Which vitamin is best for allergies

Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. When it comes to managing allergies, certain vitamins have been found to offer potential benefits in reducing symptoms and supporting immune function. While various vitamins can contribute to allergy management, understanding which specific vitamin is most effective becomes essential. This article aims to explore the most beneficial vitamin for allergies, backed by scientific evidence and expert insights.
Which Vitamin is Best for Allergies? A Detailed Look
There isn't a single "best" vitamin for allergies. Allergies are complex immune responses, and while certain vitamins play crucial roles in immune function, no vitamin can cure or prevent allergies. However, some vitamins can support a healthy immune system and potentially lessen allergy symptoms for some individuals. It's crucial to remember that this information is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making changes to your diet or supplement regimen, especially if you have allergies or other health conditions.
Vitamin C: A Powerful Antioxidant
Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant that plays a vital role in immune function. It helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to inflammation. Some studies suggest that adequate vitamin C intake may help reduce the severity of allergy symptoms, particularly in those with allergic rhinitis (hay fever). However, more research is needed to confirm these findings. Individuals should focus on obtaining Vitamin C from food sources such as citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables. Supplementing with Vitamin C should only be done after consulting a doctor.
Vitamin D: Immune System Modulation
Vitamin D is essential for immune system regulation. Studies have indicated a correlation between vitamin D deficiency and increased susceptibility to allergic diseases. Adequate vitamin D levels are crucial for the proper functioning of immune cells involved in allergic responses. While it doesn't directly treat allergies, maintaining sufficient levels through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplementation (under medical guidance) can contribute to overall immune health and potentially improve allergy symptoms. Always consult a physician before starting vitamin D supplementation.
B Vitamins: Supporting Immune Cell Function
The B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, are crucial for the production and function of immune cells. These vitamins are involved in various metabolic processes that support a strong immune response. Deficiencies in B vitamins can weaken the immune system, potentially making individuals more susceptible to allergies and increasing symptom severity. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, legumes, and leafy green vegetables generally provides sufficient B vitamins. Supplementing should only be done if a deficiency is diagnosed.
Vitamin E: Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Vitamin E, another powerful antioxidant, possesses both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a key component of allergic reactions. Although research is still ongoing, some studies suggest that vitamin E might help reduce the severity of allergic reactions, particularly skin-related ones like eczema. However, more evidence is needed to confirm these findings conclusively. Dietary sources such as nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables are preferred over supplementation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reducing Inflammation
While not strictly vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids with significant anti-inflammatory properties. They play a vital role in reducing inflammation, a key factor in allergic reactions. Including foods rich in omega-3s, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, in your diet may help manage allergy symptoms. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids should always be discussed with a doctor, especially if you're taking other medications.
| Vitamin | Role in Allergy Management | Food Sources | Important Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, supports immune function | Citrus fruits, berries, peppers | Consult doctor before supplementing |
| Vitamin D | Immune system regulation | Fatty fish, egg yolks, sunlight | Supplement only under medical supervision |
| B Vitamins | Essential for immune cell function | Whole grains, legumes, leafy greens | Supplement only if deficiency diagnosed |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory | Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables | More research needed on allergy impact |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds | Discuss supplementation with doctor |
Which Vitamin is Best for Allergies? A Detailed Look
There isn't a single "best" vitamin for allergies. Allergies are complex immune responses, and while certain vitamins play crucial roles in immune function, no vitamin can cure or prevent allergies. However, some vitamins can support a healthy immune system and potentially lessen allergy symptoms for some individuals. It's crucial to remember that this information is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making changes to your diet or supplement regimen, especially if you have allergies or other health conditions.
Vitamin C: A Powerful Antioxidant
Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant that plays a vital role in immune function. It helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to inflammation. Some studies suggest that adequate vitamin C intake may help reduce the severity of allergy symptoms, particularly in those with allergic rhinitis (hay fever). However, more research is needed to confirm these findings. Individuals should focus on obtaining Vitamin C from food sources such as citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables. Supplementing with Vitamin C should only be done after consulting a doctor.
