Is it OK to take allergy medicine everyday

For many people, allergies are an unfortunate reality that can significantly impact their daily lives. Symptoms such as watery eyes, sneezing, and congestion can make it difficult to function normally. In an attempt to alleviate these symptoms, many allergy sufferers turn to over-the-counter allergy medications. However, the question remains: is it safe to take allergy medicine every day? Let's explore the potential implications and risks associated with daily allergy medication use.
Is Daily Allergy Medicine Use Safe?
Whether it's okay to take allergy medicine every day depends heavily on several factors. While some allergy medications are designed for daily use, others are not. Consistent use without medical guidance can lead to potential side effects and may not be the most effective long-term strategy for allergy management. It's crucial to understand your specific allergies, the type of medication you're using, and any potential risks involved before making a decision to take any medication daily.
What are the different types of allergy medications?
There are various types of allergy medications available, each with its own mechanism of action and potential side effects. These include:
Antihistamines: These medications block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction. Examples include cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin). Many antihistamines are available over-the-counter for daily use, but it's crucial to follow package directions. Some newer antihistamines cause less drowsiness than older ones.
Decongestants: These medications help relieve nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages. They are often available as nasal sprays or oral medications. Prolonged use of nasal decongestant sprays can lead to rebound congestion, meaning your congestion worsens when you stop using the spray.
Corticosteroids: These are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can be taken orally or as nasal sprays. They are very effective at reducing inflammation, but long-term use can have significant side effects. They are typically reserved for more severe allergies.
Leukotriene modifiers: These medications block the action of leukotrienes, chemicals involved in inflammation. They're often prescribed for asthma and allergies, particularly for those with exercise-induced bronchospasm.
Understanding the differences between these types is crucial when deciding if daily use is appropriate.
What are the potential side effects of daily allergy medication use?
The side effects of daily allergy medication vary depending on the type of medication and individual sensitivity. Common side effects include:
Drowsiness: This is a common side effect of many antihistamines, particularly older generations.
Dry mouth: This is another common side effect of many allergy medications.
Headache: Headaches can be a side effect of some allergy medications.
Nausea: Some individuals experience nausea when taking allergy medication.
Insomnia: Some medications can interfere with sleep.
More serious side effects (rare but possible): These can vary widely depending on the drug. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist for information.
When should you consult a doctor before taking allergy medicine daily?
You should always consult a doctor before taking any medication daily, especially if you have:
Pre-existing medical conditions
Are taking other medications
Are pregnant or breastfeeding
Experience severe allergic reactions
Have concerns about side effects
Symptoms don't improve or worsen after using the medication as directed
What are the alternatives to daily allergy medication?
There are several alternatives to daily allergy medication, including:
Allergy shots (immunotherapy): These injections gradually desensitize you to allergens over time, potentially reducing your need for daily medication.
Lifestyle changes: Avoiding allergens when possible can significantly reduce symptoms. This might involve changing your diet, using air purifiers, or avoiding certain environments.
Other treatments: There are other medications that may be suitable to use on an as-needed basis rather than daily. A doctor can help you determine the best options for you.
How can I find the right allergy medication for me?
Finding the right allergy medication involves working closely with a healthcare professional. They can help you:
Identify your specific allergies.
Determine the best type of medication for your needs.
Monitor for side effects and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Discuss alternative treatments if daily medication isn't suitable.
| Medication Type | Common Side Effects | Suitable for Daily Use? |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Drowsiness, dry mouth | Often, but depends on the specific drug and individual tolerance. |
| Decongestants | Rebound congestion (with nasal sprays), insomnia | Generally not recommended for long-term daily use. |
| Corticosteroids | Increased blood sugar, weight gain, thinning of skin (with long-term use) | Usually not for daily use unless prescribed by a doctor for severe allergies. |
| Leukotriene Modifiers | Headache, abdominal pain | Often prescribed for daily use for long-term allergy management. |
Is Daily Allergy Medicine Use Safe?
Whether it's okay to take allergy medicine every day depends heavily on several factors. While some allergy medications are designed for daily use, others are not. Consistent use without medical guidance can lead to potential side effects and may not be the most effective long-term strategy for allergy management. It's crucial to understand your specific allergies, the type of medication you're using, and any potential risks involved before making a decision to take any medication daily.
What are the different types of allergy medications?
