Is it OK to take 3 allergy pills

It's allergy season, and your sinuses are suffering. You reach for the allergy pills, but then you wonder: is it OK to take three at once? After all, they're over-the-counter, so they must be safe, right? Not necessarily. Taking too many allergy pills can lead to serious side effects, including drowsiness, blurred vision, and even heart problems. So, what's the safe way to take allergy pills? And how can you tell if you're taking too many?
Is Taking Three Allergy Pills Safe?
Whether or not it's okay to take three allergy pills depends entirely on several factors. There's no universal yes or no answer. Always consult the product label and, if you have concerns, your doctor or pharmacist. Exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to serious adverse effects, even with over-the-counter medications. The severity of your allergies, the specific medication, and your overall health all play a crucial role in determining safe usage.
What are the risks of taking more than the recommended dose?
Taking more than the recommended dose of allergy medication can result in several undesirable side effects. These can range from mild discomfort to severe health complications. Common side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, upset stomach, and headaches. More serious side effects are less common but can include rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, seizures, and even liver damage in some cases. The specific risks depend on the active ingredients in the medication and your individual sensitivity. Never exceed the recommended dosage without first consulting a healthcare professional.
What if my allergies are severe?
If you have severe allergies, taking three allergy pills might not be sufficient and could even be dangerous. Severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. Instead of increasing the dosage of over-the-counter medication, it's crucial to consult an allergist or doctor. They can properly diagnose your allergies and recommend a suitable treatment plan, which may include prescription medication, allergy shots, or other interventions. Self-treating severe allergies can be risky and potentially fatal.
What are the active ingredients to watch out for?
Many allergy medications contain antihistamines (like diphenhydramine or cetirizine) or decongestants (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine). Each active ingredient has its own potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Check the label carefully to understand the ingredients and their potential risks. Some ingredients can interact negatively with other medications you may be taking, leading to unexpected and potentially dangerous consequences. Always be aware of the active ingredients and consult a professional if unsure.
What should I do if I accidentally take too many allergy pills?
If you accidentally take more than the recommended dosage of allergy medication, don't panic, but do seek immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor, a poison control center, or go to the nearest emergency room. Provide them with information about the medication you took, the amount you ingested, and any symptoms you are experiencing. Prompt medical attention can help minimize the risks and potentially prevent serious complications. Don't try to counteract the medication yourself without professional guidance.
What are some safer alternatives to taking more pills?
Before considering increasing your allergy medication dosage, explore safer alternatives. These may include trying different allergy medications, using a nasal spray, employing other preventative measures like avoiding known allergens, or consulting with a healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive allergy management plan. A doctor can help determine the underlying cause of your allergies and recommend appropriate treatment options to effectively manage your symptoms without resorting to potentially risky self-medication practices.
| Medication Type | Potential Side Effects (Increased Dosage) | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, blurred vision, constipation | Avoid driving or operating machinery; drink plenty of fluids. |
| Decongestants | Increased heart rate, nervousness, insomnia, high blood pressure | Consult your doctor if you have heart problems or high blood pressure. |
| Combination Medications | A combination of side effects from both antihistamines and decongestants. | Read the label carefully and understand potential interactions. |
Is Taking Three Allergy Pills Safe?
Whether or not it's okay to take three allergy pills depends entirely on several factors. There's no universal yes or no answer. Always consult the product label and, if you have concerns, your doctor or pharmacist. Exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to serious adverse effects, even with over-the-counter medications. The severity of your allergies, the specific medication, and your overall health all play a crucial role in determining safe usage.
What are the risks of taking more than the recommended dose?
Taking more than the recommended dose of allergy medication can result in several undesirable side effects. These can range from mild discomfort to severe health complications. Common side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, upset stomach, and headaches. More serious side effects are less common but can include rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, seizures, and even liver damage in some cases. The specific risks depend on the active ingredients in the medication and your individual sensitivity. Never exceed the recommended dosage without first consulting a healthcare professional.
What if my allergies are severe?
If you have severe allergies, taking three allergy pills might not be sufficient and could even be dangerous. Severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. Instead of increasing the dosage of over-the-counter medication, it's crucial to consult an allergist or doctor. They can properly diagnose your allergies and recommend a suitable treatment plan, which may include prescription medication, allergy shots, or other interventions. Self-treating severe allergies can be risky and potentially fatal.
What are the active ingredients to watch out for?
