How to flush out an allergic reaction

If you're battling an allergic reaction, it's crucial to take prompt action to mitigate its effects. Flushing out the allergens responsible for triggering your immune response can help alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery. This article will guide you through the steps for effectively flushing out an allergic reaction, ensuring you regain comfort and well-being.
How to Treat an Allergic Reaction: Flushing Out the Allergen
While the term "flush out" isn't medically precise for treating allergic reactions, the goal is to remove the allergen and manage the symptoms. Allergic reactions range in severity from mild to life-threatening (anaphylaxis), so immediate and appropriate action is crucial. This information is for general knowledge and doesn't replace professional medical advice. Always seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a severe allergic reaction.
Removing the Allergen
The first step in managing an allergic reaction is to identify and remove the source of the allergen. This might involve removing a piece of clothing that contains a trigger, washing off a substance from the skin, or leaving an environment where airborne allergens are present. For ingested allergens, it may mean avoiding further consumption of the food. If you don't know the source, try to eliminate potential culprits.
Managing Skin Reactions
Many allergic reactions manifest as skin problems like hives, rashes, or itching. Cool compresses can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. A cool bath or shower can also be beneficial. Over-the-counter antihistamine creams or lotions can reduce itching and swelling. Avoid scratching, as this can worsen the reaction and lead to infection.
Using Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can help alleviate symptoms like itching, hives, and sneezing. Follow the dosage instructions carefully. For severe reactions, a doctor might prescribe a stronger antihistamine or other medication.
Utilizing Epinephrine (EpiPen)
For individuals with severe allergies (anaphylaxis), carrying and knowing how to use an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is critical. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of a severe allergic reaction. If you suspect anaphylaxis, administer epinephrine immediately and seek emergency medical help. Do not delay.
Seeking Medical Attention
Always seek medical attention if your allergic reaction is severe, doesn't improve with home treatment, or if you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. Emergency services should be contacted immediately in these cases. Even mild reactions warrant medical attention if they are persistent or recurrent.
| Symptom | Mild Reaction Treatment | Severe Reaction Treatment (Anaphylaxis) |
|---|---|---|
| Hives/Rash | Cool compresses, antihistamine cream | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Itching | Antihistamine cream, cool bath | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Sneezing/Runny Nose | Oral antihistamine | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty Breathing/Swelling | Seek immediate medical attention | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
How to Treat an Allergic Reaction: Flushing Out the Allergen
While the term "flush out" isn't medically precise for treating allergic reactions, the goal is to remove the allergen and manage the symptoms. Allergic reactions range in severity from mild to life-threatening (anaphylaxis), so immediate and appropriate action is crucial. This information is for general knowledge and doesn't replace professional medical advice. Always seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a severe allergic reaction.
Removing the Allergen
The first step in managing an allergic reaction is to identify and remove the source of the allergen. This might involve removing a piece of clothing that contains a trigger, washing off a substance from the skin, or leaving an environment where airborne allergens are present. For ingested allergens, it may mean avoiding further consumption of the food. If you don't know the source, try to eliminate potential culprits.
Managing Skin Reactions
Many allergic reactions manifest as skin problems like hives, rashes, or itching. Cool compresses can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. A cool bath or shower can also be beneficial. Over-the-counter antihistamine creams or lotions can reduce itching and swelling. Avoid scratching, as this can worsen the reaction and lead to infection.
Using Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can help alleviate symptoms like itching, hives, and sneezing. Follow the dosage instructions carefully. For severe reactions, a doctor might prescribe a stronger antihistamine or other medication.
Utilizing Epinephrine (EpiPen)
For individuals with severe allergies (anaphylaxis), carrying and knowing how to use an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is critical. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of a severe allergic reaction. If you suspect anaphylaxis, administer epinephrine immediately and seek emergency medical help. Do not delay.
Seeking Medical Attention
Always seek medical attention if your allergic reaction is severe, doesn't improve with home treatment, or if you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. Emergency services should be contacted immediately in these cases. Even mild reactions warrant medical attention if they are persistent or recurrent.
| Symptom | Mild Reaction Treatment | Severe Reaction Treatment (Anaphylaxis) |
|---|---|---|
| Hives/Rash | Cool compresses, antihistamine cream | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Itching | Antihistamine cream, cool bath | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Sneezing/Runny Nose | Oral antihistamine | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty Breathing/Swelling | Seek immediate medical attention | Epinephrine, immediate medical attention |
How do you get rid of an allergic reaction asap?

