Are fried eggs healthy

In the culinary realm of quick and versatile breakfast options, fried eggs stand out as a beloved choice. Their crispy edges, soft and runny yolks, and ease of preparation have made them a staple in homes and restaurants alike. But when it comes to health, the age-old question arises: are fried eggs a nutritious addition to our diet, or a guilty indulgence best avoided? Let's delve into the facts to unravel the truth behind the nutritional value of fried eggs.
Are Fried Eggs Healthy? A Nutritional Breakdown
The healthiness of fried eggs is a complex issue, not a simple yes or no. It depends heavily on how they're prepared and what constitutes a "healthy" diet for you. While eggs themselves are packed with nutrients, the frying process can introduce factors that affect their overall health impact.
Nutritional Benefits of Eggs
Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, boasting high-quality protein, essential amino acids, and various vitamins and minerals. A single large egg provides around 6 grams of protein, contributing to satiety and muscle building. They're also a good source of choline, crucial for brain health, and vitamins D, E, and B12, often lacking in some diets. However, it’s important to remember that the nutritional profile of the egg itself doesn’t change significantly based on how it is cooked.
The Impact of Frying on Egg Health
The main concern with fried eggs lies in the cooking method. Frying eggs in butter, oil, or other high-fat options significantly increases their saturated and unhealthy fat content. This can contribute to increased cholesterol levels and heart disease risk if consumed frequently as part of an unhealthy diet. The cooking process can also lead to the formation of harmful compounds, although the amount depends on the cooking temperature and time.
Healthy Frying Alternatives
To mitigate the negative effects of frying, consider healthier alternatives. Using cooking sprays with minimal oil, or frying in a non-stick pan with a small amount of healthy fats like olive oil can help reduce the overall fat content. Cooking eggs over easy or sunny-side up minimizes the amount of oil absorbed, compared to fully frying them until they're crisp. Baking, poaching, or scrambling are even healthier alternatives.
Cholesterol Concerns and Egg Consumption
For many years, there was concern that the cholesterol in eggs could negatively impact blood cholesterol levels. However, current research suggests that dietary cholesterol has less impact than previously believed. Saturated and trans fats are more significant contributors to high cholesterol. So while eggs contain cholesterol, their overall effect on your cholesterol levels depends more on the rest of your diet and your individual health status. Always consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine a suitable egg consumption level for your specific needs.
Overall Dietary Context
The healthiness of fried eggs ultimately depends on the broader context of your diet. If you consume them as part of a balanced, varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, the impact of occasional fried eggs might be minimal. However, frequent consumption of fried eggs as part of an otherwise unhealthy diet could contribute to negative health consequences. Moderation is key, and choosing healthier cooking methods can significantly improve the nutritional profile of your eggs.
| Cooking Method | Fat Content | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fried (high-fat oil) | High | Potentially negative, increase in saturated fat |
| Fried (low-fat oil/spray) | Moderate | Less negative impact than high-fat frying |
| Baked/Poached/Scrambled | Low | Healthiest options |
Are Fried Eggs Healthy? A Nutritional Breakdown
The healthiness of fried eggs is a complex issue, not a simple yes or no. It depends heavily on how they're prepared and what constitutes a "healthy" diet for you. While eggs themselves are packed with nutrients, the frying process can introduce factors that affect their overall health impact.
Nutritional Benefits of Eggs
Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, boasting high-quality protein, essential amino acids, and various vitamins and minerals. A single large egg provides around 6 grams of protein, contributing to satiety and muscle building. They're also a good source of choline, crucial for brain health, and vitamins D, E, and B12, often lacking in some diets. However, it’s important to remember that the nutritional profile of the egg itself doesn’t change significantly based on how it is cooked.
The Impact of Frying on Egg Health
The main concern with fried eggs lies in the cooking method. Frying eggs in butter, oil, or other high-fat options significantly increases their saturated and unhealthy fat content. This can contribute to increased cholesterol levels and heart disease risk if consumed frequently as part of an unhealthy diet. The cooking process can also lead to the formation of harmful compounds, although the amount depends on the cooking temperature and time.
Healthy Frying Alternatives
To mitigate the negative effects of frying, consider healthier alternatives. Using cooking sprays with minimal oil, or frying in a non-stick pan with a small amount of healthy fats like olive oil can help reduce the overall fat content. Cooking eggs over easy or sunny-side up minimizes the amount of oil absorbed, compared to fully frying them until they're crisp. Baking, poaching, or scrambling are even healthier alternatives.
