What is the fastest way to cure allergies at home

Allergies, with their relentless symptoms such as sneezing, congestion, and itchy eyes, can put a damper on your daily routine. If you're looking for ways to manage these symptoms without relying on over-the-counter medications, natural remedies may hold the key. In this article, we'll explore the fastest ways to cure allergies at home, using simple and effective DIY treatments.
What is the Fastest Way to Cure Allergies at Home? (A Realistic Approach)
There's no magic bullet for a fast cure for allergies at home. Allergies are a result of your immune system overreacting to a harmless substance (allergen). While you can't entirely "cure" allergies at home, you can manage symptoms and potentially reduce their severity over time with a combination of strategies. It's crucial to remember that seeking professional medical advice is essential, especially if your allergies are severe or interfering with your daily life. Home remedies should be considered supportive measures, not replacements for proper medical care.
1. Identify and Eliminate the Allergen
The most effective way to manage allergies is to identify and avoid the substances that trigger your symptoms. Keep a detailed allergy diary noting times you experience symptoms, locations, and potential exposures. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, and specific foods. Once you identify the culprit, take steps to minimize your exposure. This might involve regularly cleaning your home, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, investing in hypoallergenic bedding, avoiding certain foods, or managing your pet's grooming routine.
2. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications
Many over-the-counter medications can provide fast relief from allergy symptoms. Antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, or loratadine) block histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine) can help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids (like fluticasone or mometasone) are available as nasal sprays and are highly effective for reducing nasal inflammation. Always read the label and follow the instructions carefully. Don't hesitate to consult a pharmacist if you have any questions about medication interactions or appropriate dosages.
3. Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
Several home remedies might offer some relief from allergy symptoms, although the scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness varies. A saline nasal rinse can help flush out allergens and irritants from your nasal passages. Applying a cool compress to itchy eyes or skin can soothe discomfort. Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin mucus and alleviate congestion. Some people find relief from local honey (produced in your area), though this is more of a preventative measure, aiming to gradually build tolerance. It's crucial to note that these are supplemental and not primary treatments.
4. Natural Allergy Treatments
Some individuals explore natural approaches like acupuncture, herbal remedies, or dietary changes. However, scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of many natural allergy treatments is limited. While some herbs are touted for anti-inflammatory properties, it's critical to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any herbal remedies, as they can interact with other medications or have side effects. Similarly, while a well-balanced diet supports overall health, there isn't conclusive evidence that specific diets cure allergies.
5. Importance of Proper Hygiene and Environmental Control
Maintaining a clean and allergen-free environment at home is crucial for managing allergies. Regularly dust and vacuum your home, using a HEPA filter vacuum. Wash bedding frequently in hot water. Keep pets groomed and prevent them from entering bedrooms. Control humidity levels to minimize mold growth. These preventive measures are essential for minimizing exposure to allergens and reducing the frequency and severity of allergy symptoms.
| Remedy | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | High for many allergy symptoms | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Decongestants | Effective for nasal congestion | Increased blood pressure, insomnia |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Highly effective for nasal inflammation | Nosebleeds, burning sensation |
| Saline Rinse | Good for nasal cleansing | Minimal, usually only temporary irritation |
| Local Honey | Limited evidence, possibly preventative | Rare allergic reactions possible |
What is the Fastest Way to Cure Allergies at Home? (A Realistic Approach)
There's no magic bullet for a fast cure for allergies at home. Allergies are a result of your immune system overreacting to a harmless substance (allergen). While you can't entirely "cure" allergies at home, you can manage symptoms and potentially reduce their severity over time with a combination of strategies. It's crucial to remember that seeking professional medical advice is essential, especially if your allergies are severe or interfering with your daily life. Home remedies should be considered supportive measures, not replacements for proper medical care.
1. Identify and Eliminate the Allergen
The most effective way to manage allergies is to identify and avoid the substances that trigger your symptoms. Keep a detailed allergy diary noting times you experience symptoms, locations, and potential exposures. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, and specific foods. Once you identify the culprit, take steps to minimize your exposure. This might involve regularly cleaning your home, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, investing in hypoallergenic bedding, avoiding certain foods, or managing your pet's grooming routine.
2. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications
Many over-the-counter medications can provide fast relief from allergy symptoms. Antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, or loratadine) block histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine) can help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids (like fluticasone or mometasone) are available as nasal sprays and are highly effective for reducing nasal inflammation. Always read the label and follow the instructions carefully. Don't hesitate to consult a pharmacist if you have any questions about medication interactions or appropriate dosages.
3. Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
Several home remedies might offer some relief from allergy symptoms, although the scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness varies. A saline nasal rinse can help flush out allergens and irritants from your nasal passages. Applying a cool compress to itchy eyes or skin can soothe discomfort. Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin mucus and alleviate congestion. Some people find relief from local honey (produced in your area), though this is more of a preventative measure, aiming to gradually build tolerance. It's crucial to note that these are supplemental and not primary treatments.
4. Natural Allergy Treatments
Some individuals explore natural approaches like acupuncture, herbal remedies, or dietary changes. However, scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of many natural allergy treatments is limited. While some herbs are touted for anti-inflammatory properties, it's critical to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any herbal remedies, as they can interact with other medications or have side effects. Similarly, while a well-balanced diet supports overall health, there isn't conclusive evidence that specific diets cure allergies.
5. Importance of Proper Hygiene and Environmental Control
Maintaining a clean and allergen-free environment at home is crucial for managing allergies. Regularly dust and vacuum your home, using a HEPA filter vacuum. Wash bedding frequently in hot water. Keep pets groomed and prevent them from entering bedrooms. Control humidity levels to minimize mold growth. These preventive measures are essential for minimizing exposure to allergens and reducing the frequency and severity of allergy symptoms.
| Remedy | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | High for many allergy symptoms | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Decongestants | Effective for nasal congestion | Increased blood pressure, insomnia |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Highly effective for nasal inflammation | Nosebleeds, burning sensation |
| Saline Rinse | Good for nasal cleansing | Minimal, usually only temporary irritation |
| Local Honey | Limited evidence, possibly preventative | Rare allergic reactions possible |
How do you get rid of allergies asap?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Preventing-and-Treating-Seasonal-Allergies_Danie-Drankwalter_Final-884166d09ac94425ad7e7a3b68a14249.jpg)
There's no single "get rid of allergies ASAP" solution, as allergies are a complex immune response. Eliminating them entirely requires long-term management, not a quick fix. However, you can alleviate symptoms rapidly with a multi-pronged approach focusing on immediate relief and identifying and avoiding triggers. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing future reactions. It’s crucial to consult a doctor or allergist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Over-the-Counter Medications for Immediate Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide fast relief from allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), or loratadine (Claritin), block histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants, like pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) or phenylephrine, can help clear nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids, available as nasal sprays (like fluticasone or mometasone), reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, offering longer-lasting relief. Remember to follow dosage instructions carefully.
- Antihistamines: Block histamine, reducing itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Decongestants: Clear nasal passages and reduce stuffiness.
- Nasal corticosteroids: Reduce nasal inflammation for longer-lasting relief.
Identify and Eliminate Allergens
The quickest way to alleviate allergy symptoms is to remove the source of the allergy. This requires identifying your specific allergens. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. Keep a detailed allergy diary to track symptoms and potential triggers. Allergy testing (skin prick test or blood test) can help pinpoint specific allergens. Once identified, actively remove or minimize exposure to these allergens. This might involve regular cleaning, using air purifiers, avoiding certain foods, or getting allergy shots.
- Keep an allergy diary: Track symptoms and potential triggers.
- Allergy testing: Pinpoint specific allergens through skin prick or blood tests.
- Minimize allergen exposure: Implement strategies like cleaning, air purifiers, and dietary changes.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
Several home remedies can offer temporary relief from allergy symptoms. A saline nasal rinse can help flush out allergens and mucus from your nasal passages. A warm shower or bath can help loosen congestion. Applying a cool compress to itchy eyes can soothe discomfort. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and ease congestion. However, these are supplemental and should not replace medical advice or treatment.
- Saline nasal rinse: Flush out allergens and mucus.
