dust mites and pet dander, using air filters, and showering before bed can also help alleviate symptoms. Monitoring pollen counts in your area and adjusting outdoor activities accordingly is also crucial.
- Avoid known allergens as much as possible.
- Maintain a clean home environment to minimize dust mites and pet dander.
- Monitor pollen counts and adjust activities accordingly.
5. When to See a Doctor
If Claritin remains ineffective despite adjustments to your medication and lifestyle, it's crucial to consult your doctor. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, order necessary tests (like allergy testing), and determine the root cause of your symptoms. They can also discuss more advanced treatment options, explore underlying medical conditions, or suggest alternative approaches to allergy management. Don't hesitate to seek professional medical help if your symptoms are severe, persistent, or interfering with your daily life.
- Schedule an appointment with your doctor to discuss your concerns.
- Describe your symptoms in detail, including their severity and duration.
- Be prepared to answer questions about your medical history and lifestyle.
Why do I still have allergies after taking Claritin?
Claritin, containing loratadine, is an effective antihistamine for many people with allergies. However, it's not a cure-all, and several reasons can explain why you might still experience allergy symptoms even after taking it. The effectiveness of Claritin can vary depending on the individual, the severity of the allergy, and the specific allergen involved. It's crucial to understand that Claritin primarily targets histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction, but other inflammatory mediators are also at play. If these other factors are dominant in your allergic response, Claritin may not provide complete relief.
Incorrect Dosage or Timing
Taking Claritin at the incorrect dosage or at inconsistent times can significantly impact its effectiveness. The recommended dose must be followed precisely as directed on the packaging or prescribed by a doctor. Furthermore, consistent daily intake is crucial for maintaining sufficient levels of the medication in your system to effectively combat allergy symptoms. Taking it sporadically may not provide adequate relief.
- Always check the dosage instructions carefully.
- Take Claritin at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels.
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you're unsure about the appropriate dosage or timing.
Severity of Allergy
The severity of your allergic reaction plays a pivotal role in determining the efficacy of Claritin. For mild allergies, Claritin may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. However, for severe allergies, Claritin might not be potent enough on its own to provide complete relief. In such cases, a stronger antihistamine or a combination of treatments may be necessary.
- Consider the severity of your symptoms; mild symptoms may respond well to Claritin, while severe symptoms may not.
- Severe allergies might require stronger medication or additional treatments like nasal corticosteroids.
- Consult an allergist to determine the appropriate course of treatment for severe allergies.
Other Allergens or Triggers
You might be experiencing allergies caused by allergens that Claritin doesn't effectively address. Claritin primarily targets histamine released in response to airborne allergens like pollen, but other triggers such as pet dander, dust mites, mold, or food allergies can elicit a reaction independent of histamine release. These other allergic reactions will not be alleviated by Claritin alone.
- Identify all potential allergens through allergy testing.
- Implement environmental control measures to reduce exposure to allergens.
- Explore other treatment options if Claritin is ineffective against your specific allergens.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can interfere with the effectiveness of Claritin or even exacerbate allergy symptoms. Conditions such as asthma, chronic sinusitis, or other respiratory illnesses can interact with allergies, making symptoms more pronounced. Even if Claritin is working as intended, these other medical issues could be contributing to ongoing allergy-like symptoms.
- Consult a doctor if you suspect an underlying medical condition is impacting your allergies.
- Address any underlying medical conditions to improve overall health and allergy management.
- Work with your physician to create an integrated treatment plan addressing both allergies and other health issues.
Incorrect Diagnosis or Medication Interaction
Your symptoms may not be caused by allergies at all. A misdiagnosis could lead to ineffective treatment. Furthermore, Claritin can interact with other medications you're taking, reducing its effectiveness or causing adverse effects. This interaction can manifest as either diminished allergy relief or new symptoms altogether.
- Ensure your diagnosis is accurate and specific allergy tests have been conducted.
- Provide your doctor with a complete list of all medications and supplements you are currently taking.
- Discuss any potential drug interactions and explore alternative allergy medications if necessary.