Vitamin D: Immune System Modulation
Vitamin D is essential for immune system regulation. Studies have indicated a correlation between vitamin D deficiency and increased susceptibility to allergic diseases. Adequate vitamin D levels are crucial for the proper functioning of immune cells involved in allergic responses. While it doesn't directly treat allergies, maintaining sufficient levels through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplementation (under medical guidance) can contribute to overall immune health and potentially improve allergy symptoms. Always consult a physician before starting vitamin D supplementation.
B Vitamins: Supporting Immune Cell Function
The B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, are crucial for the production and function of immune cells. These vitamins are involved in various metabolic processes that support a strong immune response. Deficiencies in B vitamins can weaken the immune system, potentially making individuals more susceptible to allergies and increasing symptom severity. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, legumes, and leafy green vegetables generally provides sufficient B vitamins. Supplementing should only be done if a deficiency is diagnosed.
Vitamin E: Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Vitamin E, another powerful antioxidant, possesses both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a key component of allergic reactions. Although research is still ongoing, some studies suggest that vitamin E might help reduce the severity of allergic reactions, particularly skin-related ones like eczema. However, more evidence is needed to confirm these findings conclusively. Dietary sources such as nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables are preferred over supplementation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reducing Inflammation
While not strictly vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids with significant anti-inflammatory properties. They play a vital role in reducing inflammation, a key factor in allergic reactions. Including foods rich in omega-3s, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, in your diet may help manage allergy symptoms. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids should always be discussed with a doctor, especially if you're taking other medications.
| Vitamin | Role in Allergy Management | Food Sources | Important Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, supports immune function | Citrus fruits, berries, peppers | Consult doctor before supplementing |
| Vitamin D | Immune system regulation | Fatty fish, egg yolks, sunlight | Supplement only under medical supervision |
| B Vitamins | Essential for immune cell function | Whole grains, legumes, leafy greens | Supplement only if deficiency diagnosed |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory | Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables | More research needed on allergy impact |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds | Discuss supplementation with doctor |
Which vitamin helps allergies?

There isn't one single vitamin that definitively "helps" allergies in the sense of curing them. Allergies are complex immune responses, and no vitamin can replace proper medical treatment prescribed by a doctor or allergist. However, some vitamins play crucial roles in supporting immune function, and deficiencies in these vitamins may worsen allergic symptoms or increase susceptibility. Vitamin D is often highlighted in this context.
Vitamin D's Role in Immune Regulation
Vitamin D isn't a direct allergy treatment, but it's a crucial player in immune system modulation. Sufficient Vitamin D levels are associated with a properly functioning immune system, making it less likely to overreact and trigger allergic responses. A deficiency, on the other hand, may contribute to an exaggerated immune response. Research is ongoing, and the exact mechanisms are complex, but a healthy balance seems important.
- Reduces inflammation: Vitamin D can help regulate inflammatory pathways involved in allergic reactions.
- Modulates immune cell activity: It can influence the activity of immune cells like T cells and B cells, helping to balance immune responses.
- Improves barrier function: Vitamin D plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, which are the body's first line of defense against allergens.
Other Vitamins and Immune Support
While Vitamin D gets the most attention, other vitamins contribute to overall immune health, indirectly impacting allergy responses. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps combat oxidative stress, a factor in inflammation. Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining the integrity of mucous membranes and skin, providing a physical barrier against allergens. Vitamin B6 plays a role in immune cell development and function, while Vitamin E, like Vitamin C, is an antioxidant that helps reduce inflammation.
- Antioxidant effects: Vitamins C and E help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress related to inflammation.
- Mucous membrane support: Vitamins A and C contribute to the strength and integrity of the body's first line of defense.
- Immune cell development: B vitamins are vital for the proper development and function of immune cells.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Rather than focusing on individual vitamins, it’s far more beneficial to ensure a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This approach provides a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that support overall health, including immune function. Focusing on a holistic approach is key, rather than relying on isolated supplements.
- Whole foods are best: Nutrient absorption from whole foods is generally superior to that from supplements.
- Variety is essential: Different fruits and vegetables offer various vitamins and minerals.
- Consult a nutritionist: A nutritionist can help personalize a diet plan to meet your specific needs.
The Limitations of Vitamin Supplements
While supplements can help address deficiencies, they are not a substitute for a healthy diet or medical treatment for allergies. Over-reliance on supplements can have negative consequences, and excessive intake of certain vitamins can be harmful. Always consult a doctor or registered dietitian before starting any new supplements.