There are various types of allergy medications available, each with its own mechanism of action and potential side effects. These include:
Antihistamines: These medications block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction. Examples include cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin). Many antihistamines are available over-the-counter for daily use, but it's crucial to follow package directions. Some newer antihistamines cause less drowsiness than older ones.
Decongestants: These medications help relieve nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages. They are often available as nasal sprays or oral medications. Prolonged use of nasal decongestant sprays can lead to rebound congestion, meaning your congestion worsens when you stop using the spray.
Corticosteroids: These are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can be taken orally or as nasal sprays. They are very effective at reducing inflammation, but long-term use can have significant side effects. They are typically reserved for more severe allergies.
Leukotriene modifiers: These medications block the action of leukotrienes, chemicals involved in inflammation. They're often prescribed for asthma and allergies, particularly for those with exercise-induced bronchospasm.
Understanding the differences between these types is crucial when deciding if daily use is appropriate.
What are the potential side effects of daily allergy medication use?
The side effects of daily allergy medication vary depending on the type of medication and individual sensitivity. Common side effects include:
Drowsiness: This is a common side effect of many antihistamines, particularly older generations.
Dry mouth: This is another common side effect of many allergy medications.
Headache: Headaches can be a side effect of some allergy medications.
Nausea: Some individuals experience nausea when taking allergy medication.
Insomnia: Some medications can interfere with sleep.
More serious side effects (rare but possible): These can vary widely depending on the drug. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist for information.
When should you consult a doctor before taking allergy medicine daily?
You should always consult a doctor before taking any medication daily, especially if you have:
Pre-existing medical conditions
Are taking other medications
Are pregnant or breastfeeding
Experience severe allergic reactions
Have concerns about side effects
Symptoms don't improve or worsen after using the medication as directed
What are the alternatives to daily allergy medication?
There are several alternatives to daily allergy medication, including:
Allergy shots (immunotherapy): These injections gradually desensitize you to allergens over time, potentially reducing your need for daily medication.
Lifestyle changes: Avoiding allergens when possible can significantly reduce symptoms. This might involve changing your diet, using air purifiers, or avoiding certain environments.
Other treatments: There are other medications that may be suitable to use on an as-needed basis rather than daily. A doctor can help you determine the best options for you.
How can I find the right allergy medication for me?
Finding the right allergy medication involves working closely with a healthcare professional. They can help you:
Identify your specific allergies.
Determine the best type of medication for your needs.
Monitor for side effects and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Discuss alternative treatments if daily medication isn't suitable.
| Medication Type | Common Side Effects | Suitable for Daily Use? |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Drowsiness, dry mouth | Often, but depends on the specific drug and individual tolerance. |
| Decongestants | Rebound congestion (with nasal sprays), insomnia | Generally not recommended for long-term daily use. |
| Corticosteroids | Increased blood sugar, weight gain, thinning of skin (with long-term use) | Usually not for daily use unless prescribed by a doctor for severe allergies. |
| Leukotriene Modifiers | Headache, abdominal pain | Often prescribed for daily use for long-term allergy management. |
What happens if you take allergy medicine every day?
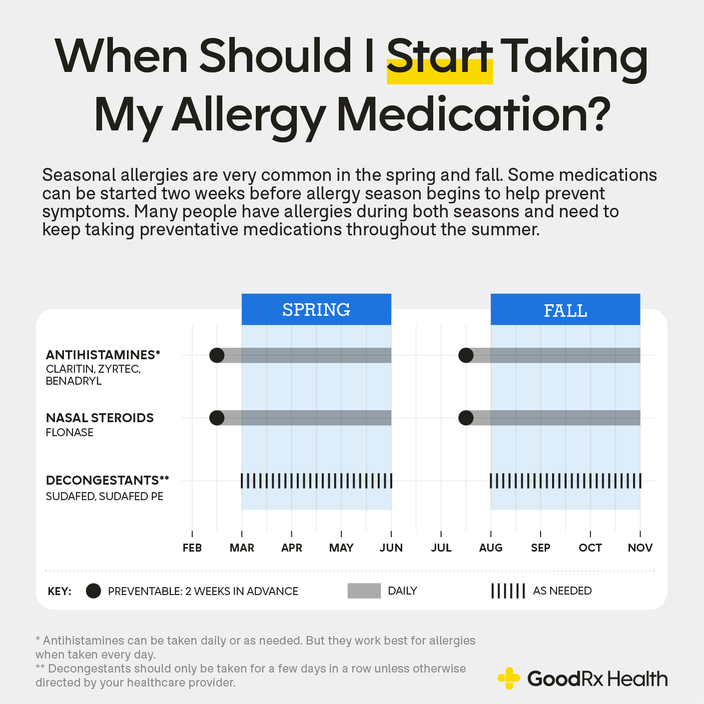
What Happens If You Take Allergy Medicine Every Day?