Cholesterol Concerns and Egg Consumption
For many years, there was concern that the cholesterol in eggs could negatively impact blood cholesterol levels. However, current research suggests that dietary cholesterol has less impact than previously believed. Saturated and trans fats are more significant contributors to high cholesterol. So while eggs contain cholesterol, their overall effect on your cholesterol levels depends more on the rest of your diet and your individual health status. Always consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine a suitable egg consumption level for your specific needs.
Overall Dietary Context
The healthiness of fried eggs ultimately depends on the broader context of your diet. If you consume them as part of a balanced, varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, the impact of occasional fried eggs might be minimal. However, frequent consumption of fried eggs as part of an otherwise unhealthy diet could contribute to negative health consequences. Moderation is key, and choosing healthier cooking methods can significantly improve the nutritional profile of your eggs.
| Cooking Method | Fat Content | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fried (high-fat oil) | High | Potentially negative, increase in saturated fat |
| Fried (low-fat oil/spray) | Moderate | Less negative impact than high-fat frying |
| Baked/Poached/Scrambled | Low | Healthiest options |
Is it unhealthy to fry an egg?
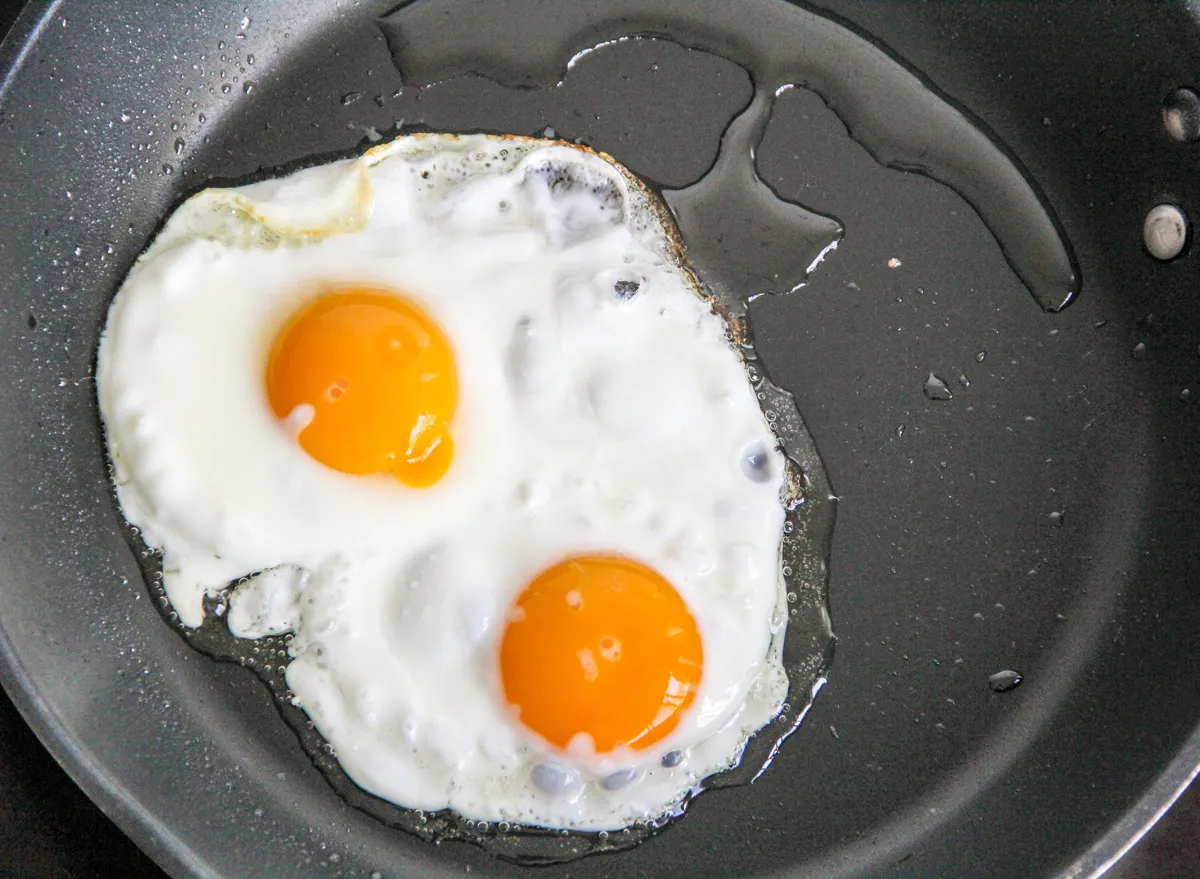

Whether frying an egg is unhealthy depends on several factors. It's not inherently bad for you, but the way you prepare it significantly impacts its nutritional profile and potential health effects. A fried egg provides protein, choline, and some vitamins and minerals. However, the frying process can increase its fat and cholesterol content, particularly if you use a lot of oil or butter. The type of oil used is also crucial; using saturated or trans fats will significantly increase the unhealthy aspects of the dish compared to using unsaturated fats like olive oil. Portion size is another critical element; a single fried egg occasionally is unlikely to be problematic for most people, but regularly consuming large quantities of fried eggs, especially with added saturated fat, could contribute to health problems over time. Ultimately, moderation and mindful food choices are key.