- Potential side effects: Some vitamins can interact with medications or have adverse effects at high doses.
- Nutrient interactions: Some vitamins may interfere with the absorption or effectiveness of others.
- No cure for allergies: Supplements cannot cure allergies; they can only support overall health.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing allergic symptoms, it's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Self-treating allergies can be dangerous, and professional guidance is necessary to manage your condition effectively and safely. Your doctor can help determine if you have any vitamin deficiencies and advise you on appropriate treatment strategies, which may include medications, immunotherapy, or lifestyle changes.
- Accurate diagnosis: Only a doctor can properly diagnose your allergy and its severity.
- Personalized treatment plan: A doctor will create a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
- Allergy management: Professional guidance will help you manage your allergies safely and effectively.
Which vitamin deficiency causes allergies?

There isn't one specific vitamin deficiency directly causing allergies. Allergies are complex immune responses triggered by exposure to allergens (like pollen, pet dander, or food proteins). While no vitamin deficiency causesallergies, several deficiencies can weaken the immune system, potentially making allergic reactions more severe or frequent. A compromised immune system might struggle to regulate its response to allergens effectively, leading to an exacerbation of symptoms. It's crucial to remember that a vitamin deficiency is not the causeof the allergy itself but rather a contributing factor to its severity or presentation.
Vitamin D and Allergy Severity
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune regulation. Studies suggest that individuals with lower vitamin D levels may experience more severe allergic symptoms, particularly respiratory allergies like asthma. This is because vitamin D influences the production and function of immune cells involved in allergic inflammation. A deficiency might lead to an overactive immune response.
- Reduced immune regulation: Vitamin D deficiency can impair the balance of immune responses, potentially increasing the severity of allergic reactions.
- Increased inflammation: Lower vitamin D levels are associated with higher levels of inflammatory markers involved in allergic responses.
- Asthma exacerbation: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to more frequent and severe asthma attacks in individuals with allergic asthma.
Vitamin A and Immune Function
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining the integrity of mucosal barriers, which are the first line of defense against allergens entering the body. A deficiency in vitamin A can weaken these barriers, making individuals more susceptible to allergen penetration and subsequent immune activation. This can contribute to the development or worsening of allergic symptoms.
- Weakened mucosal barriers: Vitamin A deficiency compromises the skin and mucous membranes, allowing allergens easier access to the body.
- Impaired immune cell function: Vitamin A is vital for the development and function of various immune cells involved in allergic responses.
- Increased susceptibility to infections: Weakened immunity due to vitamin A deficiency can also exacerbate allergic reactions indirectly through increased susceptibility to infections.
B Vitamins and Immune Response
B vitamins are crucial co-factors in many enzymatic processes necessary for proper immune function. Deficiencies in B vitamins, especially B6, B12, and folate, can disrupt immune cell development and activity, indirectly affecting how the body responds to allergens. This could lead to heightened allergic reactions.
- Impaired cell growth and development: B vitamins are essential for the proper growth and differentiation of immune cells.
- Reduced antibody production: Some B vitamins are involved in the production of antibodies that help fight off allergens.
- Increased inflammation: B vitamin deficiencies can contribute to chronic inflammation, making allergic reactions more severe.
Vitamin C and Antioxidant Defense
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals generated during allergic reactions. Deficiency in vitamin C can result in increased oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially worsening allergic symptoms. By supporting antioxidant defenses, vitamin C helps maintain immune balance.
- Reduced antioxidant capacity: Vitamin C deficiency leads to lower levels of antioxidants, exacerbating oxidative damage from allergic reactions.
- Increased inflammation: Oxidative stress and inflammation are linked to the severity of allergic responses.
- Impaired immune cell function: Vitamin C plays a vital role in supporting various aspects of immune cell function.
Zinc and Immune Regulation
Zinc is vital for numerous aspects of immune function. It's essential for the development and function of immune cells, including those involved in allergic reactions. Zinc deficiency can impair immune regulation, potentially leading to an exaggerated or dysregulated response to allergens.
- Impaired immune cell development: Zinc is critical for the maturation and differentiation of various immune cells.