Many allergy medications contain antihistamines (like diphenhydramine or cetirizine) or decongestants (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine). Each active ingredient has its own potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Check the label carefully to understand the ingredients and their potential risks. Some ingredients can interact negatively with other medications you may be taking, leading to unexpected and potentially dangerous consequences. Always be aware of the active ingredients and consult a professional if unsure.
What should I do if I accidentally take too many allergy pills?
If you accidentally take more than the recommended dosage of allergy medication, don't panic, but do seek immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor, a poison control center, or go to the nearest emergency room. Provide them with information about the medication you took, the amount you ingested, and any symptoms you are experiencing. Prompt medical attention can help minimize the risks and potentially prevent serious complications. Don't try to counteract the medication yourself without professional guidance.
What are some safer alternatives to taking more pills?
Before considering increasing your allergy medication dosage, explore safer alternatives. These may include trying different allergy medications, using a nasal spray, employing other preventative measures like avoiding known allergens, or consulting with a healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive allergy management plan. A doctor can help determine the underlying cause of your allergies and recommend appropriate treatment options to effectively manage your symptoms without resorting to potentially risky self-medication practices.
| Medication Type | Potential Side Effects (Increased Dosage) | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, blurred vision, constipation | Avoid driving or operating machinery; drink plenty of fluids. |
| Decongestants | Increased heart rate, nervousness, insomnia, high blood pressure | Consult your doctor if you have heart problems or high blood pressure. |
| Combination Medications | A combination of side effects from both antihistamines and decongestants. | Read the label carefully and understand potential interactions. |
What happens if you take three allergy relief pills?

What happens if you take three allergy relief pills depends entirely on the specific medication, the dosage of each pill, your individual body weight and health conditions, and whether you have any other medications in your system. There is no single answer. Taking more than the recommended dosage of any over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medication is dangerous and could lead to serious consequences. Always follow the directions on the label and consult a doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
Potential Side Effects of Overdosing on Allergy Medication
Taking three allergy relief pills instead of the recommended dose can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing adverse side effects. These effects can range from mild to severe, depending on the factors mentioned above. It's crucial to remember that even seemingly harmless medications can have dangerous consequences when misused.
- Increased drowsiness: Many allergy medications cause drowsiness as a side effect. Taking a higher dose intensifies this effect, potentially leading to impaired judgment, difficulty concentrating, and slowed reaction times. This can be incredibly dangerous if you are driving or operating machinery.
- Gastrointestinal distress: Upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common side effects of allergy medications, especially when taken in excess. These symptoms can be debilitating and interfere with daily activities.
- Nervous system effects: In some cases, an overdose can lead to more serious nervous system effects, such as anxiety, restlessness, tremors, or even seizures. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Interaction with Other Medications
Many allergy medications interact with other drugs. Taking three pills instead of one can dramatically increase the risk of dangerous interactions. For example, combining allergy medication with alcohol or certain pain relievers can amplify sedative effects or create harmful chemical reactions within your body. Always check the label for potential drug interactions and inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications you're taking.
- Increased risk of bleeding: Some allergy medications, particularly those containing antihistamines, can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners or other medications that affect blood clotting.
- Cardiovascular issues: Certain allergy medications, especially those containing decongestants, can elevate blood pressure and heart rate. Taking a larger dose could exacerbate these issues, potentially leading to serious cardiovascular problems.
- Drug interactions with prescription medications: Overdosing on allergy medicine can have unpredictable interactions with other prescription medications you may be taking, potentially leading to unpredictable and dangerous outcomes. Always disclose all medications you are taking, both over-the-counter and prescription, to your doctor.
The Importance of Following Dosage Instructions
The dosage instructions on allergy medication are crucial for ensuring your safety and effectiveness. Taking more than the recommended dose does not necessarily mean faster or better relief. In fact, it can lead to the opposite result, causing more side effects and hindering the desired effect. Always read the label carefully and follow the directions.
- Understanding recommended dosages: Pay close attention to the recommended dosage of your specific allergy medication. This information is critical to your safety and the effectiveness of the medication.
- Seeking professional advice: If you are unsure about the correct dosage or have any concerns, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking the medication.
- Understanding the active ingredients: Be aware of the active ingredients in your allergy medication and potential side effects associated with them. This can help inform your decision on whether or not it is safe to increase the dosage.