What is stronger than Claritin for allergies?
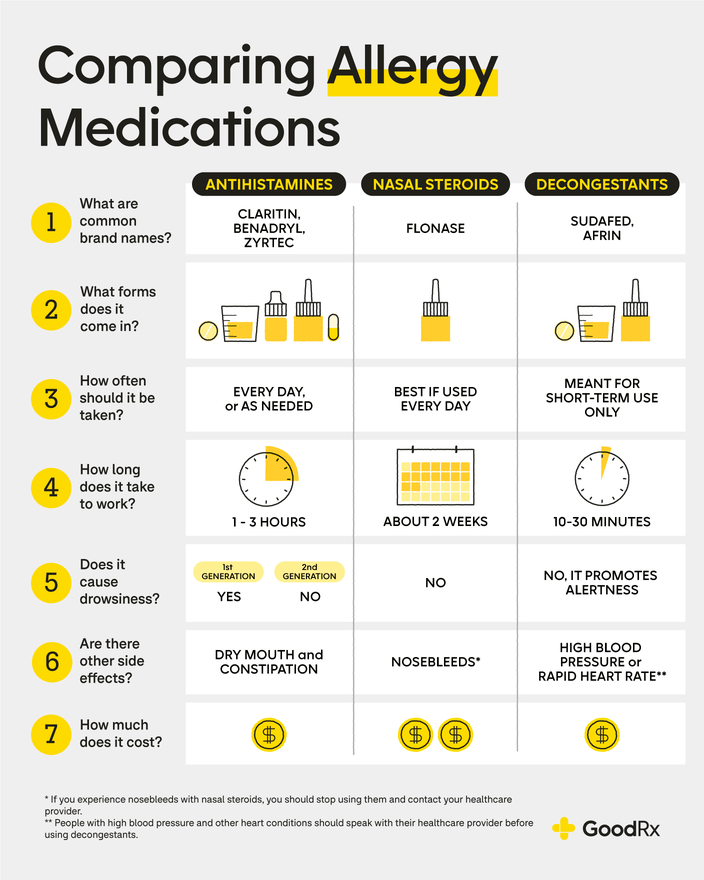
Claritin (loratadine) is a popular over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamine used to treat allergy symptoms. However, its effectiveness varies between individuals, and some people may require a stronger medication. Several options exist that may provide more relief than Claritin, depending on the severity and type of allergy symptoms experienced. The choice of a stronger medication should always be made in consultation with a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional.
Prescription Antihistamines
If Claritin isn't providing sufficient relief, your doctor may prescribe a stronger antihistamine. These often work by blocking histamine more effectively than OTC options like Claritin. Some examples include cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and levocetirizine (Xyzal). These medications are generally well-tolerated, but side effects can occur. The appropriate choice depends on individual needs and potential drug interactions.
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec): Often considered similar in strength to loratadine but can be more effective for some individuals.
- Fexofenadine (Allegra): Known for causing fewer side effects like drowsiness than some other antihistamines.
- Levocetirizine (Xyzal): A newer antihistamine that's also generally well-tolerated.
Corticosteroids (Nasal Sprays)
For allergy symptoms primarily affecting the nose, such as nasal congestion, runny nose, and sneezing, corticosteroid nasal sprays like fluticasone (Flonase), mometasone (Nasonex), and beclomethasone (Beconase AQ) can be very effective. These aren't antihistamines, but they work by reducing nasal inflammation. They are usually prescribed for longer-term management of allergy symptoms, and are often used in conjunction with oral antihistamines.
- Fluticasone (Flonase): A commonly prescribed corticosteroid nasal spray known for its efficacy.
- Mometasone (Nasonex): Another popular choice, often effective for even severe nasal allergies.
- Beclomethasone (Beconase AQ): A less common option, but still effective for many patients.
Decongestants
Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) and phenylephrine, primarily target nasal congestion. While not stronger than Claritin in the sense of being a more potent antihistamine, they address a different aspect of allergy symptoms. They can be used in combination with antihistamines for more comprehensive relief. However, they can have side effects and are not recommended for long-term use.
- Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed): A more effective decongestant than phenylephrine.
- Phenylephrine: A less potent decongestant, often found in combination products.
- Important Note: Always follow the recommended dosage and consult a doctor before using decongestants, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Leukotriene Modifiers
Leukotriene modifiers, such as montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate), are a different class of allergy medication. They work by blocking the effects of leukotrienes, chemicals involved in the allergic response. They're often used for individuals with asthma or persistent allergy symptoms that don't respond well to antihistamines alone. They are usually prescribed medications.
- Montelukast (Singulair): A commonly prescribed leukotriene modifier.
- Zafirlukast (Accolate): Another option, although less commonly used than montelukast.
- Important Note: Leukotriene modifiers are not a replacement for rescue medications like inhalers in the case of asthma.
Combination Medications
Many allergy medications combine different active ingredients to address multiple symptoms simultaneously. For instance, some over-the-counter medications combine an antihistamine with a decongestant. Prescription combination medications may combine an antihistamine with a corticosteroid or another active ingredient, offering potentially more comprehensive relief than a single-ingredient medication like Claritin.
- Examples: Specific combinations vary and depend on the individual's needs and physician's assessment.
- Important Note: Always check with your doctor or pharmacist about potential interactions before taking combination medications.
- Tailored Treatment: The best approach is a personalized plan that incorporates the right combination of medications to manage specific allergy symptoms effectively.
Can I take 2 Claritin in 24 hours?

Whether you can take 2 Claritin in 24 hours depends entirely on the specific Claritin product you're using and your individual circumstances. Always refer to the product label for the recommended dosage. Exceeding the recommended dose can lead to side effects and is not advised without consulting a doctor or pharmacist. The information below is for general knowledge only and should not be considered medical advice.
Claritin 24-Hour Dosage
Claritin 24-Hour is formulated for once-daily use. Taking more than one tablet in a 24-hour period is generally not recommended. Taking two tablets might lead to increased side effects without providing significantly more allergy relief. If your symptoms are not adequately controlled with one tablet, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist to discuss alternative treatment options.
- Always check the label: Carefully read the instructions on the Claritin 24-Hour packaging for the recommended dosage.
- Consider alternative options: If one tablet isn't sufficient, discuss other allergy medications with your healthcare provider.
- Potential side effects: Taking more than the recommended dose may increase the risk of side effects like drowsiness, headache, or nausea.
Claritin Immediate-Release Dosage
Claritin Immediate-Release typically has a different dosage recommendation than the 24-hour formulation. The label will specify how many tablets can be taken within a specified timeframe. Taking more than the recommended dose could result in adverse reactions. Always adhere to the instructions printed on the product packaging.
- Frequency of Doses: The label will indicate the appropriate time interval between doses.
- Maximum Daily Dose: Never exceed the maximum daily dose stated on the label.
- Consult a professional: If you are unsure about the proper dosage, always seek guidance from a doctor or pharmacist.
Interactions with Other Medications
It's crucial to be aware of potential drug interactions when taking any medication, including Claritin. Some medications can interact negatively with Claritin, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or reducing the effectiveness of either medication. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications, vitamins, and supplements you're currently taking before starting a new medication.
- Prescription Medications: Disclose all prescription drugs you take to your doctor or pharmacist.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Include all over-the-counter medications in your disclosure.
- Supplements and Herbs: Mention any supplements or herbal remedies you use.
Pre-Existing Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain pre-existing medical conditions may need to exercise extra caution when taking Claritin. Conditions like liver or kidney disease can affect how the body processes medication, potentially leading to increased side effects or toxicity. Always consult your doctor before taking Claritin if you have any pre-existing health concerns.
- Liver Disease: Claritin metabolism might be affected by liver impairment.
- Kidney Disease: Claritin excretion may be affected by kidney problems.
- Other Conditions: Inform your physician about any other relevant medical condition.