Taking allergy medicine daily, especially over-the-counter (OTC) medications like antihistamines or decongestants, can lead to various consequences depending on the type of medication, dosage, and individual factors. While these medications can provide effective relief from allergy symptoms, daily use can result in both short-term and long-term effects, some of which can be undesirable and even harmful.
Potential Side Effects
Daily use of allergy medications can lead to a range of side effects, varying in severity depending on the individual and the specific medication. Some common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, and headache. More serious, though less common, side effects may also occur. The severity and frequency of side effects can increase with prolonged daily use. It's crucial to be aware of these potential side effects and to consult a doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
- Drowsiness: This is a common side effect of many antihistamines and can impair cognitive function and reaction time.
- Dry mouth: This can lead to discomfort, difficulty swallowing, and increased risk of dental problems.
- Dizziness: This can make it unsafe to operate machinery or drive.
Reduced Effectiveness Over Time
Your body can become accustomed to the effects of allergy medication with prolonged daily use, leading to reduced effectiveness. This means you might need to increase your dosage to achieve the same level of relief, which increases the risk of side effects. This phenomenon, called tolerance, is particularly relevant for decongestants which can even lead to a rebound effect where symptoms worsen when the medication is stopped. It's vital to discuss this with your doctor before increasing the dose.
- Tolerance: The body adjusts to the medication, requiring higher doses for the same effect.
- Rebound effect (decongestants): Nasal congestion can worsen after stopping the medication.
- Ineffective symptom relief: The medication may no longer provide adequate relief from allergy symptoms.
Interactions with Other Medications
Allergy medications, particularly some antihistamines and decongestants, can interact with other medications you are taking. These interactions can range from mild to severe, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or reducing the effectiveness of other medications. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, to avoid potentially dangerous interactions. Careful monitoring is essential.
- Increased drowsiness: Combining allergy medicine with other sedatives can lead to excessive drowsiness.
- Altered blood pressure: Some allergy medicines can interact with blood pressure medications.
- Reduced effectiveness of other medications: Certain interactions may diminish the effects of other necessary drugs.
Long-Term Health Risks
While rare, long-term daily use of some allergy medications, particularly decongestants, has been associated with potential long-term health risks. These can include cardiovascular problems, elevated blood pressure, and sleep disturbances. It is crucial to discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor before undertaking long-term daily use. Regular check-ups and monitoring of vital signs might be necessary.
- Cardiovascular issues: Some studies have linked long-term decongestant use to increased risk of heart problems.
- Elevated blood pressure: Decongestants can raise blood pressure, posing a risk to individuals with hypertension.
- Sleep disturbances: Certain allergy medications can interfere with sleep patterns, even with prolonged use.
Importance of Consulting a Doctor
It is crucial to consult a doctor before starting any daily medication regimen for allergies, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. A doctor can assess your specific needs, recommend the appropriate medication and dosage, and monitor for any potential side effects. They can also explore alternative treatment options if necessary, such as immunotherapy or lifestyle changes. Self-treating can be dangerous and may mask underlying medical conditions.
- Personalized treatment plan: A doctor can tailor the treatment to your specific needs and allergies.
- Monitoring for side effects: Regular check-ups help identify and manage potential problems.
- Alternative treatment options: Your doctor can suggest other approaches like immunotherapy or lifestyle adjustments.
Is it bad to take Zyrtec every day for years?

Taking Zyrtec (cetirizine) daily for years is a complex issue with no simple yes or no answer. It depends heavily on individual factors and the specific reasons for taking it. While Zyrtec is generally considered safe for short-term use, long-term daily use can potentially lead to various side effects and complications. The decision to take Zyrtec daily for an extended period should always be made in consultation with a doctor, who can assess individual risks and benefits.