How much cholesterol is in a fried egg?
A large fried egg contains approximately 186mg of cholesterol. While dietary cholesterol's impact on blood cholesterol is less significant than previously believed, consuming excessive cholesterol can still contribute to high blood cholesterol levels in some individuals, especially those with pre-existing conditions. It's important to consider cholesterol intake as part of an overall healthy diet.
- Cholesterol content varies slightly depending on the size of the egg and the cooking method.
- Other dietary factors, like saturated fat intake, play a more significant role in blood cholesterol levels than dietary cholesterol alone.
- Individuals with high cholesterol should monitor their intake of cholesterol-rich foods, including fried eggs.
What are the benefits of eating fried eggs?
Fried eggs, despite some drawbacks, offer several nutritional benefits. They are a good source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues. They also contain choline, a nutrient vital for brain health and liver function. Additionally, they provide certain vitamins and minerals, though the amounts can vary depending on factors such as the type of egg and cooking method. The nutritional benefits are best realized when the eggs are prepared using healthier cooking methods and in moderation.
- Protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair.
- Choline supports brain function and liver health.
- Fried eggs offer some vitamins and minerals like vitamin D and selenium.
What are the drawbacks of frying eggs?
The primary drawbacks of frying eggs are the increased fat and calorie content. Frying often uses significant amounts of oil or butter, leading to a substantial increase in saturated fat intake if unhealthy fats are utilized. Excessive saturated fat consumption can increase LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels, potentially raising the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, overcooking can reduce the nutritional value of the egg and lead to the formation of harmful compounds.
- High fat content increases calorie intake.
- Saturated fat raises LDL cholesterol, increasing heart disease risk.
- Overcooking can reduce nutrient density and form potentially harmful compounds.
What are healthier alternatives to frying eggs?
There are several healthier ways to cook eggs, minimizing the added fat and preserving more nutrients. Boiling, poaching, or scrambling eggs without added oil are excellent choices. Baking eggs in a muffin tin is another healthy option, providing portion control and limiting added fat. These methods retain more of the egg's nutritional value and reduce the overall calorie and fat content.
- Boiling and poaching are low-fat cooking methods.
- Scrambled eggs can be made with minimal or no added oil.
- Baking eggs in a muffin tin offers portion control and avoids excess oil.
How often is it okay to eat fried eggs?
The frequency with which you can safely consume fried eggs depends on your overall diet, health status, and individual needs. For most healthy individuals, occasional consumption of a fried egg prepared with healthier oils is unlikely to cause harm. However, regular consumption of fried eggs, particularly those prepared with excessive amounts of saturated fat, should be limited to maintain a balanced and heart-healthy diet. Consulting a doctor or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health profile.
- Occasional consumption is generally acceptable for healthy individuals.
- Regular consumption should be limited, especially if using saturated or trans fats.
- Consult a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice.
How often should you eat fried eggs?