- Warm shower/bath: Loosen congestion.
- Cool compress: Soothe itchy eyes.
- Hydration: Thin mucus and ease congestion.
Prescription Medications for Severe Allergies
For more severe allergies that don't respond to OTC medications, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications. Prescription antihistamines can be more potent than OTC versions. Leukotriene modifiers (like montelukast) reduce inflammation in the airways and are particularly helpful for asthma associated with allergies. Immunotherapy (allergy shots) is a long-term treatment that gradually desensitizes you to specific allergens. This is a longer-term solution, but can greatly reduce allergy symptoms over time.
- Prescription antihistamines: Stronger than OTC options.
- Leukotriene modifiers: Reduce airway inflammation.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): Long-term treatment to desensitize to allergens.
Seek Professional Medical Advice
Consulting an allergist or doctor is crucial for proper diagnosis and management of allergies. They can perform tests to identify your specific allergens, recommend appropriate treatments, and advise on how to best manage your symptoms. Ignoring allergies can lead to serious complications. Don't hesitate to seek professional medical help, especially if your symptoms are severe or interfere with your daily life. A personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs is essential for long-term allergy management.
- Allergy testing: Professional identification of triggers.
- Personalized treatment plan: Tailored to individual needs and severity.
- Management of severe allergies: Avoid complications and potential emergencies.
What to drink for an allergy?

What to drink for an allergy depends heavily on the type of allergy and its symptoms. There's no one-size-fits-all answer, and in severe cases, you should always consult a doctor or allergist. However, certain beverages can be helpful in managing some allergy symptoms. It's crucial to avoid anything that might trigger your allergy. For example, if you have a dairy allergy, avoid milk and milk products. Similarly, if you have a nut allergy, avoid beverages containing nuts or nut extracts. Some people find that staying well-hydrated is key to managing allergy symptoms. Water is always a good choice. Electrolyte drinks can be helpful if you're experiencing dehydration due to vomiting or diarrhea associated with allergic reactions. Some people find that warm drinks, such as herbal teas (avoiding any potential allergens), can be soothing.
Hydration is Key
Staying well-hydrated is crucial when dealing with allergy symptoms. Dehydration can worsen allergy symptoms, making you feel worse overall. Drinking plenty of fluids helps to thin mucus, which can ease congestion. Aim for water as your primary source of hydration.
- Water is the best choice for hydration. It's calorie-free, readily available, and doesn't contain any potential allergens.
- Electrolyte drinks can help replenish electrolytes lost due to vomiting or diarrhea, common symptoms of some allergic reactions.
- Broth-based soups (check for allergens) provide hydration along with electrolytes and nutrients.
Herbal Teas (with Cautions)
Some find that warm drinks can be comforting during an allergic reaction. Herbal teas, excluding any known allergens, can offer a soothing effect. However, always check the ingredients carefully to avoid cross-contamination or unexpected allergens.
- Chamomile tea is known for its calming properties, potentially reducing anxiety associated with allergy symptoms.
- Ginger tea may help soothe nausea associated with some allergic reactions.
- Avoid teas containing known allergens or those that might interact with medications you are taking.
Electrolyte Drinks for Dehydration
If vomiting or diarrhea accompanies your allergic reaction, electrolyte drinks are essential. These drinks replace vital electrolytes lost through fluid loss, preventing further dehydration and its associated complications.
- Choose commercially available electrolyte drinks or make your own with water, salt, and sugar.
- Check labels carefully to ensure the drink doesn't contain any allergens.
- Don't overuse these drinks, as excessive consumption can have negative health consequences.
Avoiding Allergenic Beverages
This is perhaps the most important aspect. Strictly avoid any beverages that contain known allergens for you. This includes obvious ones like dairy milk if you're lactose intolerant or specific nuts if you have a nut allergy, but also be aware of hidden allergens in processed drinks and be cautious about cross-contamination.
- Read labels carefully before consuming any beverage. Pay attention to ingredients, potential allergens and manufacturing processes.
- Avoid drinks with unclear labeling, or those that don't clearly list potential allergens.