Potential Side Effects of Long-Term Zyrtec Use
While Zyrtec is often well-tolerated, prolonged daily use can increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects. These can range from mild to more serious. It's crucial to remember that everyone reacts differently to medications. Some individuals may experience minimal side effects even with long-term use, while others may find the side effects intolerable.
- Common Side Effects: Drowsiness, dry mouth, fatigue, headache, and nausea are frequently reported.
- Less Common Side Effects: These may include dizziness, constipation, increased appetite, and nervousness.
- Serious Side Effects (rare): Although rare, serious side effects such as allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), liver problems, and heart problems have been reported. Immediate medical attention is required if serious side effects occur.
The Importance of Doctor Consultation
Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital when taking any medication long-term, including Zyrtec. Your doctor can monitor your overall health, assess the effectiveness of the medication, and adjust the dosage or treatment plan as needed. They can also help identify and manage any potential side effects that may arise.
- Regular Blood Tests: May be recommended to monitor liver function and other vital parameters, particularly if you're on other medications.
- Dosage Adjustments: Your doctor may recommend adjustments to the dosage based on your response to the medication and the severity of your allergies.
- Alternative Treatments: Your doctor may explore alternative treatments or management strategies for your allergies, possibly reducing or eliminating the need for daily Zyrtec.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Pre-existing medical conditions can influence the decision to take Zyrtec daily for extended periods. Individuals with certain liver or kidney issues, for instance, may require dosage adjustments or alternative medications. It's crucial to be completely transparent with your doctor about your complete medical history.
- Kidney Disease: Zyrtec is primarily metabolized by the kidneys. Impaired kidney function can affect how the body processes the drug, increasing the risk of side effects.
- Liver Disease: While rare, Zyrtec can potentially affect liver function in susceptible individuals. Monitoring liver enzymes may be warranted.
- Other Medications: Interaction with other medications is a possibility. Always inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Alternatives to Daily Zyrtec
Depending on the nature and severity of your allergies, your doctor may suggest alternatives to daily Zyrtec. These could involve other antihistamines, immunotherapy (allergy shots), or lifestyle changes such as allergen avoidance.
- Other Antihistamines: Different antihistamines have varying side effect profiles and durations of action. Your doctor may recommend a different antihistamine better suited for your needs.
- Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy): This treatment aims to desensitize your immune system to specific allergens, potentially reducing your reliance on daily medication.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding triggers such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, as well as using air purifiers and other environmental control measures, can significantly reduce allergy symptoms.
Considering the Risks and Benefits
The decision to use Zyrtec daily for years is a personal one, influenced by numerous factors including the severity of your allergies, your overall health, and the potential side effects. Weighing the benefits of allergy symptom control against the potential long-term risks is essential, and this should always be done in close consultation with a healthcare professional.
- Severity of Allergies: If your allergies are significantly impacting your quality of life, the benefits of daily Zyrtec might outweigh the risks.
- Individual Response: Some individuals tolerate Zyrtec well, even with long-term use, while others experience significant side effects.
- Alternative Treatment Options: Exploring alternative treatment options may allow you to reduce or eliminate the need for daily Zyrtec, minimizing potential long-term risks.
What are the long-term side effects of allergy medication?
