How do you get rid of an allergic reaction asap

If you're reading this, you're probably suffering from an allergic reaction and want to know how to get rid of it ASAP. An allergic reaction is an immune system response to a foreign substance, such as food, pollen, or pet dander. Symptoms can range from mild, such as a runny nose and watery eyes, to severe, such as difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis. While there is no cure for allergies, there are a number of things you can do to relieve symptoms and prevent future reactions. In this article, we'll discuss some of the most effective ways to get rid of an allergic reaction as quickly as possible.
How to Treat an Allergic Reaction Quickly
Dealing with an allergic reaction requires prompt action. The severity of the reaction dictates the necessary steps. Mild reactions might only need home remedies, while severe reactions demand immediate medical attention. Never hesitate to call emergency services (911 in the US, or your local equivalent) if you suspect anaphylaxis (a life-threatening allergic reaction). Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat necessitate immediate medical help.
Identifying the Allergen
First, try to identify the allergen if possible. This helps in future avoidance. Was it a food, medication, insect sting, pollen, or something else? Keeping a record of your reactions and potential triggers is crucial for future management and informing your doctor. This information is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning by your healthcare provider. Knowing the allergen allows for better preparation and prevents future reactions whenever possible.
Administering Medication
If you have a known allergy and carry an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen), use it immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction. Follow the instructions carefully. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of anaphylaxis. Even if symptoms seem to improve after using the auto-injector, seek immediate medical attention. For milder reactions, over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help alleviate symptoms like itching and hives. Always follow the dosage instructions on the medication label.
Home Remedies for Mild Reactions
For mild allergic reactions, certain home remedies might offer temporary relief. A cool compress can help reduce swelling and itching. Removing the allergen from contact with your skin is crucial. If a food caused the reaction, rinse your mouth and throat thoroughly. A lukewarm bath with oatmeal can soothe itchy skin. These measures can provide comfort, but they are not substitutes for medical attention if the reaction is severe.
Monitoring Symptoms
Closely monitor the symptoms. Are they improving or worsening? Note the time of onset, the severity of the symptoms, and any changes you observe. This information is important to share with medical professionals. Take note of any unusual symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness. If symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention. Accurate symptom tracking is essential for effective treatment and management of your allergy.
Seeking Medical Attention
Seek medical attention immediately if your symptoms are severe, worsening, or if you experience any symptoms of anaphylaxis. This includes difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or loss of consciousness. A doctor can provide appropriate treatment, including medications such as corticosteroids or epinephrine, to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Early intervention is critical in managing severe allergic reactions and preventing potentially life-threatening situations. Delaying treatment can lead to serious health consequences.
| Symptom | Mild Reaction Treatment | Severe Reaction Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Itching | Antihistamine, cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Hives | Antihistamine, cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Swelling (mild) | Cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical attention | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Dizziness | Seek medical attention | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
How to Treat an Allergic Reaction Quickly
Dealing with an allergic reaction requires prompt action. The severity of the reaction dictates the necessary steps. Mild reactions might only need home remedies, while severe reactions demand immediate medical attention. Never hesitate to call emergency services (911 in the US, or your local equivalent) if you suspect anaphylaxis (a life-threatening allergic reaction). Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat necessitate immediate medical help.
Identifying the Allergen
First, try to identify the allergen if possible. This helps in future avoidance. Was it a food, medication, insect sting, pollen, or something else? Keeping a record of your reactions and potential triggers is crucial for future management and informing your doctor. This information is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning by your healthcare provider. Knowing the allergen allows for better preparation and prevents future reactions whenever possible.
Administering Medication
If you have a known allergy and carry an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen), use it immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction. Follow the instructions carefully. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of anaphylaxis. Even if symptoms seem to improve after using the auto-injector, seek immediate medical attention. For milder reactions, over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help alleviate symptoms like itching and hives. Always follow the dosage instructions on the medication label.
Home Remedies for Mild Reactions
For mild allergic reactions, certain home remedies might offer temporary relief. A cool compress can help reduce swelling and itching. Removing the allergen from contact with your skin is crucial. If a food caused the reaction, rinse your mouth and throat thoroughly. A lukewarm bath with oatmeal can soothe itchy skin. These measures can provide comfort, but they are not substitutes for medical attention if the reaction is severe.