- Be mindful of cross-contamination, particularly if you have severe allergies. This means avoiding beverages prepared in facilities that also process known allergens.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While these suggestions might help manage milder allergy symptoms, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, hives, or dizziness. These could indicate a life-threatening anaphylactic reaction, requiring prompt treatment.
- Do not self-treat severe allergic reactions.
- Contact emergency services immediately.
- Follow your doctor's or allergist's instructions regarding medication and treatment.
What is the fastest allergy relief?
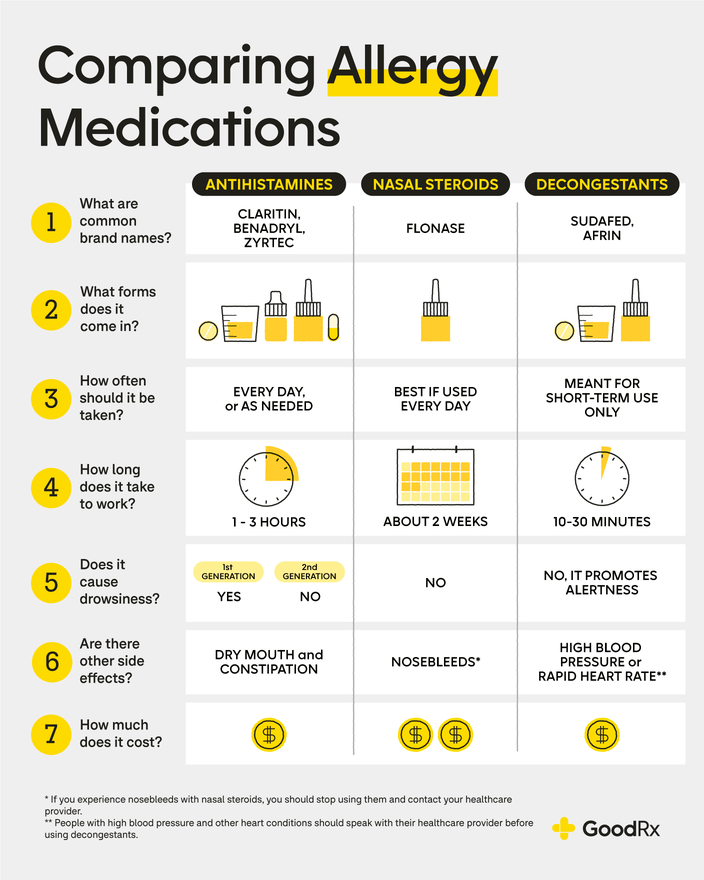
There's no single "fastest" allergy relief that works for everyone, as the speed of relief depends on the severity of your allergies, the allergen, and your individual response. However, some methods offer quicker relief than others. Over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines, particularly those containing cetirizine or loratadine, often provide relief within 30-60 minutes. However, some individuals might experience a slightly delayed response. For immediate relief from severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis, an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) is essential and provides the fastest possible action. Always consult a doctor to determine the best course of treatment for your specific allergies.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) allergy medications offer readily accessible relief. Antihistamines, like cetirizine (Zyrtec) and loratadine (Claritin), block the effects of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction. These are typically non-drowsy options, although some individuals may experience mild drowsiness. Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, can help relieve nasal congestion, but should be used cautiously as they can elevate blood pressure. Always follow the directions on the packaging.
- Antihistamines: Cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine
- Decongestants: Pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine (use with caution)
- Combination Medications: Many OTC products combine antihistamines and decongestants for broader relief.
Prescription Medications
For more severe allergies or those that don't respond well to OTC treatments, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications. These include stronger antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and leukotriene modifiers. Nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase), reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and provide longer-lasting relief than antihistamines alone, but the effects are not immediate. Leukotriene modifiers help prevent the release of substances that cause allergic reactions and are often used for long-term management of allergy symptoms.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: Fluticasone, mometasone
- Stronger Antihistamines: Some prescription antihistamines may offer faster relief than OTC options.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: Montelukast, zafirlukast (usually for long-term management).