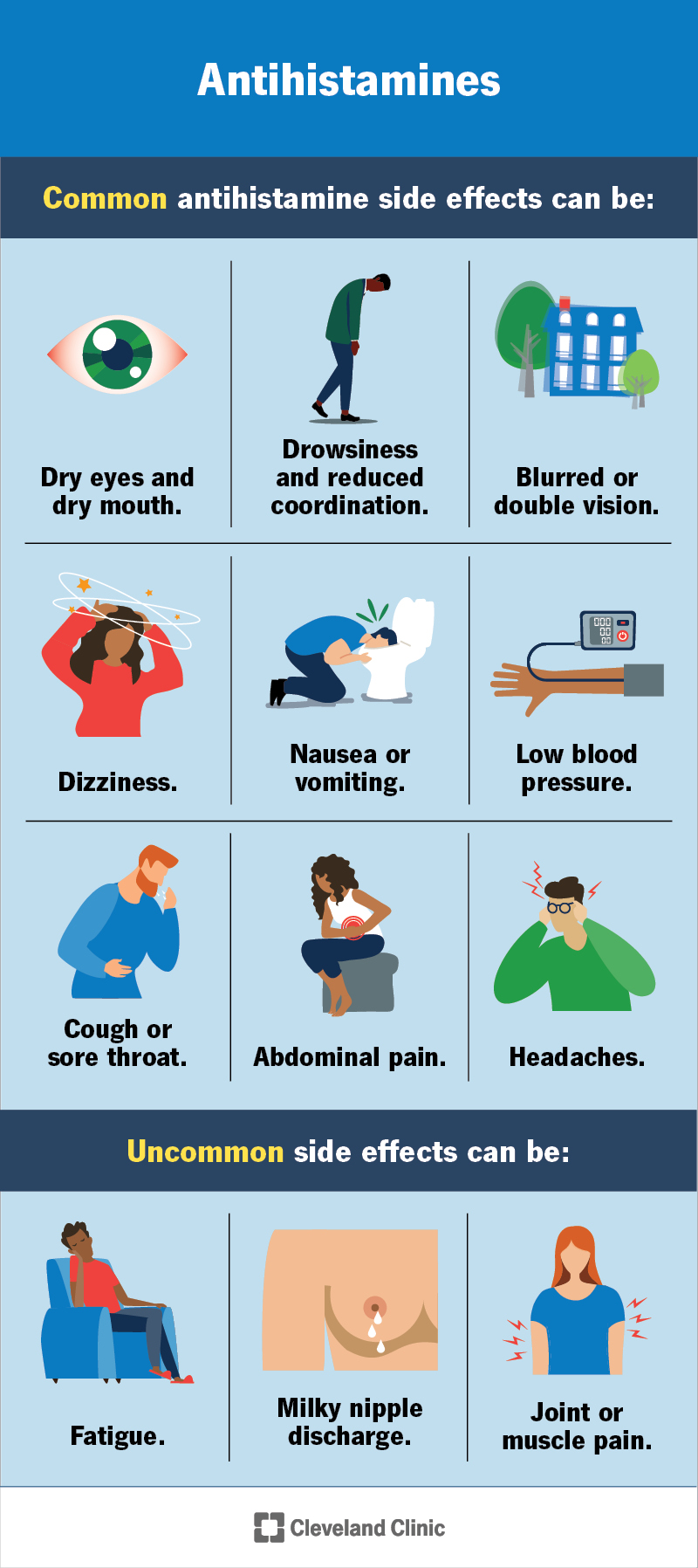
The long-term side effects of allergy medications, like any medication, vary depending on the specific drug, dosage, duration of use, and individual patient factors. While many experience minimal issues, some individuals may experience more significant long-term consequences. It's crucial to remember that this information is for general knowledge and should not replace consultation with a healthcare professional. Always discuss any concerns about medication side effects with your doctor or pharmacist.
Antihistamine-Related Long-Term Effects
Many over-the-counter and prescription antihistamines are generally safe for short-term use. However, long-term use of certain antihistamines, particularly older sedating ones, can lead to several issues. These can range from relatively mild to more concerning effects. It's important to note that newer, non-sedating antihistamines typically have a lower risk of these long-term effects.
- Drowsiness and fatigue: This is a common side effect, particularly with older antihistamines, that can persist with prolonged use, impacting daily activities and cognitive function.
- Dry mouth and eyes: These symptoms can become chronic with extended use, potentially leading to discomfort and oral health problems.
- Constipation: Some antihistamines can slow down bowel movements, leading to constipation if taken for an extended period.
Decongestant-Related Long-Term Effects
Decongestants, often used in combination with antihistamines, can also have long-term side effects if used excessively or for prolonged durations. The primary concern lies in the potential for rebound congestion, where the nasal congestion worsens when the medication is stopped. This necessitates continued use and forms a vicious cycle.
- Rebound congestion: This is a significant concern with long-term decongestant use. The body adjusts to the medication, and nasal congestion returns, often worse than before.
- Increased blood pressure: Some decongestants can elevate blood pressure, particularly in individuals with pre-existing hypertension.
- Insomnia: Some decongestants can interfere with sleep patterns, leading to long-term sleep disturbances.
Corticosteroid-Related Long-Term Effects (Inhaled & Oral)
Corticosteroids, whether inhaled (for asthma or allergic rhinitis) or oral (for severe allergies), are potent anti-inflammatory medications. While highly effective, long-term use carries potential risks, especially with oral corticosteroids.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term use of oral corticosteroids significantly increases the risk of bone thinning and fractures.