How do you get rid of an allergic reaction ASAP? There's no single answer, as the best course of action depends heavily on the severity of the reaction and the allergen involved. However, some steps can be taken to alleviate symptoms quickly. Immediate action is crucial, especially if the reaction is severe (anaphylaxis) which can be life-threatening. If you suspect anaphylaxis, call emergency services immediately. For milder reactions, the following steps can help.
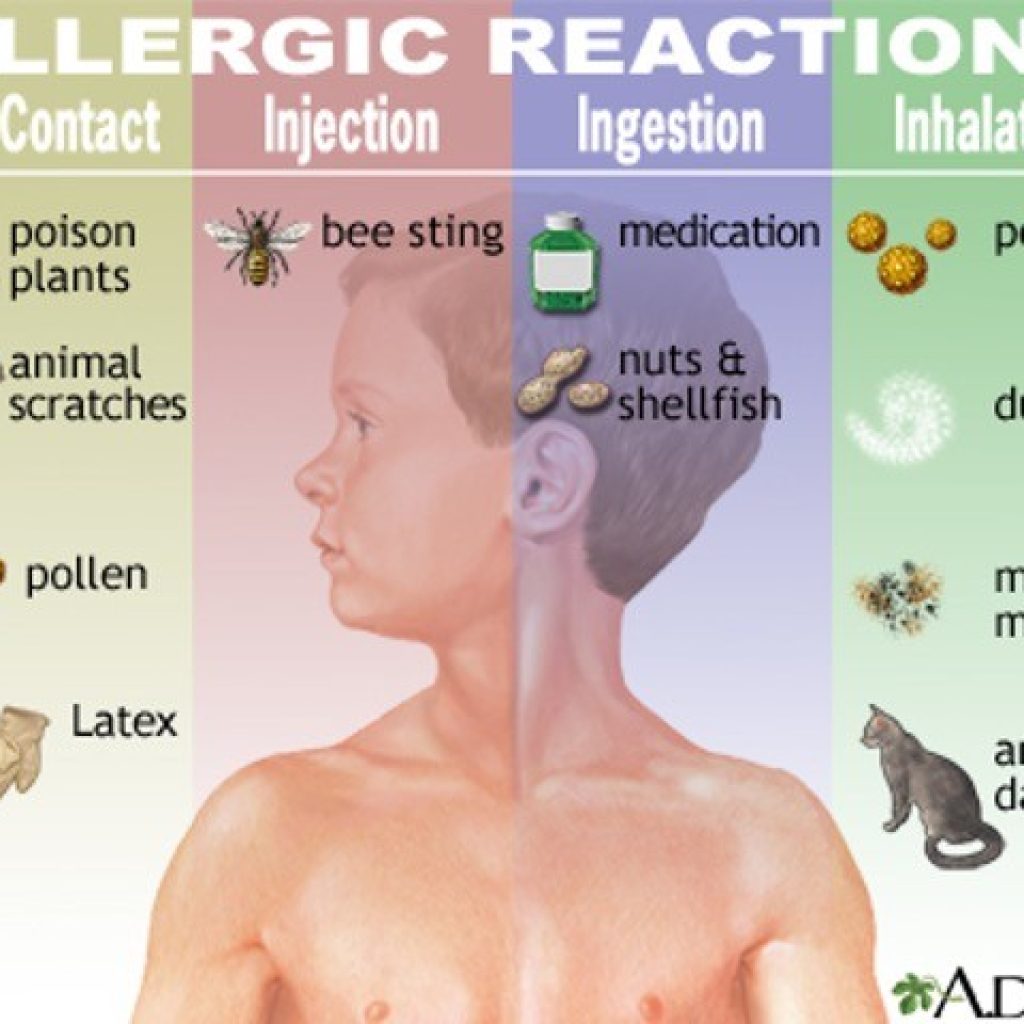
Identify and Remove the Allergen
The first and most important step is to identify and remove the source of the allergic reaction. This could be anything from pollen and pet dander to certain foods or medications. Removing the allergen will prevent further exposure and worsening of the symptoms. Once identified, try to remove it from contact with your skin or from your environment.
- If it's a food allergy, don't consume any more of that food.
- If it's contact dermatitis from a plant, wash the affected area thoroughly.
- If it's an airborne allergen, move to a cleaner environment, such as indoors with air conditioning.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Many over-the-counter (OTC) medications can help alleviate mild to moderate allergic reactions. Antihistamines are a cornerstone of treatment, blocking the release of histamine, a chemical responsible for many allergy symptoms. These come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and nasal sprays.