When to Seek Medical Attention After Taking Too Much Allergy Medication
Even if you only experience mild side effects, it's essential to monitor your body's response. If you experience any concerning symptoms after taking more than the recommended dose of allergy medication, seek immediate medical attention. This is especially critical if you are experiencing severe side effects such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe allergic reactions, or changes in heart rate or blood pressure.
- Severe allergic reactions: Symptoms like hives, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, difficulty breathing, or dizziness could indicate a severe allergic reaction requiring immediate emergency medical care.
- Persistent or worsening symptoms: If your symptoms are not improving or are worsening despite taking the medication, contact your doctor immediately.
- Uncertain about the effects: If you’re unsure whether your symptoms are caused by the medication or are a result of another medical issue, contacting a medical professional is always the best option.
Long-Term Effects of Overdosing on Allergy Medications
While the immediate effects of overdosing on allergy medication are concerning, it's crucial to understand that there may also be long-term effects on your health. Repeated or chronic overuse of allergy medication can lead to a tolerance build-up requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. It can also strain your liver and kidneys, leading to organ damage. This underscores the importance of adhering to recommended dosages and only using allergy medication as directed.
- Organ damage: Prolonged overuse of certain allergy medications can strain your liver and kidneys, leading to possible organ damage over time.
- Development of tolerance: The body can develop a tolerance to allergy medication over time, meaning that you will need higher doses to achieve the same effect.
- Increased risk of adverse health conditions: Habitual misuse of allergy medications might increase the risk of developing various adverse health conditions later in life.
Can you take 3 different allergy pills in a day?

No. You should never take three different allergy pills in a day without first consulting your doctor or pharmacist. This is because different allergy medications contain different active ingredients and taking them together can lead to dangerous interactions and an overdose of certain medications. Even if the pills seem to address different allergy symptoms (like nasal congestion versus itching), combining them increases the risk of side effects significantly. Always follow the dosage instructions provided on the packaging of each individual medication, and if you have concerns about managing multiple allergy symptoms, seek professional medical advice.
Potential Drug Interactions
Taking multiple allergy medications concurrently can lead to unpredictable drug interactions. Some antihistamines, decongestants, and other allergy medications interact negatively when combined. This can result in:
- Increased risk of side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, or heart palpitations.
- Reduced effectiveness of one or more medications.
- Serious health complications in rare cases.
Overdosing on Active Ingredients
Many over-the-counter allergy medications contain similar active ingredients, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), cetirizine (Zyrtec), or loratadine (Claritin). Taking multiple medications containing the same or similar active ingredients can quickly lead to an overdose, causing potentially serious health problems. The severity of the overdose will depend on the specific medication, the amount taken, and the individual's health.
Managing Multiple Allergy Symptoms
If you are experiencing multiple allergy symptoms, it's important to address them strategically. Instead of taking multiple medications simultaneously, consider the following approaches:
- Consult a doctor or pharmacist to discuss your symptoms and find a safe and effective treatment plan.
- Prioritize your symptoms. Focus on treating the most bothersome symptom first.
- Explore alternative treatments such as nasal sprays, eye drops, or home remedies, alongside medication, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Reading Medication Labels Carefully
Always read the labels of your allergy medications carefully. Pay close attention to the active ingredients listed, as well as the dosage instructions and warnings. This will help you avoid accidentally taking the same ingredient twice from different medications, which can contribute to an overdose. Understand the potential side effects of each medication to better anticipate any issues that may arise.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice
If you're unsure about which allergy medications to take, or if you're experiencing multiple allergy symptoms, always consult a doctor or pharmacist. They can help you determine the best course of action, considering your specific health conditions and potential drug interactions. They can also advise on how to manage your allergies effectively and safely.
What happens if I take 3 antihistamines?