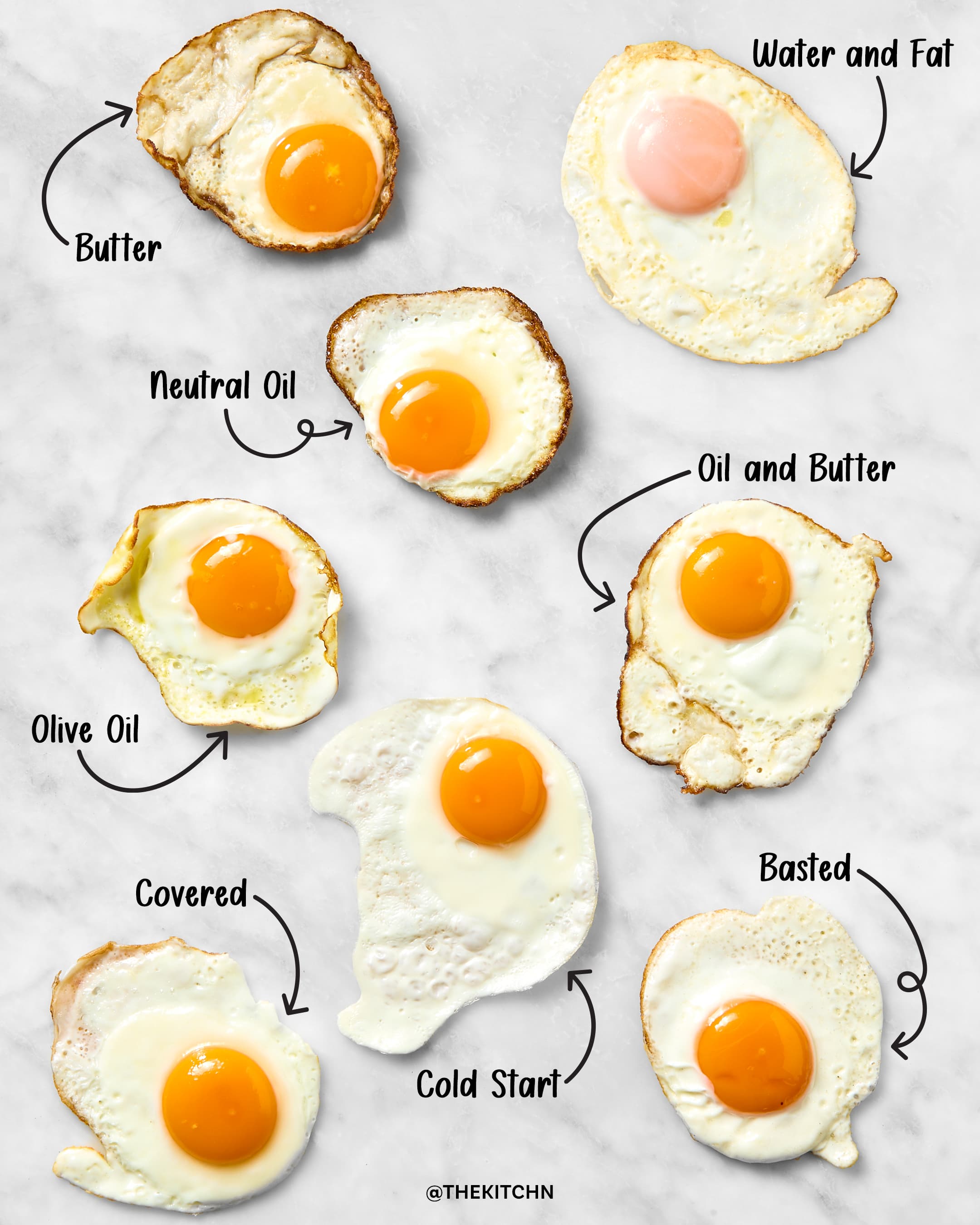
How Often Should You Eat Fried Eggs?
There's no single definitive answer to how often you should eat fried eggs. It depends heavily on your overall diet, health conditions, and personal preferences. While fried eggs can be a part of a healthy diet, overconsumption can contribute to various health problems due to their high saturated fat and cholesterol content. Moderation is key.
Dietary Considerations
The frequency with which you consume fried eggs should align with your broader dietary goals. If you're aiming for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, fried eggs can be an occasional treat. However, if you're trying to reduce saturated fat intake or manage cholesterol levels, you should limit your consumption. Consider the overall nutritional profile of your meals and how fried eggs fit into that picture.
- Prioritize whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for most of your meals.
- Incorporate lean protein sources like fish, chicken, and beans regularly.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and trans fats.
Cholesterol and Heart Health
Fried eggs are relatively high in cholesterol. While the link between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol levels is less clear-cut than previously thought, consuming too much saturated fat, often found in fried foods, can negatively impact your cholesterol profile and increase your risk of heart disease. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or high cholesterol should be particularly mindful of their fried egg intake. Consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Monitor your cholesterol levels regularly, especially if you have a family history of heart disease.