Monitoring Symptoms
Closely monitor the symptoms. Are they improving or worsening? Note the time of onset, the severity of the symptoms, and any changes you observe. This information is important to share with medical professionals. Take note of any unusual symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness. If symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention. Accurate symptom tracking is essential for effective treatment and management of your allergy.
Seeking Medical Attention
Seek medical attention immediately if your symptoms are severe, worsening, or if you experience any symptoms of anaphylaxis. This includes difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or loss of consciousness. A doctor can provide appropriate treatment, including medications such as corticosteroids or epinephrine, to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Early intervention is critical in managing severe allergic reactions and preventing potentially life-threatening situations. Delaying treatment can lead to serious health consequences.
| Symptom | Mild Reaction Treatment | Severe Reaction Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Itching | Antihistamine, cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Hives | Antihistamine, cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Swelling (mild) | Cool compress | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical attention | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
| Dizziness | Seek medical attention | Epinephrine auto-injector, immediate medical attention |
What is the quickest way to stop an allergic reaction?
The quickest way to stop an allergic reaction depends heavily on the severity of the reaction and the allergen involved. For mild reactions, like mild hives or itching, simple home remedies might suffice. However, for more severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or face (angioedema), or a significant drop in blood pressure (anaphylaxis), immediate medical attention is crucial. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate epinephrine injection and emergency medical services (EMS).
1. Identifying the Allergen
The first step, even before treatment, is to try and identify the allergen causing the reaction. This helps inform future preventative measures and also guides medical professionals in providing the most appropriate care. Knowing the allergen helps prevent future exposure and allows for targeted treatment.
- Keep a detailed record of any foods eaten, medications taken, or environments visited prior to the onset of symptoms.
- Consider wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace identifying known allergies.
- Inform family, friends, and colleagues about your allergies and potential reactions.
2. Using Epinephrine (EpiPen) for Severe Reactions
For severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), epinephrine is the most critical treatment. It's a fast-acting medication that counteracts the effects of the allergic reaction by constricting blood vessels, opening airways, and improving heart function. It must be administered immediately. Delay in administering epinephrine can be life-threatening.
- Administer epinephrine as directed by your doctor or allergist. If you have a prescription for an auto-injector (like an EpiPen or Auvi-Q), use it immediately.
- Even after administering epinephrine, call emergency medical services (911 or your local emergency number) immediately.
- Remain under medical supervision until the reaction is fully resolved.
3. Antihistamines for Mild to Moderate Reactions
For milder allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, or mild swelling, over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can provide relief. These medications block the release of histamine, a chemical responsible for many allergic symptoms. However, antihistamines are NOT effective for anaphylaxis.
- Follow the dosage instructions on the label carefully.
- If symptoms worsen or do not improve after taking an antihistamine, seek immediate medical attention.
- Consider keeping antihistamines on hand, especially if you have known allergies.
4. Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or face, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat, seek immediate medical attention. Don't hesitate to call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room. Prompt medical intervention is crucial for preventing life-threatening complications.
- Call emergency services immediately (911 or your local emergency number).
- Describe your symptoms clearly and accurately to the dispatcher.
- Follow the instructions given by the emergency medical personnel.
5. Preventing Future Reactions
Preventing future allergic reactions involves identifying and avoiding the allergen that triggers the response. This might involve dietary changes, environmental modifications, or medication adjustments. Allergy testing can help identify specific allergens, allowing for personalized avoidance strategies.
- Work with an allergist or immunologist to determine the specific allergen(s) causing your reactions.
- Develop and implement an avoidance plan based on identified allergens.
- Learn how to properly read food labels and identify hidden allergens.
How do you flush out an allergic reaction?