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl): A widely available antihistamine effective for many symptoms.
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec) or Loratadine (Claritin): Non-drowsy antihistamines suitable for daytime use.
- Hydrocortisone cream: Effective for localized skin reactions like hives or eczema.
Home Remedies
Certain home remedies can provide temporary relief from mild allergy symptoms. These are not substitutes for medical treatment, but they can complement medication and ease discomfort. Always consult a doctor if symptoms worsen or persist.
- Cold compresses: Can soothe itchy skin and reduce swelling.
- Elevating affected limbs: Helps reduce swelling in affected areas.
- Oatmeal baths: Soothes itchy skin; use colloidal oatmeal for best results.
Epipen/Auto-injector
For individuals with severe allergies, particularly those with a history of anaphylaxis, an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is crucial. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of a severe allergic reaction. If you experience symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, or dizziness, use your auto-injector immediately and call emergency services.
- Always carry your auto-injector with you and ensure it's not expired.
- Learn how to use it properly before you need it; proper training is essential.
- Seek immediate medical attention after using an auto-injector, even if symptoms improve.
Seek Medical Attention
If your allergic reaction is severe, worsening, or doesn't improve with home treatment, seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms requiring urgent medical care include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, dizziness, rapid pulse, or a drop in blood pressure. Early medical intervention is key in managing severe allergic reactions and preventing complications.
- Don't hesitate to call emergency services if you suspect anaphylaxis.
- Describe your symptoms accurately to medical professionals.
- Follow your doctor's instructions carefully regarding treatment and follow-up care.
How do you flush an allergic reaction out of your system?
There's no way to "flush" an allergic reaction out of your system in the sense of quickly removing the allergen and its effects. The body's immune response, once triggered, takes time to resolve. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further exposure to the allergen. However, certain actions can help mitigate the effects and speed up recovery.
Identifying and Removing the Allergen
The first and most crucial step is to identify and remove the source of the allergic reaction. This might involve removing a food from your mouth, leaving a location with airborne allergens (like pollen or pet dander), or removing irritating clothing. The quicker you remove the allergen, the better your chances of minimizing the severity of the reaction. If you're unsure of the allergen, seeking immediate medical attention is paramount.
- Thoroughly wash any area of skin that has come into contact with the allergen.
- Change your clothing if you suspect that was the source.
- If it's a food allergy, try to identify what you ate recently.
Administering Medications
Antihistamines are often the first line of defense against allergic reactions. They help block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic response. For more severe reactions, epinephrine (adrenaline), via an auto-injector like an EpiPen, may be necessary. This medication can counteract the effects of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) and buy crucial time until professional medical help arrives. Always follow the instructions on your medication and consult your doctor about appropriate dosage.
- Keep a readily accessible supply of your prescribed antihistamines and epinephrine.
- Learn how to correctly use an epinephrine auto-injector.
- Contact emergency medical services if symptoms worsen or don’t improve.
Supporting Your Body's Natural Processes
Your body naturally works to combat the allergic reaction. Hydration is key; drinking plenty of water helps flush out inflammatory chemicals. Rest allows your body to focus its energy on recovery. Avoiding strenuous activity can also reduce stress on your system, allowing it to heal more efficiently. While not directly "flushing" the reaction, these actions aid in your body's natural recovery process.
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as water or clear broths.
- Get ample rest; avoid strenuous activities.
- Listen to your body and take it easy.
Seeking Medical Attention
Severe allergic reactions require immediate medical attention. Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or face, hives spreading rapidly, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat all warrant a call to emergency services. Even if symptoms seem to be improving, a doctor's evaluation is essential to rule out potential complications and ensure proper management of the condition. Don't hesitate to seek professional help.
- Call emergency services immediately if experiencing severe symptoms.
- Follow your doctor's instructions regarding any tests or follow-up appointments.
- Inform your doctor about the allergy to aid in future preventative measures.
Preventing Future Allergic Reactions
Once you know your allergen, preventative measures are key. This might involve avoiding specific foods, environments, or substances. Using preventative medications, such as allergy shots (immunotherapy), can also desensitize your immune system over time, reducing the severity of future reactions. Careful planning and adherence to your doctor's recommendations are crucial for long-term allergy management.
- Identify and avoid your known allergens.
- Discuss allergy testing and immunotherapy options with your doctor.
- Keep a detailed record of your allergic reactions and triggers.
What neutralizes an allergic reaction?