- Choose cooking methods that minimize added fat, such as baking, grilling, or poaching.
- Consider alternatives like scrambled eggs or egg whites, which are lower in fat and cholesterol.
Nutritional Value of Fried Eggs
Despite the potential drawbacks, fried eggs do offer some nutritional benefits. They are a good source of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues. They also contain choline, an important nutrient for brain health. However, the frying process can negate some of these benefits by adding extra fat and potentially reducing the availability of certain nutrients. The nutritional value of your fried eggs depends significantly on the cooking method and the type of oil used.
- Use healthier cooking oils like olive oil or avocado oil.
- Avoid deep-frying, which significantly increases fat content.
- Consider adding vegetables to your fried eggs to increase the nutrient density of your meal.
Health Conditions and Medications
Certain health conditions and medications can impact how often you should eat fried eggs. For example, individuals with high cholesterol, diabetes, or kidney disease may need to limit their intake of saturated fat and cholesterol. Some medications can also interact with dietary cholesterol. Always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have any underlying health concerns or are taking medication.
- Discuss your diet with your doctor, particularly if you have any pre-existing health conditions.
- Be aware of potential medication interactions with dietary cholesterol and saturated fats.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations regarding dietary restrictions.
Personal Preferences and Portion Sizes
Ultimately, how often you eat fried eggs comes down to your personal preferences and dietary habits. Even if fried eggs are part of a healthy diet, paying attention to portion sizes is crucial. A single fried egg might be acceptable as part of a balanced breakfast, but consuming multiple fried eggs daily is likely excessive for most people. Listen to your body and adjust your intake based on how you feel.
- Be mindful of your portion sizes.
- Don't feel guilty about enjoying fried eggs occasionally as part of a balanced diet.
- Pay attention to your body's response to fried eggs and adjust your consumption accordingly.
Is fried egg healthy for weight loss?

Is a fried egg healthy for weight loss? The answer is nuanced and depends heavily on several factors. While a fried egg itself isn't inherently unhealthy, its impact on weight loss hinges on its preparation method, portion size, and its place within a broader dietary plan. A single fried egg provides a decent source of protein and essential nutrients, contributing to satiety. However, the added fat from frying can significantly increase the calorie count, potentially hindering weight loss efforts if not carefully managed. Consider the overall caloric intake and macro-nutrient balance of your diet.
Nutritional Content of a Fried Egg
A fried egg, especially one cooked in a significant amount of oil, presents a higher calorie count than a poached or boiled egg. The added oil contributes significantly to the total fat content. However, it also contains valuable nutrients: protein, which aids in satiety and muscle maintenance; choline, beneficial for brain health; and some essential vitamins and minerals. The nutritional profile, therefore, is a double-edged sword in weight loss.
- Protein content: Approximately 6 grams per egg, important for satiety and metabolism.
- Fat content: Highly variable depending on the cooking method and oil used. Frying significantly increases fat content.
- Vitamins and minerals: Provides a source of Vitamins A, D, and B12, as well as choline and selenium.
Impact of Frying on Caloric Intake
The frying process itself adds considerable calories. The type of oil used dramatically impacts the overall calorie density. Using excessive oil or unhealthy fats like saturated or trans fats adds significant calories and unhealthy fats to your diet, making it harder to lose weight. Opting for healthier cooking methods like poaching or boiling minimizes the added fat and therefore the extra calories.
- Oil type matters: Use small amounts of healthy oils like olive oil or avocado oil.
- Cooking spray: Reduces the amount of oil used significantly.
- Alternative cooking methods: Poaching, boiling, or baking provide healthier options.
Fried Eggs within a Calorie Deficit
The key to incorporating fried eggs into a weight-loss diet is maintaining a calorie deficit. Consuming fewer calories than your body burns is the fundamental principle of weight loss. If your overall daily calorie intake remains within a deficit, including a fried egg occasionally shouldn't derail your progress. However, excessive consumption of fried eggs, due to their higher calorie content compared to other cooking methods, can make it more difficult to maintain that deficit.
- Track your calories: Use a food diary or app to monitor your daily intake.
- Portion control: Stick to one or two eggs, not more.
- Balanced diet: Combine the fried egg with other nutritious foods like vegetables and whole grains.