- Reduced immune cell activity: Zinc deficiency can reduce the effectiveness of immune cells in responding to allergens.
- Increased susceptibility to infections: A weakened immune system due to zinc deficiency may increase susceptibility to infections, potentially exacerbating allergic reactions.
What is the strongest thing you can take for allergies?
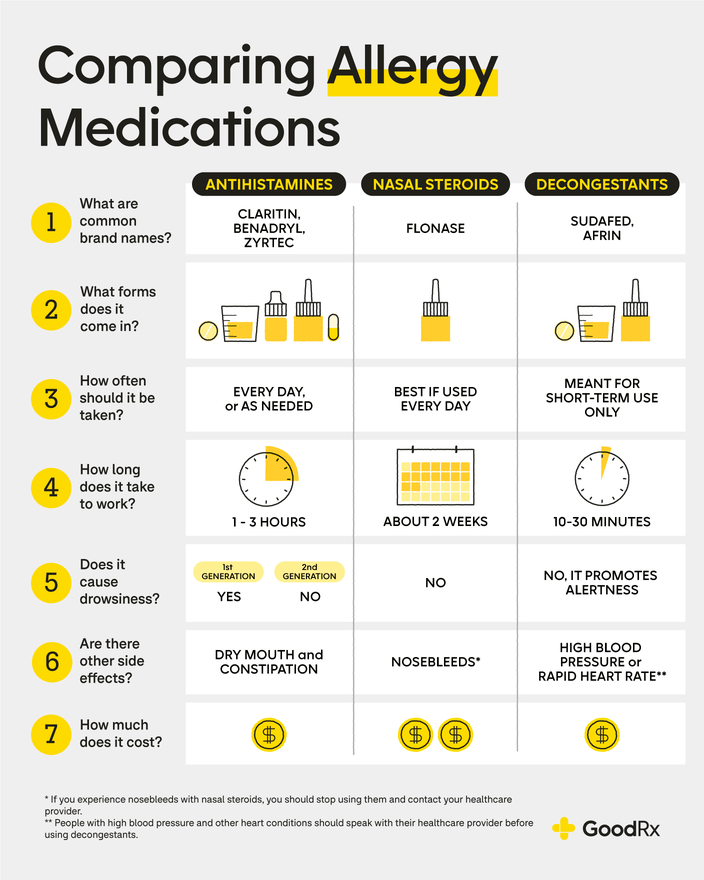
There isn't a single "strongest" allergy medication because the best treatment depends on the severity and type of allergy, as well as individual patient factors. The strength of a medication is also relative; what's strong for one person might be weak for another, and what works well for one type of allergy might not be effective for another. However, some medications are generally considered more potent or effective for managing severe allergic reactions than others. For severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), epinephrine (adrenaline) via an auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is the strongest and most crucial treatment. For less severe symptoms, a doctor might prescribe stronger antihistamines or other medications.
Prescription Medications for Severe Allergies
For individuals with moderate to severe allergies, a doctor might prescribe stronger medications than what's available over-the-counter. These often offer more targeted relief and can be more effective for managing significant symptoms. Some examples include prescription antihistamines (like fexofenadine or cetirizine in higher doses than available OTC), leukotriene inhibitors (like montelukast or zafirlukast), or nasal corticosteroids (like fluticasone or mometasone). These medications work through different mechanisms to control inflammation and allergic responses, and a doctor can tailor the prescription based on your specific needs.
- Prescription antihistamines: These offer stronger relief than OTC options, effectively blocking histamine's effects.
- Leukotriene inhibitors: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways, beneficial for allergy-induced asthma or severe nasal congestion.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, providing relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, and itching.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Allergy Medications
Over-the-counter allergy medications provide relief for mild to moderate symptoms. These are readily available but generally less potent than prescription options. Common OTC medications include antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), loratadine (Claritin), and cetirizine (Zyrtec). Decongestants like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion, but they can have side effects and should be used cautiously. The effectiveness of these varies significantly between individuals.
- Antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine): These block the effects of histamine, reducing symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Decongestants (e.g., pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine): These constrict blood vessels in the nasal passages, reducing swelling and congestion.