Side Effects of Claritin
Even when taken as directed, Claritin can cause side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, headache, and nausea. While generally mild, these side effects can be exacerbated by taking more than the recommended dose. If you experience any unusual or severe side effects, discontinue use and seek medical attention immediately.
- Drowsiness: Avoid driving or operating machinery if you experience drowsiness.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers may help alleviate headaches.
- Nausea: If nausea is severe, contact a doctor.
Why isn't Claritin relieving my allergies?
There are several reasons why Claritin (loratadine) might not be effectively relieving your allergy symptoms. One possibility is that you're experiencing a different type of allergy than what Claritin targets. Claritin is an antihistamine, primarily effective against allergic rhinitis (hay fever) symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes caused by airborne allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. However, if your symptoms are caused by something else, such as a food allergy, an irritant, or a viral infection, Claritin won't be as helpful. Another factor is the severity of your allergies. For some individuals with mild allergies, Claritin may provide sufficient relief. However, those with severe allergies might require a stronger medication or a combination of treatments. Dosage is also crucial. Ensure you're taking the correct dosage as recommended on the label or by your doctor. Taking less than the recommended dose may not provide adequate relief. Finally, consider the timing of your medication. If you're taking it inconsistently or too late in the day, it might not be working effectively. It's best to take it regularly, as prescribed, to maintain consistent allergy relief. If you're still experiencing significant symptoms despite taking Claritin correctly, it's essential to consult a doctor or allergist to rule out other conditions and explore alternative treatment options.
I've been taking Claritin for weeks, but my symptoms persist. What should I do?
If your allergy symptoms persist despite consistent use of Claritin for several weeks, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Several factors could explain the lack of effectiveness. Firstly, your allergies might be more severe than initially thought, requiring a stronger medication or a different approach. Claritin may not be powerful enough to manage your specific allergic response. Secondly, you may have a different underlying condition mimicking allergy symptoms. Conditions such as sinusitis, a nasal polyp, or even a chronic respiratory infection can present with symptoms similar to allergies. A doctor can perform an examination and necessary tests to rule these out. Thirdly, you could be experiencing a secondary allergic reaction or a reaction to another substance. It's important to carefully consider your environment and recent exposures to eliminate any potential triggers. Furthermore, your current Claritin dosage might be insufficient. A doctor can assess your situation and determine if an adjustment to your dosage is needed or if another medication is more suitable. In some cases, combining Claritin with other allergy medications, such as a nasal steroid spray, could be beneficial. Never attempt to change medication or dosage without consulting a healthcare professional.
Could I be allergic to Claritin itself?
While rare, it's possible to have an allergic reaction to Claritin or any medication. Allergic reactions can range from mild (skin rash, itching, hives) to severe (anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition). Symptoms of an allergic reaction to Claritin typically appear shortly after taking the medication. If you experience any unusual symptoms such as skin rashes, swelling, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or rapid heartbeat after taking Claritin, you should stop taking it immediately and seek medical attention. It's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist to determine if you're experiencing an allergic reaction. They might conduct tests to confirm the allergy and recommend alternative allergy medications that are safe for you. If you suspect an allergic reaction, be sure to clearly explain your symptoms and the timeline of events to the medical professional for accurate diagnosis and management.
Is there a stronger alternative to Claritin for my allergies?
If Claritin isn't providing sufficient relief, several stronger allergy medications are available. Your doctor can help determine the best option based on your specific needs and medical history. These might include other second-generation antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra), which may be more effective for some individuals. Prescription-strength antihistamines offer higher potency and could be necessary for severe allergies. Another approach might involve combining Claritin with other allergy medications, such as a nasal corticosteroid spray (like fluticasone or mometasone) to reduce nasal inflammation. In some cases, leukotriene inhibitors (like montelukast or zafirlukast) can also be helpful, particularly for individuals with asthma or allergies affecting the lungs. A decongestant, either oral or nasal spray, might be added to help relieve nasal congestion. However, it's important to be aware that long-term use of decongestants can lead to rebound congestion. Your doctor can guide you in selecting the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy based on your specific allergy symptoms and overall health.
Deja una respuesta