Considering Macronutrient Balance
While protein is beneficial for weight loss, a diet high in fat can hinder progress. The balance of macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) is crucial for effective weight management. Fried eggs, depending on cooking methods, can be higher in fat than other protein sources. It's important to carefully consider the total fat intake from all sources in your diet and balance it with sufficient protein and moderate carbohydrates to optimize satiety and weight loss.
- Protein intake: Aim for a sufficient intake of protein from multiple sources.
- Healthy fat intake: Include healthy unsaturated fats but limit saturated and trans fats.
- Carbohydrate choices: Opt for complex carbohydrates over refined sugars.
Overall Dietary Context
The impact of a fried egg on weight loss is largely determined by the broader context of your overall diet. A single fried egg, in moderation and as part of a well-balanced, calorie-controlled diet, is unlikely to hinder weight loss significantly. However, if it's frequently consumed in large quantities, prepared with excessive oil, and not complemented by other healthy choices, it could contribute to weight gain.
- Regular exercise: Combine a healthy diet with regular physical activity for optimal results.
- Consult a professional: Seek guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist for personalized advice.
- Sustainable habits: Focus on long-term dietary changes rather than quick fixes.
Is fry egg good for health?
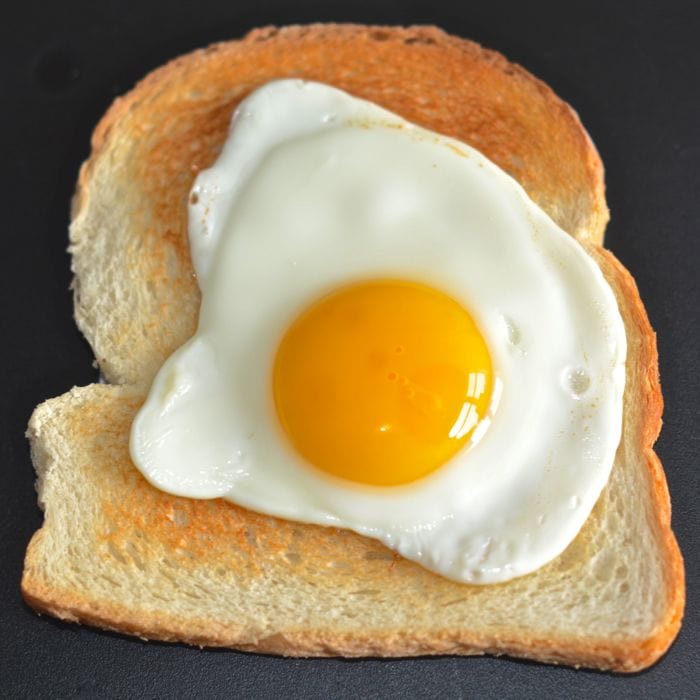

Whether a fried egg is good for health is complex and depends heavily on several factors. A single fried egg provides a good source of protein and several essential nutrients. However, the preparation method significantly impacts its nutritional value and potential health effects. The frying process, particularly if done with excessive oil or butter, dramatically increases the fat and cholesterol content. This can be detrimental to individuals with high cholesterol or heart disease risks. Conversely, a fried egg prepared with a minimal amount of oil can still offer some health benefits, but it's crucial to consider the overall dietary context.
Nutritional Value of Fried Eggs
Fried eggs are a good source of protein, crucial for building and repairing tissues. They also contain choline, a nutrient vital for brain function and cell membranes. Furthermore, they provide vitamin D, essential for calcium absorption and bone health, as well as riboflavin (vitamin B2), important for energy metabolism. However, the nutrient content can vary based on the size of the egg and the cooking method.
- High-quality protein: Contributes to muscle growth and repair.
- Choline: Supports brain health and cognitive function.
- Vitamins D and B2: Essential for bone health and energy production.
Cholesterol Content in Fried Eggs
Fried eggs are relatively high in cholesterol. One large egg contains approximately 186mg of cholesterol. While dietary cholesterol's impact on blood cholesterol levels is less significant than previously believed, individuals with high cholesterol or heart disease should still monitor their intake carefully. The added fat from frying further increases the overall caloric and fat content of the egg, potentially contributing to weight gain and other health issues.
- High cholesterol levels: May be a concern for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
- Increased saturated fat: From frying with butter or oil, raising LDL cholesterol.
- Potential for weight gain: Due to higher calorie and fat content compared to boiled or poached eggs.