- Combination medications: Many OTC products combine antihistamines and decongestants to address multiple allergy symptoms.
Epinephrine: The Emergency Treatment for Anaphylaxis
Epinephrine (adrenaline) is the only effective treatment for anaphylaxis, a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. It's administered via an auto-injector like an EpiPen or Auvi-Q. Epinephrine acts quickly to reverse the effects of anaphylaxis, including airway constriction, low blood pressure, and circulatory collapse. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention even after administering epinephrine, as further treatment may be necessary.
- Immediate action: Epinephrine should be administered immediately upon recognizing the signs of anaphylaxis.
- Life-saving treatment: It's a crucial intervention to prevent death from anaphylaxis.
- Medical follow-up: Even after administering epinephrine, seek immediate medical attention.
Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy)
Allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, are a long-term treatment option for individuals with moderate to severe allergies. They involve gradually introducing increasing amounts of allergen extracts to build tolerance over time. This process can significantly reduce allergy symptoms and, in some cases, lead to long-term remission. It's a treatment plan administered by allergy specialists and requires regular injections over several months or years.
- Long-term treatment: Immunotherapy involves a series of injections over an extended period.
- Symptom reduction: It aims to reduce the severity and frequency of allergic reactions.
- Potential remission: In some cases, immunotherapy can lead to long-term relief from allergy symptoms.
Factors Influencing Allergy Medication Choice
The choice of the "strongest" allergy medication is highly individualized. Several factors influence this decision: the type of allergy, the severity of symptoms, the presence of other health conditions, and the patient's age and overall health. A doctor considers these factors to determine the most appropriate and safest treatment strategy. Furthermore, some medications may interact negatively with other drugs; therefore, a thorough medical history review is important.
- Allergy type: Different medications work better for different types of allergies (e.g., seasonal allergies, food allergies).
- Symptom severity: Mild symptoms may respond well to OTC medications, while severe symptoms may require prescription medications.
- Other health conditions: Pre-existing conditions can influence medication choices due to potential drug interactions or contraindications.
What is the best vitamin for antihistamine?

There isn't a single "best" vitamin that acts as an antihistamine. Vitamins don't directly counteract histamines in the same way that antihistamine medications do. However, certain vitamins and nutrients can support immune function and potentially reduce the severity of allergy symptoms. It's important to understand that these vitamins are supportive, not a replacement for prescribed medication. Always consult a doctor before starting any new supplements, especially if you're already taking medication for allergies.
Vitamin C's Role in Allergy Relief
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce inflammation throughout the body. While it doesn't directly block histamine, its anti-inflammatory properties may lessen allergy symptoms like congestion and sneezing. Furthermore, a strong immune system is crucial in fighting allergens. Vitamin C plays a vital role in supporting a healthy immune response.
- Reduces inflammation: Helps to lessen swelling and irritation in the airways.
- Boosts immune function: A strong immune system is better equipped to handle allergens.
- Antioxidant properties: Neutralizes free radicals that can exacerbate inflammation.
Vitamin D and Its Impact on Allergic Reactions
Studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and increased susceptibility to allergies and asthma. Vitamin D plays a role in regulating the immune system, and adequate levels may help to moderate the immune response to allergens, potentially reducing the severity of symptoms. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings conclusively.
- Immune system modulation: Helps regulate the body's response to allergens.
- Reduced inflammation: May contribute to decreased inflammation in the airways.
- Potential link to allergy severity: Studies suggest a correlation between vitamin D levels and allergy symptoms.
Quercetin: A Natural Anti-Inflammatory Compound
Quercetin is a plant-based flavonoid with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It's often found in fruits, vegetables, and tea. While not a vitamin, it's a bioactive compound that may help to stabilize mast cells, preventing the release of histamine. It's important to note that the efficacy of quercetin in allergy relief varies.
- Mast cell stabilization: May prevent the release of histamine from mast cells.
- Antioxidant effects: Helps to combat free radical damage contributing to inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory action: Reduces swelling and irritation associated with allergies.
The Importance of B Vitamins for Immune Support
B vitamins are crucial for a healthy immune system, and a weakened immune system can make you more susceptible to allergies. Several B vitamins, including B6, B12, and folate, are involved in various immune functions. Ensuring adequate intake of B vitamins supports overall health and can indirectly contribute to better allergy management.