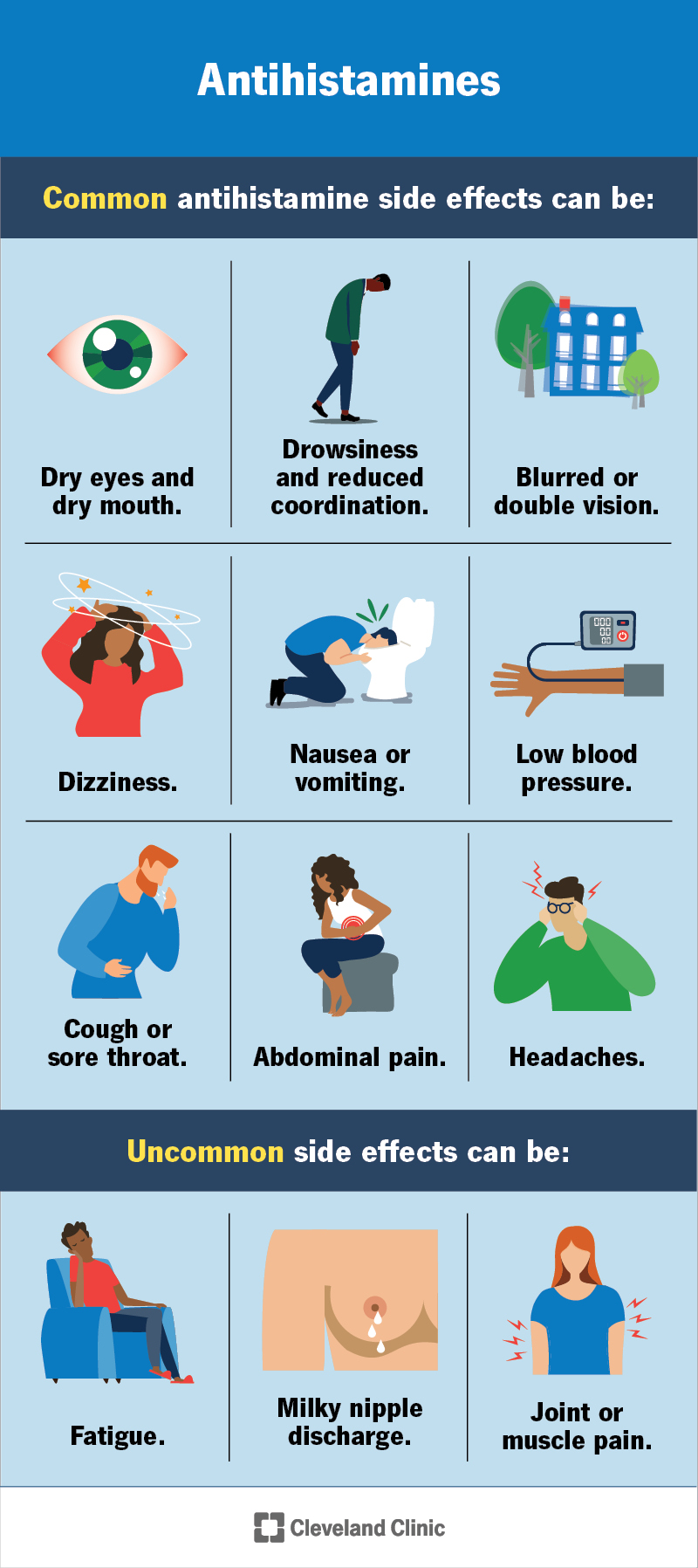
What Happens if I Take 3 Antihistamines?
Taking three times the recommended dose of antihistamines can lead to a range of unpleasant and potentially dangerous side effects. The severity of these effects depends on several factors, including the specific antihistamine, the individual's metabolism, and their overall health. It's crucial to understand that exceeding the recommended dosage is not simply a matter of amplified relief; it introduces significant risks.
Overdose Symptoms
Taking three times the recommended dose of antihistamines can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects. These range from mild to severe, and can include: drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating, and rapid heartbeat. In more severe cases, seizures, respiratory depression, and even coma can occur. The specific symptoms will vary depending on the type of antihistamine taken.
- Sedation: Most antihistamines cause drowsiness, and taking a triple dose dramatically intensifies this effect. This can impair judgment, coordination, and reaction time, making driving or operating machinery extremely dangerous.
- Cardiovascular effects: Some antihistamines can affect heart rate and blood pressure. A significant overdose might lead to tachycardia (rapid heart rate) or arrhythmias.
- Neurological effects: Overdosing can cause confusion, disorientation, hallucinations, tremors, and seizures. These effects are particularly concerning and can require immediate medical attention.
Interactions with Other Medications
Antihistamines can interact negatively with other medications. Taking a triple dose significantly increases the risk and severity of these interactions. Some medications, like certain sedatives or antidepressants, can synergistically enhance the sedative effects of antihistamines, potentially leading to dangerous respiratory depression. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications you are taking before using any antihistamine.
- Sedatives and opioids: Combining antihistamines with sedatives or opioids drastically increases the risk of respiratory depression.
- Alcohol: Alcohol intensifies the sedative effects of antihistamines.