Fat and Calorie Content
The amount of fat and calories in a fried egg can vary significantly depending on the cooking method and the type of fat used. Frying in butter or oil drastically increases the fat content, often exceeding the fat in other cooking methods like boiling or poaching. This extra fat contributes to the overall calorie count, making fried eggs a less healthy option than lower-fat alternatives if consumed regularly in large quantities.
- Increased saturated and unsaturated fats: Depends on cooking oil used.
- Higher calorie count: Compared to boiled or poached eggs.
- Potential for weight gain: If consumed frequently as part of a high-calorie diet.
Health Risks Associated with Fried Eggs
Consuming fried eggs regularly, especially those cooked with excessive oil or butter, could increase the risk of several health problems. High cholesterol levels and increased saturated fat intake could contribute to heart disease. Excessive calorie consumption from fried eggs can lead to weight gain and obesity, increasing the risk of other health complications like type 2 diabetes. It is important to consider the overall dietary intake and consume fried eggs in moderation.
- Increased risk of heart disease: Due to high cholesterol and saturated fat.
- Weight gain and obesity: From high calorie and fat content.
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes: Due to high calorie and fat intake.
Healthier Alternatives to Fried Eggs
If you enjoy eggs but are concerned about the health implications of frying, consider healthier alternatives. Boiling, poaching, or baking eggs minimizes the added fat and calories. These methods retain most of the nutritional benefits while reducing the potential health risks associated with frying. Furthermore, using cooking sprays instead of oil or butter can reduce the fat content of fried eggs significantly.
- Boiling or poaching: Minimizes added fat and calories.
- Baking: Another low-fat cooking method preserving nutrients.
- Using cooking sprays: Reduces the amount of oil used during frying.
Are fried eggs healthy?
Whether fried eggs are healthy depends heavily on how they're prepared and how often you consume them. A single fried egg isn't inherently unhealthy; it's a good source of protein, choline (important for brain health), and other nutrients like vitamin D and vitamin B12. However, the frying process introduces some drawbacks. The use of butter or oil adds significant saturated fat and calories, potentially contributing to weight gain and increasing the risk of heart disease if consumed regularly in large quantities. Furthermore, high heat frying can lead to the formation of harmful compounds like advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are linked to inflammation and various chronic diseases. Therefore, the overall health impact of fried eggs hinges on moderation and mindful preparation. Opting for a small amount of healthy oil like olive oil and avoiding overcooking can mitigate some of the negative effects.
How many fried eggs can I eat per week and still be healthy?
There's no magic number of fried eggs you can eat per week and guarantee perfect health. The ideal amount depends on your overall diet, lifestyle, health goals, and individual needs. If you're already consuming a diet rich in saturated fats and cholesterol, limiting fried eggs (or any high-cholesterol foods) is advisable. For someone with a generally healthy diet and moderate physical activity, a few fried eggs per week probably won't cause significant harm. However, consistently consuming multiple fried eggs daily increases your risk of adverse health consequences. Moderation is key. Consider balancing the nutritional benefits of eggs with the potential downsides of frying and high fat intake. If you have any pre-existing health conditions, it's best to consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized guidance on egg consumption.
Are there healthier ways to cook eggs than frying?
Absolutely! Frying isn't the only way to enjoy eggs. Many healthier cooking methods preserve the nutritional value while minimizing the addition of unhealthy fats. Boiling, poaching, and baking are excellent alternatives. These methods require little to no added oil, resulting in a lower calorie and fat count. Scrambled eggs can also be a healthier option than fried eggs, provided you use a non-stick pan with minimal oil or cooking spray. Experiment with different cooking methods to find your preferred taste and texture while prioritizing healthier choices. Consider adding vegetables to your eggs for an extra nutritional boost.
What are the potential health risks associated with eating fried eggs regularly?
Regular consumption of fried eggs carries several potential health risks, primarily linked to the high saturated fat content and the formation of AGEs during frying. High saturated fat intake is a known risk factor for heart disease, increasing levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol. AGEs contribute to inflammation throughout the body, potentially increasing the risk of developing chronic conditions like diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, frequent consumption of fried eggs may contribute to weight gain due to their relatively high calorie density. The potential risks can be significantly reduced by choosing healthier cooking methods and limiting the frequency of fried egg consumption. Individuals with high cholesterol or other heart-related conditions should especially be mindful of their fried egg intake.
Deja una respuesta