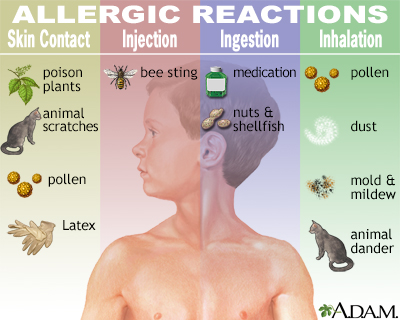
There's no single method to "flush out" an allergic reaction, as the term itself is misleading. Allergic reactions involve the body's immune system overreacting to a harmless substance (allergen). The goal is to manage the symptoms and prevent a severe reaction (anaphylaxis). Treatment depends on the severity and location of the reaction. For mild reactions like hives or mild itching, home management is often sufficient. Severe reactions requiring immediate medical attention include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or face, and loss of consciousness.
Identifying and Removing the Allergen
The first step in managing an allergic reaction is to identify and remove the allergen. This might involve taking off jewelry that's causing contact dermatitis, leaving a space that contains pet dander, or rinsing the mouth out after eating something that triggers a reaction. Once the allergen is removed, the body can begin to naturally reduce the allergic reaction. This step is crucial, as ongoing exposure will only worsen symptoms.
- Identify the source: Carefully consider what you’ve touched, eaten, or inhaled recently.
- Remove the allergen completely: Wash skin, change clothes, or leave the area completely.
- Prevent further exposure: Avoid future contact with that allergen.
Over-the-Counter Medications
For mild allergic reactions, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide relief. Antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can help reduce itching, hives, and sneezing. Oral corticosteroids, like prednisone (prescription required), can be used to help calm the immune system further, but this requires prescription from a doctor, and are not intended for self-administration. Always follow the dosage instructions on the label carefully. Do not self-treat severe reactions with OTC medicines only.
- Antihistamines: Block histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions.
- Nasal sprays (corticosteroid): Reduce nasal inflammation and congestion.
- Pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen): Address any associated pain or fever.
Home Remedies for Mild Reactions
Some home remedies may provide temporary relief from mild symptoms. A cool compress can soothe itchy skin, while a lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal can help alleviate itching and inflammation. Remember that these are supportive measures and do not replace medical treatment for severe reactions. Do not rely solely on these for severe reactions as they can lead to the progression of a serious medical event.
- Cool compresses: Reduce swelling and itching.
- Oatmeal baths: Soothe irritated skin.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to support the body’s natural processes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), dizziness, rapid pulse, or a drop in blood pressure. These are signs of a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). Delaying treatment can be dangerous; an epinephrine injection (EpiPen) may be necessary and should be administered as quickly as possible. Always seek medical attention even if you've used your epinephrine injector, to ensure there isn't a lingering reaction requiring treatment and monitoring.
- Difficulty breathing: Wheezing, shortness of breath, or tightness in the chest.
- Swelling: In the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Severe hives or itching: Widespread rash, significant discomfort.
Prevention and Allergy Management
The best way to "flush out" an allergic reaction is to avoid it in the first place. This requires identifying your allergens and implementing preventative measures. Allergy testing can help determine what you are allergic to. Once identified, avoid contact, use preventative medications like antihistamines, and possibly consider immunotherapy (allergy shots). Consistent management minimizes future occurrences.
- Allergy testing: Identify specific allergens.
- Avoidance: Stay away from known allergens.
- Preventative medications: Take antihistamines regularly, as prescribed by a doctor.
What neutralizes an allergic reaction?
There isn't a single substance that universally neutralizes all allergic reactions. The approach depends heavily on the severity and the specific allergen involved. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further exposure to the allergen. Mild reactions can often be managed at home, while severe reactions (anaphylaxis) require immediate medical attention.
1. Antihistamines
Antihistamines are medications that block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction. Histamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of allergies, such as itching, sneezing, runny nose, and hives. Antihistamines are available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription, with varying degrees of effectiveness and side effects. They are particularly useful for managing mild to moderate allergic reactions.
- Examples: Cetirizine (Zyrtec), Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), Loratadine (Claritin)
- Mechanism: They competitively bind to histamine receptors, preventing histamine from binding and triggering an allergic response.
- Limitations: They might not be effective for severe reactions and can cause drowsiness in some individuals.
2. Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
For severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, epinephrine is a life-saving medication. It's a potent vasoconstrictor and bronchodilator, rapidly reversing the effects of a severe allergic reaction by constricting blood vessels, opening airways, and increasing heart rate. Epinephrine is administered via auto-injector (like an EpiPen) and should be used immediately upon the onset of symptoms.