There isn't a single substance that universally neutralizes all allergic reactions. The approach to treating an allergic reaction depends on its severity and the specific allergen involved. Mild reactions often resolve on their own, while more severe reactions require immediate medical intervention. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further release of inflammatory mediators. Epinephrine (adrenaline) is a crucial medication for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), as it counteracts the effects of histamine and other inflammatory substances. Antihistamines block the action of histamine, a key chemical involved in allergic responses, reducing symptoms like itching, sneezing, and swelling. Corticosteroids, like prednisone, are used to reduce inflammation in more severe cases. For some allergies, immunotherapy (allergy shots) can modify the immune system's response over time, reducing the severity of future reactions. Ultimately, the "neutralization" is a multifaceted process aiming to control the body's overactive immune response.
Antihistamines: Blocking Histamine's Effects
Antihistamines are medications that work by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction. Histamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of allergy, such as itching, sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes. Antihistamines effectively reduce these symptoms but do not address the underlying cause of the allergy. They are available over-the-counter (OTC) or by prescription.
- First-generation antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine) can cause drowsiness.
- Second-generation antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine, fexofenadine) are less likely to cause drowsiness.
- Oral and topical antihistamines are available for different applications.
Epinephrine: A Lifesaving Intervention in Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Epinephrine (adrenaline) is the cornerstone of anaphylaxis treatment. It acts quickly to constrict blood vessels, relax airways, and counteract the effects of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Epinephrine is typically administered via an auto-injector (EpiPen, Auvi-Q) in emergencies, allowing for rapid self-administration or administration by a bystander.
- Epinephrine is a vasoconstrictor, helping to raise blood pressure.
- It's a bronchodilator, opening the airways to improve breathing.
- It must be administered promptly to be effective in anaphylaxis.
Corticosteroids: Reducing Inflammation
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications. They are often used in conjunction with other treatments for more severe allergic reactions or to prevent severe reactions. Corticosteroids work by suppressing the immune system's inflammatory response, reducing swelling, redness, and itching. They are typically administered orally or intravenously depending on the severity of the reaction.
- Corticosteroids are effective in reducing inflammation caused by allergens.
- They may have side effects with prolonged use.
- They are often prescribed for conditions like allergic asthma and severe skin reactions.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots): Modifying the Immune Response
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, is a long-term treatment option for certain allergies. It works by gradually desensitizing the immune system to the allergen over time. Small, increasing doses of the allergen are injected, prompting the immune system to develop tolerance. This approach can significantly reduce the severity or frequency of allergic reactions.
- Immunotherapy is a long-term commitment, often requiring multiple injections over several years.
- It's most effective for specific types of allergies like pollen, dust mites, and insect venom.
- The effectiveness of immunotherapy is dependent on the individual's response.
Managing Allergic Reactions: Avoidance and Emergency Preparedness
Avoiding contact with known allergens is a crucial aspect of managing allergic reactions. This might involve lifestyle changes, such as avoiding certain foods, using air purifiers, and taking other preventative measures. In cases of severe allergies, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector and knowing how to use it is essential. Developing an action plan with a doctor, including emergency contacts and steps to take in case of a severe reaction, is paramount for safety.
- Reading food labels carefully is important to identify potential allergens.
- Using medications as prescribed by a doctor can help manage symptoms.
- Seeking medical attention promptly is crucial for severe reactions.
How long does it take for an allergic reaction to go away?