- Increased blood sugar: Corticosteroids can raise blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing diabetes or worsening existing diabetes.
- Cataracts and glaucoma: Long-term use of oral corticosteroids increases the risk of developing these eye conditions.
- Suppression of the immune system: This is a significant risk, particularly with oral corticosteroids, making the individual more susceptible to infections.
Leukotriene Modifier-Related Long-Term Effects
Leukotriene modifiers are a class of medications used to treat asthma and allergies. While generally well-tolerated, they can have some long-term side effects, although less frequently than other allergy medications.
- Neuropsychiatric effects: Some individuals may experience changes in mood, behavior, or sleep patterns.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Such as abdominal pain, nausea, or diarrhea, are occasionally reported.
- Elevated liver enzymes: Rare cases of liver enzyme elevation have been observed.
Other Potential Long-Term Side Effects
Beyond the specific drug classes, some general long-term side effects related to allergy medication use can occur. These effects often stem from the body's adaptation to the medication or interactions with other drugs or conditions.
- Medication dependence: For some, continued use becomes necessary to manage symptoms, leading to a form of dependence.
- Drug interactions: Long-term use can increase the risk of interactions with other medications, leading to unforeseen consequences.
- Development of resistance: The body's response to the medication may diminish over time, making it less effective.
Is taking antihistamines daily bad for you?

Whether taking antihistamines daily is bad for you depends on several factors, including the type of antihistamine, the dose, your individual health, and the reason for taking them. While short-term use is generally safe for most people, long-term daily use can carry potential risks and side effects. It's crucial to consult a doctor before starting any long-term medication regimen, including daily antihistamine use. They can assess your specific situation and determine if the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Types of Antihistamines and Their Effects
Antihistamines are broadly categorized into first-generation and second-generation. First-generation antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), are more likely to cause drowsiness and other side effects due to their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin), are less likely to cause drowsiness because they have a lower ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. However, even second-generation antihistamines can have side effects with prolonged use.
- First-generation antihistamines: Often cause drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and urinary retention.
- Second-generation antihistamines: Generally cause fewer side effects, but can still lead to headache, fatigue, and dry mouth with long-term use.
- Individual responses vary: The impact of antihistamines can differ significantly from person to person.
Potential Side Effects of Long-Term Antihistamine Use
While many people tolerate daily antihistamine use without significant issues, prolonged use can lead to various side effects. These can range from mild inconveniences like dry mouth and drowsiness to more serious concerns such as heart problems, seizures, and liver damage (although rare). The risk of these serious side effects is often related to higher doses and longer duration of use. The specific side effects depend greatly on the type of antihistamine being used.
- Drowsiness and Sedation: A common side effect, particularly with first-generation antihistamines.
- Dry Mouth, Nose, and Eyes: Reduces mucus production, leading to dryness and discomfort.
- Constipation: Can be a significant issue, especially with first-generation antihistamines.
Underlying Medical Conditions and Drug Interactions
Individuals with certain pre-existing medical conditions, such as glaucoma, enlarged prostate, heart disease, or high blood pressure, may experience exacerbated symptoms or increased risk of complications when taking antihistamines daily. Furthermore, antihistamines can interact with other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. It's crucial to inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking before starting antihistamine treatment. This includes over-the-counter medications and herbal remedies.
- Glaucoma: Antihistamines can increase intraocular pressure.
- Enlarged Prostate: Antihistamines can worsen urinary retention.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Some antihistamines can affect heart rate and blood pressure.
Alternatives to Daily Antihistamine Use
Depending on the reason for taking antihistamines, there may be alternative treatment options available. If your daily antihistamine use is for allergies, your doctor might suggest allergy shots (immunotherapy), lifestyle changes to reduce exposure to allergens, or other medications. For other conditions, alternative treatments could be explored to minimize or eliminate the need for daily antihistamines.
- Allergy Immunotherapy: A long-term treatment that can help desensitize you to allergens.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding triggers like dust mites, pollen, or pet dander.
- Alternative Medications: Such as nasal corticosteroids or leukotriene inhibitors for allergies.
Importance of Consulting a Doctor
Before starting any long-term medication regimen, it's absolutely essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual health status, determine the appropriateness of daily antihistamine use, and monitor for any potential side effects. Self-treating with antihistamines can be risky and might mask underlying medical conditions. A doctor can help you develop a safe and effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
- Personalized Assessment: A doctor can assess your medical history and allergies.