Epinephrine Auto-Injectors (EpiPens)
In cases of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), which can be life-threatening, an epinephrine auto-injector is the fastest and most critical treatment. Epinephrine constricts blood vessels, opens airways, and reverses the effects of an allergic reaction. It's crucial to seek immediate medical attention after using an EpiPen, even if symptoms improve.
- Immediate Action: EpiPen provides the fastest possible response in anaphylaxis.
- Life-Saving: It's a vital medication for individuals with severe allergies.
- Emergency Use Only: Should only be used in life-threatening situations.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
While not offering immediate relief, certain home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can help manage allergy symptoms and prevent future reactions. Rinsing nasal passages with saline solution can help clear out allergens. Avoiding known allergens whenever possible is key. Using air purifiers with HEPA filters and keeping your home clean can minimize exposure to allergens. These strategies won't provide instant relief but contribute to overall symptom management.
- Saline Nasal Rinse: Helps clear nasal passages.
- Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial.
- Clean Home Environment: Reduces allergen exposure.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you're experiencing severe or persistent allergy symptoms, or if OTC medications aren't providing sufficient relief, it's essential to consult a doctor or allergist. A doctor can properly diagnose your allergies, conduct allergy testing, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs. They can also help determine if you need an EpiPen and provide guidance on its proper use.
- Diagnosis and Testing: Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
- Personalized Treatment Plan: Doctors tailor treatment based on individual needs.
- Allergy Management: Long-term strategies to reduce allergy symptoms.
Can a hot shower help with allergies?

Whether a hot shower helps with allergies is complex and depends on the type of allergy and the individual. While a hot shower won't cure allergies, it can provide temporary relief for some allergy symptoms. The heat from the shower can help to dilate blood vessels in the nasal passages, potentially reducing congestion. The steam produced can also help to loosen mucus, making it easier to clear from the nasal passages and sinuses. However, this relief is often short-lived and may not be effective for all types of allergies.
How Hot Showers Affect Allergen Exposure
A hot shower can indirectly influence allergen exposure. The steam generated can help to remove some allergens from the air in the bathroom, particularly dust mites and pollen that may have settled on surfaces. However, this is not a comprehensive solution, and the temporary reduction in allergens won't address the underlying allergy. Many allergens are microscopic and will not be easily removed by a hot shower.
- Reduced allergen concentration: The steam can temporarily decrease the amount of airborne allergens in the immediate vicinity.
- Limited effectiveness against major allergens: The effect is limited, and does not significantly impact outdoor allergens like pollen.
- Not a substitute for other treatments: Hot showers should not replace other allergy management strategies such as medication or allergen avoidance.
Hot Showers and Nasal Congestion
For allergies that cause nasal congestion, a hot shower can offer temporary relief. The heat and steam can help thin and loosen mucus, improving drainage and reducing stuffiness. The warm, moist air can also soothe irritated nasal passages, providing a temporary sense of comfort. However, the underlying cause of congestion (allergens) remains, so relief is temporary.
- Improved mucus drainage: Heat and steam help to thin mucus, making it easier to drain.
- Soothed nasal passages: Warm, moist air can calm irritation.
- Temporary relief only: The congestion will likely return as allergens remain in the environment.
Hot Showers and Itchiness
The heat from a hot shower can temporarily alleviate itchiness associated with some allergies, especially skin allergies like eczema. The warmth can relax the skin and reduce inflammation. This effect is primarily due to the heat itself and not a direct interaction with allergens. However, the long-term impact on itchiness is minimal.
- Reduced inflammation: Heat can reduce skin inflammation, easing itchiness.
- Skin relaxation: Warm water helps to relax and soothe irritated skin.
- Not effective for all itchiness: This effect is not a solution for all allergy-related itchiness.
Potential Drawbacks of Hot Showers for Allergies
While a hot shower might offer temporary comfort, excessive heat can also have negative effects on allergy symptoms. Very hot water can dry out the skin, potentially worsening eczema or other skin allergies. Also, the steam can irritate already inflamed nasal passages in some individuals. Therefore, moderation is crucial.
- Skin dryness: Hot water can remove essential oils from the skin, causing dryness and irritation.
- Nasal irritation: Excessive steam can irritate sensitive nasal passages.
- Not a long-term solution: Hot showers alone do not address the root causes of allergies.