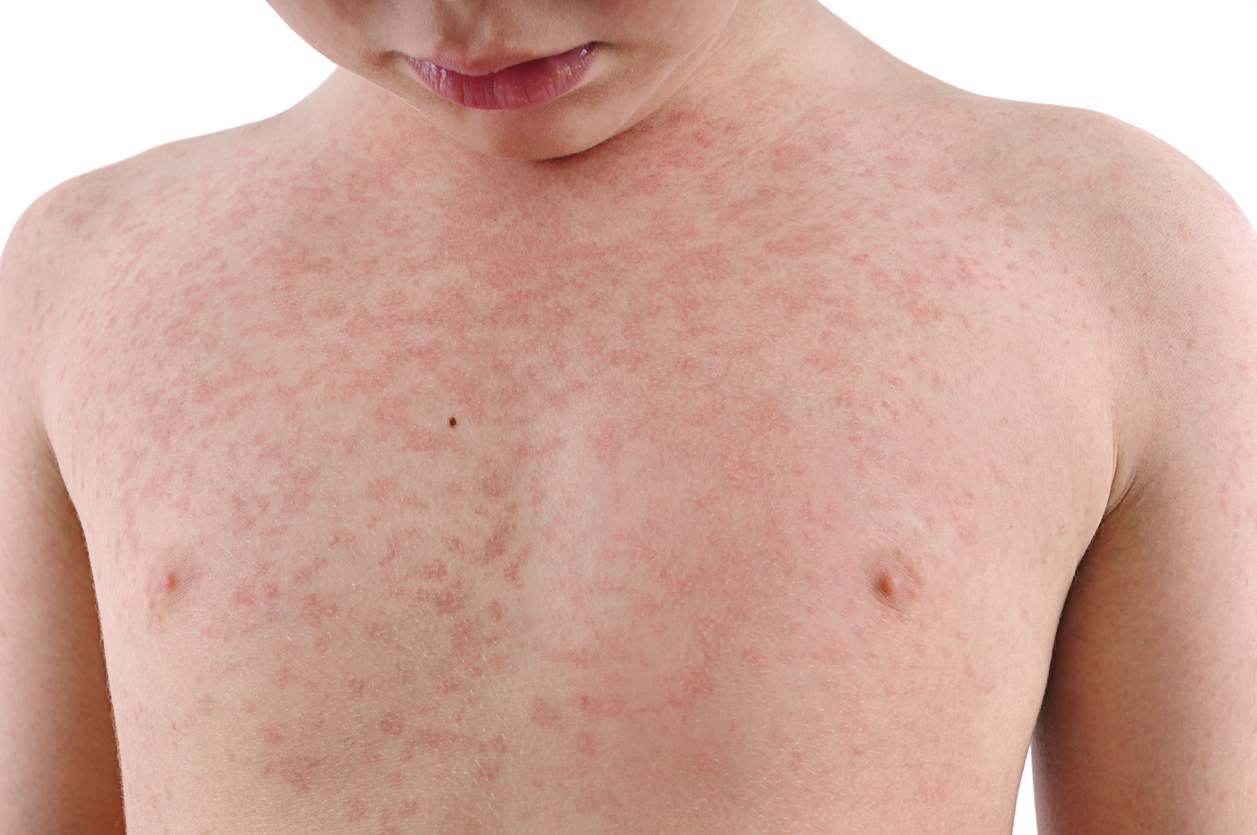
The duration of an allergic reaction is highly variable and depends on several factors, including the allergen, the route of exposure (e.g., ingestion, inhalation, contact), the severity of the reaction, and the individual's sensitivity. Mild allergic reactions, like mild hives or itchy skin, might resolve within a few hours to a day with over-the-counter medication like antihistamines. However, more severe reactions, such as anaphylaxis, require immediate medical attention and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Anaphylaxis symptoms, which include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, and a rapid drop in blood pressure, can be ongoing unless treated with epinephrine and other supportive measures. In such cases, the recovery process can take days to weeks, depending on the severity of the initial reaction and the effectiveness of treatment.
Severity of the Allergic Reaction
The severity of the allergic reaction is the most significant determinant of its duration. Mild reactions, characterized by localized symptoms such as skin rashes, itching, or sneezing, usually subside within a few hours to a day with appropriate treatment. Moderate reactions, involving more widespread symptoms like widespread hives or swelling, might take longer to resolve, potentially lasting several days. Severe reactions, such as anaphylaxis, can have lingering effects for weeks or even months. The recovery period for anaphylaxis involves addressing potential organ damage, managing lingering symptoms, and ensuring complete recovery of bodily functions.
- Mild reactions: Often resolve within 24 hours.
- Moderate reactions: May persist for several days.
- Severe reactions (anaphylaxis): Can have lasting effects for weeks or even months.
Type of Allergen
Different allergens can trigger reactions of varying durations. For instance, allergic reactions to pollen might last for the duration of pollen season, while reactions to certain foods might resolve more quickly after the offending food is digested. Insect stings can cause reactions ranging from minor local swelling to severe systemic symptoms, with duration depending on the type of insect and the individual's reaction. Understanding the specific allergen involved can provide insight into the expected duration of the reaction.
- Pollen allergies: Duration tied to pollen season.
- Food allergies: Often resolve after the allergen is eliminated.
- Insect stings: Duration varies greatly depending on the severity of the reaction.
Treatment Received
The type and timeliness of treatment significantly impacts the duration of an allergic reaction. Prompt administration of antihistamines or epinephrine in severe cases can dramatically reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. However, delayed or inadequate treatment can prolong the reaction and increase the risk of complications. Furthermore, ongoing management of allergy symptoms, such as through immunotherapy, can reduce the frequency and intensity of future reactions.