- MAO inhibitors: Certain antidepressants (MAO inhibitors) interact negatively with antihistamines, possibly leading to severe side effects.
Long-Term Effects
While most side effects from an acute overdose are temporary, repeatedly exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to longer-term health problems. Liver or kidney damage is a possibility with chronic overuse. Furthermore, building a tolerance to the medication might necessitate even higher doses to achieve the desired effect, leading to a dangerous cycle of increased intake and escalating risks.
- Liver damage: Some antihistamines are metabolized by the liver, and excessive use can stress this organ.
- Kidney problems: Antihistamines can impact kidney function, and chronic overuse increases the risk of kidney-related complications.
- Medication dependence: Repeatedly taking high doses can lead to dependence, making it difficult to discontinue use.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect you or someone else has taken an overdose of antihistamines, seek immediate medical attention. Don't hesitate to call emergency services or go to the nearest hospital. Providing information about the type and amount of antihistamine taken is crucial for effective treatment. Early intervention is key to minimizing potential harm.
- Call emergency services: Do not attempt to treat the overdose yourself.
- Go to the nearest hospital: Immediate medical care can prevent serious complications.
- Provide information: Tell the medical professionals the type and quantity of antihistamine ingested.
Preventing Antihistamine Overdose
Always follow the recommended dosage instructions on the medication label. Never take more than the prescribed amount, even if you feel your symptoms aren't improving. If you have any questions or concerns about your medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist before adjusting your dosage. Proper medication management is key to avoiding potentially harmful side effects.
- Follow dosage instructions: Never exceed the recommended dose.
- Consult a doctor or pharmacist: Seek professional advice if you have questions about your medication.
- Store medications safely: Keep medications out of reach of children and others who might misuse them.
Can I take 3 Zyrtec in one day?

No, you should not take 3 Zyrtec in one day unless specifically instructed to do so by a doctor. Zyrtec (cetirizine) is an antihistamine available over-the-counter, but exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to several adverse effects. The recommended adult dose is typically one 10mg tablet once daily. Taking more than the recommended dose won't necessarily make your allergy symptoms go away faster, and it could increase your risk of experiencing side effects. Always follow the dosage instructions on the label or as directed by your physician or pharmacist.
Zyrtec Dosage and Overdose Risks
Exceeding the recommended dosage of Zyrtec can lead to a range of unpleasant side effects. While a single extra tablet might not cause serious problems for most people, consistently taking more than the recommended dose increases the likelihood of experiencing more significant adverse effects. It's crucial to remember that more is not always better when it comes to medication. Your body can only process a certain amount of the active ingredient, and exceeding that threshold may lead to unwanted consequences. Always consult a healthcare professional before altering the prescribed or recommended dosage.
- Drowsiness: One of the most common side effects of Zyrtec is drowsiness, and this risk significantly increases with higher doses.
- Dry Mouth: Excessive dryness in the mouth can be uncomfortable and may impact your ability to eat or swallow easily.
- Headache: Increased doses can potentially worsen or trigger headaches.
Side Effects of Taking More Than Recommended
Taking three Zyrtec tablets in one day may significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects. These side effects can vary in severity depending on individual factors such as age, weight, and overall health. It's essential to be aware of the potential risks and to prioritize your health and safety. If you experience any concerning side effects after taking Zyrtec, even if you followed the recommended dosage, you should immediately contact your doctor or other qualified medical professional.
- Severe Drowsiness: This could impair your ability to drive or operate machinery.
- Gastrointestinal Distress: This can manifest as nausea, vomiting, or stomach upset.
- Allergic Reactions: Though rare, more severe allergic reactions are possible.
When to Consult a Doctor About Zyrtec
If you're experiencing persistent allergy symptoms despite taking the recommended dose of Zyrtec, you should consult a doctor. Don't attempt to self-treat by increasing the dosage. Your doctor can help determine the underlying cause of your allergy symptoms and recommend the appropriate treatment plan, which might include a different medication or a change in dosage.
- Persistent symptoms despite taking the recommended dosage.
- Experiencing any concerning or unusual side effects.
- Have other underlying health conditions that could interact with Zyrtec.
Alternatives to Increasing Zyrtec Dosage
If your allergy symptoms aren't adequately controlled by a single daily dose of Zyrtec, there are other options available that you should discuss with your doctor or pharmacist. They may recommend a different antihistamine, a nasal spray, or another treatment approach. Increasing the dosage without professional guidance is not the recommended approach to managing allergy symptoms.