- Administration: Typically administered via intramuscular injection.
- Mechanism: Acts on multiple receptors to counteract the effects of histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
- Importance: Crucial in treating life-threatening anaphylactic reactions.
3. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, like prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can help reduce the severity of allergic reactions. They work by suppressing the immune system's response and reducing inflammation. They are often used in conjunction with other treatments, especially for severe or prolonged reactions. While effective, they are usually prescribed for longer-term management of allergies rather than immediate relief of acute reactions.
- Examples: Prednisone, methylprednisolone.
- Mechanism: Suppress the inflammatory cascade, decreasing the release of inflammatory mediators.
- Use: Often used for more severe reactions or to prevent future reactions.
4. Avoiding Allergens
The most effective way to prevent an allergic reaction is to avoid exposure to the allergen that triggers it. This may involve identifying and eliminating allergens from the environment, carefully reading food labels, or wearing protective gear when exposed to environmental allergens like pollen.
- Identification: Allergy testing can help identify specific allergens.
- Elimination: Removing triggers from the home or work environment.
- Prevention: Using preventative measures such as air purifiers or allergy medications.
5. Medical Treatment and Monitoring
In severe cases or for individuals with a history of anaphylaxis, ongoing medical care is crucial. This includes regular check-ups with an allergist, the development of a personalized allergy management plan, and potentially immunotherapy (allergy shots) to desensitize the individual to the allergen over time. Close monitoring of symptoms and prompt treatment are essential for managing allergic reactions effectively.
- Allergist Consultation: Regular visits to discuss treatment options and monitor progress.
- Allergy Shots: Immunotherapy aiming to build tolerance to allergens.
- Emergency Plan: Having a clear plan for managing severe reactions.
How do you treat an immediate allergy?

Treating an immediate allergic reaction, also known as anaphylaxis, requires a swift and decisive response. The severity of the reaction dictates the treatment, ranging from self-administered medication to emergency medical care. Immediate action is crucial because allergic reactions can rapidly worsen and become life-threatening.
1. Administering Epinephrine (EpiPen/Auvi-Q)
For individuals with known severe allergies, like those to peanuts or bee stings, carrying and knowing how to use an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen or Auvi-Q) is paramount. Epinephrine is a powerful medication that counteracts the effects of the allergic reaction by constricting blood vessels, relaxing airways, and improving blood pressure. It should be administered immediately at the first sign of a severe allergic reaction.
- Inject epinephrine into the outer thigh, through clothing if necessary.
- Call emergency medical services (EMS) immediately after injecting, even if symptoms improve.
- Keep the individual lying down and elevate their legs to improve blood flow.
2. Calling Emergency Medical Services (EMS)
Calling 911 or your local emergency number is essential, regardless of whether you've administered epinephrine. EMS personnel are trained to handle allergic reactions and can provide advanced medical support, including intravenous fluids, oxygen, and further medication to stabilize the individual. They can also transport the individual to the nearest hospital for observation and treatment.
- Clearly explain the situation to the dispatcher, including the allergen involved and the symptoms experienced.
- Follow the dispatcher’s instructions carefully.
- Remain on the phone with the dispatcher until help arrives.
3. Managing Mild to Moderate Allergic Reactions
Mild to moderate allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, or mild swelling, may not require epinephrine. However, immediate attention is still important. Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can help relieve symptoms. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream may ease skin irritation. If symptoms worsen or don't improve, seek medical attention immediately.
- Take an oral antihistamine, following the directions on the label.
- Apply a cool compress to reduce swelling and itching.
- Monitor the individual closely for any worsening of symptoms.
4. Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Even after the acute phase of an allergic reaction has passed, close monitoring is crucial. Individuals who have experienced a severe allergic reaction should be observed for at least 24 hours, as a delayed reaction can occur. Follow-up appointments with an allergist are essential to develop an appropriate allergy management plan, including identifying triggers and discussing potential preventative measures.
- Keep a detailed record of the allergic reaction, including the time of onset, symptoms, treatment administered, and response.