- Prompt treatment: Significantly reduces duration and severity.
- Delayed or inadequate treatment: Can prolong the reaction and increase risk of complications.
- Immunotherapy: Reduces future reaction frequency and intensity.
Individual Sensitivity
Individual sensitivity to allergens varies widely. Some individuals experience mild reactions, while others are highly sensitive and prone to severe reactions even with minimal exposure to an allergen. This individual variation makes it challenging to predict the exact duration of an allergic reaction. Genetic predisposition, previous exposure to the allergen, and overall health status all influence the duration and intensity of the reaction.
- Genetic predisposition: Plays a significant role in sensitivity.
- Prior exposure: Can influence the intensity of subsequent reactions.
- Overall health: A weakened immune system might prolong recovery.
Route of Exposure
The way an individual is exposed to an allergen can influence how long the allergic reaction lasts. For instance, inhalation of allergens (such as pollen or pet dander) may result in longer-lasting symptoms compared to skin contact with an allergen, which might cause a localized reaction that resolves relatively quickly. Ingestion of an allergen may lead to gastrointestinal symptoms that last for several hours or even days. The method of exposure helps determine the affected systems and the timeframe of recovery.
- Inhalation: Often leads to longer-lasting symptoms.
- Skin contact: Usually causes localized, faster-resolving reactions.
- Ingestion: Can lead to protracted gastrointestinal symptoms.
What are the common symptoms of an allergic reaction that require flushing out?
Allergic reactions manifest in various ways, and the need for "flushing out" (which generally refers to supportive care and potentially medical intervention) depends on the severity. Mild allergic reactions might involve skin symptoms like hives (urticaria), itching, or localized swelling. These often don't require aggressive interventions beyond antihistamines. However, more severe reactions necessitate immediate action. These can include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), difficulty breathing (dyspnea or wheezing), a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), dizziness or lightheadedness, and even a drop in blood pressure (hypotension). Anaphylaxis, a life-threatening, systemic allergic reaction, presents with several of these severe symptoms simultaneously. If you experience any symptoms beyond mild itching or hives, particularly those affecting your breathing or circulation, immediate medical attention is crucial. Don't try to self-treat a severe allergic reaction; seek emergency medical help immediately.
What are the first aid steps for flushing out a mild allergic reaction?
For mild allergic reactions, characterized mainly by skin symptoms like hives or itching, certain first aid steps can provide relief. First, identify and remove the allergen if possible. This might involve taking off jewelry that's causing contact dermatitis, removing a food from your mouth, or moving away from a pollen source. Next, take an over-the-counter antihistamine like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) as directed on the label. These medications help block the release of histamine, a chemical responsible for many allergic symptoms. Cool compresses applied to itchy areas can provide soothing relief. Avoid scratching, as this can worsen the reaction and lead to infection. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical advice. It's important to note that these steps are only for mild reactions. For any signs of a severe reaction, immediately call emergency services.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for an allergic reaction?
Immediate medical attention is absolutely necessary if you experience symptoms indicating a severe allergic reaction. These include but are not limited to: difficulty breathing or wheezing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema); dizziness or lightheadedness; rapid heartbeat; a drop in blood pressure; and feeling faint or weak. Anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition, involves several of these symptoms occurring simultaneously. If you suspect anaphylaxis, don't hesitate—call emergency services immediately. Even if symptoms initially seem mild but worsen rapidly, seek immediate medical care. The progression of an allergic reaction can be unpredictable, and delaying treatment can have serious consequences. Time is of the essence in managing severe allergic reactions. Don't try to self-treat a severe reaction; professional medical intervention is crucial.
What is the role of epinephrine (EpiPen) in flushing out a severe allergic reaction?
Epinephrine (adrenaline), administered via an auto-injector like an EpiPen, is a life-saving medication for severe allergic reactions, especially anaphylaxis. It acts quickly to constrict blood vessels, open airways, and increase heart rate, counteracting the dangerous effects of the allergic reaction. If you have a known severe allergy and have been prescribed an EpiPen, learn how to use it properly and always carry it with you. When administered correctly, epinephrine can significantly improve chances of survival during a severe reaction. It's crucial to understand that epinephrine is not a cure; it buys time until professional medical help arrives. Even after administering epinephrine, you must still seek immediate medical attention. The EpiPen should be used as soon as symptoms of a severe allergic reaction appear, not waiting to see if the reaction worsens. Improper use or delayed administration can have dire consequences.

Deja una respuesta