- Different Antihistamines: Explore other antihistamines with varying mechanisms of action.
- Decongestants: These can help alleviate nasal congestion.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These are effective for long-term management of nasal allergies.
Understanding the Active Ingredient in Zyrtec
Zyrtec contains cetirizine, an antihistamine that blocks histamine, a substance released by the body in response to allergens. Understanding how the medication works and its potential effects is crucial for safe and effective use. Always read the medication label carefully and follow the prescribed or recommended dosage instructions to minimize the risk of adverse effects. If uncertain about any aspect of your medication, contact your pharmacist or healthcare provider.
- Mechanism of Action: How cetirizine blocks histamine receptors.
- Pharmacokinetics: How the body processes and eliminates cetirizine.
- Drug Interactions: Potential interactions with other medications.
Is it okay to take three allergy pills at once?
Taking three allergy pills at once depends entirely on the specific medication and the dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer. Never exceed the recommended dosage printed on the label unless explicitly instructed to do so by your doctor. Many over-the-counter allergy medications contain antihistamines or decongestants, both of which can have adverse effects if taken in excessive amounts. Taking three times the recommended dose could lead to a number of unpleasant side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, and even more serious complications depending on the medication and your individual health. Always carefully read the patient information leaflet enclosed with the medication. If you're unsure about the appropriate dosage, consult a pharmacist or your physician. They can advise you on the safest and most effective way to manage your allergy symptoms and determine whether a higher dose is appropriate for your specific needs. Ignoring the recommended dosage could potentially mask serious underlying health issues or exacerbate existing conditions. Remember that a higher dose doesn't necessarily equate to faster or better relief, and in many cases, it can be counterproductive and harmful. Prioritizing safety and following the instructions is paramount.
What are the potential side effects of taking too many allergy pills?
The potential side effects of taking more allergy pills than recommended vary greatly depending on the type of medication and the amount ingested. Common side effects associated with exceeding the recommended dose of over-the-counter allergy medications include excessive drowsiness, making it unsafe to drive or operate machinery. You might experience dizziness, blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, and headaches. In more serious cases, taking too many allergy pills can lead to nausea, vomiting, rapid or irregular heartbeat (tachycardia), high blood pressure, and anxiety. Some medications can also cause seizures or severe allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to certain ingredients. Specific decongestants can raise blood pressure significantly, posing a particular risk for individuals with pre-existing hypertension. Antihistamines, while generally well-tolerated, can cause significant drowsiness, especially in higher than recommended dosages. If you suspect you've taken too many allergy pills, seek immediate medical attention. Do not attempt to self-treat; prompt medical intervention is crucial to mitigate potential complications. The severity of the side effects will also depend on your individual health status, pre-existing conditions, and other medications you might be taking concurrently.
If I'm not getting relief from my allergy symptoms with the recommended dosage, what should I do?
If the recommended dosage of your allergy medication isn't providing sufficient relief, do not simply increase the dose yourself. This is a common mistake that can lead to serious side effects. Instead, you should consult your physician or pharmacist. There might be several reasons why your current medication isn't effectively managing your symptoms. It's possible that the type of medication isn't appropriate for your specific allergies, or you may have a more severe allergic reaction than initially anticipated. Your doctor might recommend a different medication, adjust the dosage of your current medication, or suggest additional treatment options like nasal sprays, eye drops, or even a short course of corticosteroids for particularly severe cases. They can also assess for underlying conditions that might be contributing to or exacerbating your allergy symptoms. Ignoring insufficient relief and attempting to self-treat could delay appropriate medical care and prolong your suffering. It's always best to seek professional advice rather than risking potential harm through self-medication.
When should I seek immediate medical attention after taking allergy medication?
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe or concerning side effects after taking allergy medication, even if you took the recommended dose. This includes symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), hives, severe dizziness, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, seizures, or loss of consciousness. These are signs of a potentially serious allergic reaction or other adverse event requiring immediate medical intervention. Even if the symptoms seem mild initially, it's important to monitor them closely. If they worsen or persist, seek medical help immediately. Do not hesitate to call emergency services if you experience any life-threatening symptoms. Delaying treatment can have serious consequences. The same applies if you suspect you've accidentally taken a significantly higher dose than recommended. Prompt medical attention can help prevent or manage potentially serious complications. Always keep a record of the medications you're taking and their dosages, and be sure to share this information with medical professionals.
Deja una respuesta