- Schedule a follow-up appointment with an allergist to discuss the incident and develop a long-term plan.
- Consider wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace.
5. Preventing Future Allergic Reactions
The best way to treat an immediate allergy is to prevent it from happening in the first place. This involves identifying and avoiding known allergens. Working with an allergist, individuals can develop strategies to minimize exposure to allergens through dietary changes, environmental modifications, and medication such as allergy shots (immunotherapy). This can significantly reduce the risk of future allergic reactions.
- Identify and avoid known triggers.
- Consider allergy testing to determine specific allergens.
- Discuss immunotherapy with your allergist as a potential preventative measure.
What are the immediate steps I should take if I have an allergic reaction?
If you suspect you're experiencing an allergic reaction, time is of the essence. The first and most crucial step is to identify and remove the allergen if possible. This could be anything from removing a bee sting, washing off a plant irritant, or getting away from the source of airborne allergens. Next, if you carry an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen), use it immediately, following the instructions carefully. This is especially important for severe reactions like anaphylaxis. Even if symptoms seem mild at first, a seemingly minor reaction can quickly escalate. After administering epinephrine, call emergency services immediately (911 in the US, or your local equivalent). Explain the situation clearly, including the suspected allergen, the symptoms you're experiencing, and the fact that you've already used an epinephrine auto-injector, if applicable. While waiting for help, lie down and keep your legs elevated to help maintain blood flow to your vital organs. If you have an antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), you can take it as directed; however, epinephrine should always be prioritized in severe reactions. Monitoring your breathing and pulse, remaining calm as possible, and staying conscious are also essential in the waiting period. Do not attempt to self-treat further if the reaction is severe; professional medical intervention is crucial.
What are the signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)?
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening, whole-body allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing the signs is critical. Some common symptoms include difficulty breathing or wheezing, which can range from mild shortness of breath to a complete inability to inhale. You might experience swelling in the throat or tongue, making it difficult to swallow or speak. Hives or widespread itching are another key indicator, often accompanied by a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting. Rapid pulse and nausea or vomiting are also common symptoms. Chest tightness and a feeling of impending doom or anxiety can occur as well. While not all of these symptoms will necessarily present in every case, the appearance of several of these symptoms simultaneously is a very strong indicator of anaphylaxis. It is important to note that the symptoms can progress rapidly and unexpectedly. Even the appearance of seemingly mild symptoms like itching or mild swelling should warrant careful observation and prompt action if they worsen or are accompanied by other symptoms listed above. If you are unsure, always err on the side of caution and seek immediate medical help.
What home remedies can help alleviate mild allergic reactions?
For mild allergic reactions, some home remedies can provide temporary relief, but they should never replace professional medical attention if the reaction is severe or worsening. Cool compresses applied to itchy areas can soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. Oral antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can help relieve symptoms like itching, hives, and sneezing. However, always follow the dosage instructions carefully. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help manage any associated pain or fever. Elevate swollen limbs to reduce swelling. Plenty of rest is also beneficial. However, if your symptoms are not improving or are getting worse, you should immediately seek medical advice. These remedies are meant for minor reactions only and should not be used to treat severe allergic reactions, which require immediate emergency medical attention. Knowing your limitations and seeking professional help when needed is crucial. Always check with your doctor or pharmacist before using any new over-the-counter medication.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for an allergic reaction?
You should always seek immediate medical attention if your allergic reaction involves any symptoms that could indicate anaphylaxis, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, or a sudden drop in blood pressure. Even if your initial symptoms seem mild, seek immediate medical attention if they worsen rapidly. This includes increasing swelling, spreading hives, persistent vomiting, or any indication of worsening respiratory distress. If you have any doubt about the severity of your reaction, err on the side of caution and call for medical assistance. Don't delay seeking help; early intervention is crucial for preventing serious complications. Also, seek immediate medical attention if you've administered epinephrine and your symptoms are not improving or are returning after a short period of improvement. Your life is more important than hesitating. Calling emergency services is paramount, and you should not attempt to drive yourself to the hospital in a severe reaction; emergency medical personnel are best equipped to manage your condition while en route to the hospital.

Deja una respuesta