Hot Showers vs. Other Allergy Treatments
A hot shower should be considered a complementary measure, not a replacement for other allergy treatments. Medication, immunotherapy, and allergen avoidance are essential for managing allergies effectively. A hot shower can provide temporary relief from certain symptoms, but it does not address the underlying cause of the allergic reaction. It's important to consult with an allergist for personalized treatment recommendations.
- Complementary, not primary treatment: Hot showers should supplement other allergy treatments.
- Not a cure: They don't eliminate allergens or address the immune system response.
- Consult a healthcare professional: Personalized advice is crucial for managing allergies effectively.
What are some quick home remedies for allergy symptoms?
While there's no magic bullet for a fast allergy cure at home, several remedies can offer quick relief from symptoms. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are your first line of defense. Antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can effectively reduce sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Remember to follow the dosage instructions carefully. Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed), can help clear nasal passages, but overuse can lead to rebound congestion. Saline nasal sprays can also provide instant relief by flushing out allergens and moisturizing dry nasal passages. Beyond medication, simple home remedies can be surprisingly effective. A warm shower or bath can help open up airways and soothe irritated skin. A neti pot, used with distilled water, can effectively rinse nasal passages of irritants. Finally, focusing on proper hydration can help thin mucus, making it easier to clear your sinuses. Remember that these remedies offer symptom relief, not a cure, and consulting a doctor is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Can I use essential oils to treat my allergies at home?
While some essential oils are touted for their allergy-relieving properties, scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited. Many claims lack rigorous research and are often anecdotal. It's crucial to understand that essential oils are not a replacement for medical treatment and should not be used as the sole approach to managing allergies. Certain essential oils, such as eucalyptus and peppermint, have properties that might temporarily relieve congestion by opening airways. However, they are used more as a complementary therapy, rather than a primary treatment. It's essential to always dilute essential oils properly before topical application to avoid skin irritation. Inhaling diluted essential oils might provide some temporary relief from congestion, but it's important to be cautious and conduct a patch test beforehand to check for any allergic reactions to the oils themselves. Consult with an allergist or aromatherapist before incorporating essential oils into your allergy management strategy, especially if you have pre-existing respiratory conditions or sensitivities.
How can I identify and avoid allergens in my home?
Identifying and avoiding allergens is key to long-term allergy management. Start by identifying potential triggers in your home environment. Common indoor allergens include dust mites, pet dander, mold, and pollen tracked indoors. Dust mites thrive in bedding, carpets, and upholstery. Regular cleaning and using dust mite-proof covers for mattresses and pillows can significantly reduce exposure. If you have pets, regular grooming and keeping them out of bedrooms can minimize pet dander. Mold often grows in damp areas, so inspect bathrooms and basements for signs of moisture and address any leaks promptly. Regular cleaning and using a dehumidifier can help control mold growth. For pollen, keeping windows closed during peak pollen seasons and changing clothes and showering after being outdoors can significantly reduce indoor allergen levels. Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in your home's air conditioning and heating systems can help remove airborne allergens. These preventative measures, alongside other allergy treatments, are important steps toward long-term allergy relief. Regular vacuuming, particularly using a vacuum with a HEPA filter, significantly reduces allergen levels in your home.
When should I seek professional medical help for my allergies?
While home remedies can provide temporary relief, it's vital to understand when professional medical attention is necessary. Seek immediate medical help if you experience any severe allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, hives, or dizziness. These symptoms indicate a potential anaphylactic reaction, a life-threatening emergency. If your allergy symptoms are persistent, severe, or don't respond to over-the-counter medications, consulting an allergist is crucial. An allergist can perform allergy testing to identify specific triggers, develop a personalized treatment plan, and potentially recommend immunotherapy (allergy shots) for long-term management. If your symptoms significantly impact your daily life, such as sleep disruption, work performance, or social activities, consulting a doctor is important. Moreover, if you have any underlying health conditions, such as asthma, it’s vital to discuss your allergy symptoms with your physician before starting any treatment. Your doctor can ensure that the chosen treatment won’t negatively interact with any other medications you are taking.
Deja una respuesta