- Cell growth and repair: Essential for the production and function of immune cells.
- Neurotransmitter production: Impacts the communication between immune cells.
- Energy production: Supports the energy demands of the immune system.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Allergy Management
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, possess anti-inflammatory properties. They can help to reduce the production of inflammatory molecules and support immune regulation. While not vitamins, they are essential fatty acids that can benefit those with allergies by reducing the severity of inflammation associated with allergic reactions.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Reduce the production of inflammatory molecules.
- Immune regulation: Help to modulate the immune response to allergens.
- Reduction of allergy symptoms: May help lessen symptoms like inflammation and congestion.
Which vitamin is best for preventing allergies?
There is no single vitamin that is definitively proven to prevent allergies. While some vitamins and nutrients play crucial roles in immune system function, and a healthy immune system is vital for managing allergic reactions, no vitamin acts as a guaranteed allergy preventer. Studies have explored the potential links between various vitamins and allergy development or severity. For example, some research suggests a possible association between vitamin D deficiency and increased risk of developing allergies, particularly asthma and eczema. However, this doesn't mean supplementing with vitamin D will prevent allergies; it indicates a correlation that requires further investigation. Similarly, vitamin A plays a significant role in immune regulation, and deficiencies could potentially increase vulnerability to allergic responses. However, simply taking extra vitamin A won’t magically prevent allergies. The development of allergies is complex and influenced by multiple genetic and environmental factors, making a simple "best vitamin" solution unlikely. A balanced diet rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, and others, is always recommended for overall health, including supporting a strong immune system. It's crucial to remember that vitamin supplementation should only be undertaken under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as excessive intake can be harmful.
Can vitamins help manage allergy symptoms?
While no vitamin directly cures allergies, some vitamins can potentially help manage symptoms. Vitamin C, for example, is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce inflammation. Allergic reactions often involve inflammation, so supplementing with vitamin C might offer some relief from symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itching. However, the effectiveness varies greatly among individuals. Vitamin E, another antioxidant, has shown some promise in reducing inflammation and improving immune function, potentially easing allergy symptoms. However, more research is needed to establish definitive efficacy. It's essential to remember that vitamins should not replace prescribed allergy medications. If you're experiencing severe allergy symptoms, it's crucial to consult an allergist or doctor for appropriate treatment. They can help you determine the best course of action, which might include medication along with lifestyle modifications and possibly vitamin supplementation as a complementary approach, but only under their supervision. Always prioritize consulting with a healthcare professional before significantly altering your vitamin intake.
Are there specific vitamins for specific allergies?
No, there aren't specific vitamins tailored to particular allergy types (e.g., pollen allergy, food allergy, etc.). While some vitamins might support overall immune health and potentially reduce the severity of some allergy symptoms, their effects aren't allergy-type specific. The underlying mechanisms of allergic reactions are complex and involve various immune system components. While a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for overall health and a functioning immune system, it won't target one specific allergy over another. For example, vitamin C's anti-inflammatory properties could theoretically offer some relief from symptoms in various allergies, but it doesn't treat the root cause of the allergy itself. Instead of relying on vitamins as a primary treatment, it's vital to identify the allergen and work with an allergist or doctor to develop a comprehensive management plan that may include immunotherapy, medication, and avoidance strategies. Vitamins can play a supportive role but shouldn't be considered a standalone solution for allergy treatment.
Should I take vitamin supplements for allergies?
Whether you should take vitamin supplements for allergies is a decision that should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. While a balanced diet is generally sufficient for most people to obtain adequate vitamins, some individuals might benefit from supplementation under specific circumstances. If you have existing allergies and are considering vitamin supplementation, it's crucial to discuss it with your doctor or allergist. They can assess your individual needs, consider any potential interactions with medications you might be taking, and determine if supplementation is appropriate and beneficial. Self-treating with vitamins without professional guidance can be risky, as excessive intake can have negative consequences. The focus should always be on managing your allergies effectively through appropriate medical treatment and lifestyle modifications, with vitamin supplementation considered only as a potentially complementary strategy under professional supervision. Your doctor will help determine the most suitable approach tailored to your specific situation and health status.
Deja una respuesta