- Appropriate Dosage and Type: A doctor can prescribe the correct antihistamine and dosage.
- Monitoring for Side Effects: Regular checkups can help manage any potential side effects.
Is it safe to take allergy medicine every day?
Whether it's safe to take allergy medicine every day depends heavily on several factors. First and foremost is the type of allergy medication. Antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra) are generally considered safe for daily use in the long term, provided you follow the recommended dosage. However, some older antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can cause significant drowsiness and shouldn't be taken daily unless specifically prescribed by a doctor. Secondly, the severity of your allergies plays a crucial role. If your allergies are mild and well-managed with daily medication, then it might be perfectly acceptable. However, if you experience severe allergic reactions, daily medication may only be a part of a larger treatment plan, possibly including other medications or allergy immunotherapy. Finally, individual tolerance varies. While some individuals can take daily medication without side effects, others might experience undesirable consequences like drowsiness, dry mouth, or digestive issues. If you're concerned about taking allergy medication daily, always consult your doctor or pharmacist. They can assess your specific situation, weigh the risks and benefits, and recommend the most appropriate course of action. They can also help you identify and manage potential side effects. Self-medicating for extended periods, without professional guidance, can be risky, so always prioritize a consultation.
What are the potential side effects of taking allergy medicine daily?
The side effects of daily allergy medication vary significantly depending on the type of medication. Common side effects of many antihistamines include drowsiness, dry mouth, headache, and constipation. Some individuals might also experience dizziness, blurred vision, or difficulty concentrating. The severity of these side effects can range from mild and manageable to quite debilitating, depending on the individual and the dosage. Furthermore, long-term use of some allergy medications can potentially lead to other issues, although this is often less common with newer generation antihistamines. For example, some older antihistamines can have a greater impact on the central nervous system, potentially leading to more significant drowsiness or other cognitive effects over time. It is also important to note that certain medications interact with other drugs, and taking daily allergy medication alongside other medications could lead to unforeseen side effects or reduced effectiveness. If you experience any concerning side effects while taking allergy medication daily, it's vital to discontinue use and consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately. They can adjust your dosage, recommend an alternative medication, or explore other management strategies.
Are there alternatives to taking allergy medicine every day?
Yes, several alternatives exist to taking allergy medicine daily. One important approach is allergy immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). This involves gradually desensitizing your body to specific allergens, leading to a long-term reduction in allergy symptoms. While it requires a commitment over several months or years, immunotherapy can provide long-lasting relief and potentially reduce or eliminate the need for daily medication. Another approach focuses on environmental control. This involves minimizing exposure to known allergens through measures such as regular cleaning, using air filters, and avoiding triggers like pet dander or pollen. A healthy lifestyle, including adequate sleep, proper hydration, and stress management, can also impact allergy symptoms. Finally, depending on the specific allergy and its severity, your doctor might recommend other medications to be taken as needed, rather than daily. This might involve using nasal sprays, eye drops, or other medications only when symptoms flare up. The best alternative to daily allergy medication will depend on your individual circumstances, the severity of your allergies, and a consultation with a healthcare professional to discuss all options and determine the safest and most effective course of action for your specific situation.
When should I talk to a doctor about daily allergy medication use?
You should consult your doctor about daily allergy medication use under several circumstances. Firstly, if you're experiencing significant side effects from your medication, it's crucial to seek medical advice immediately. This includes but isn't limited to severe drowsiness, persistent headaches, or any other adverse reaction. Secondly, if your allergy symptoms aren't improving despite daily medication, it’s important to discuss alternative treatment strategies with your doctor. This might involve switching to a different medication, adding additional treatments, or exploring alternative approaches like immunotherapy. Thirdly, if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications, you should inform your doctor before starting or continuing daily allergy medication. This is essential to prevent potential drug interactions and ensure the safety of your treatment plan. Fourthly, if you're considering long-term use of daily allergy medication, a consultation is essential to assess potential risks and benefits. Finally, if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have children who require allergy medication, it is crucial to get professional guidance to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment. Don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you have any concerns or questions about your allergy medication, as this is crucial for managing your allergies effectively and safely.
Deja una respuesta