How can I reduce my immune system naturally

In today's fast-paced world, maintaining a robust immune system is paramount to our overall health and well-being. When our immune system weakens, we become more susceptible to infections, viruses, and other health ailments. While there are numerous prescription medications and supplements available to boost immunity, it is crucial to explore natural methods as well. This article delves into practical, evidence-based strategies to effectively reduce inflammation, strengthen the immune response, and enhance overall health by harnessing the power of nature. By implementing these holistic approaches, individuals can empower themselves with a stronger immune system, promoting a life filled with vitality and resilience.
Naturally Suppressing an Overactive Immune System
It's crucial to understand that intentionally suppressing your immune system is generally not recommended. A healthy immune system is vital for fighting off infections and diseases. However, in certain situations, like autoimmune disorders where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, or following an organ transplant to prevent rejection, managing an overactive immune response might be necessary. The following information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health regimen, especially if you suspect an immune system issue.
Dietary Changes to Modulate Immune Response
Certain dietary choices can influence immune function. Reducing inflammatory foods like processed foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats is often advised. Instead, focus on an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health. Specifically, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish) and antioxidants (like berries and leafy greens) may help to moderate immune responses. It's also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. However, drastic dietary changes should always be discussed with a doctor or registered dietitian.
Stress Management Techniques for Immune Regulation
Chronic stress can significantly impact the immune system, potentially leading to an overactive response. Practicing stress-reduction techniques is crucial. This could include regular exercise, mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature. These activities help to lower cortisol levels (a stress hormone) and promote a sense of calm, which can contribute to a more balanced immune response. Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is essential for long-term immune health.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements (Consult a Doctor First!)
Some herbal remedies and supplements are traditionally used to modulate immune function. However, it's vital to consult a doctor before using any of these, as they can interact with medications or have side effects. Examples include turmeric (curcumin), ginger, and certain types of mushrooms. These have shown promise in preliminary studies, but more research is needed. Self-treating can be risky, so professional guidance is paramount.
Sleep Hygiene and Immune Function
Sufficient sleep is essential for a healthy immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool. Lack of sleep can weaken the immune system and make it more prone to overreacting.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Immune System Support
Beyond diet and stress management, other lifestyle changes can impact immune function. Regular exercise strengthens the immune system, but avoid overtraining. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the immune system. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking are also crucial steps. These healthy habits can contribute to a more balanced and effective immune system.
| Factor | Impact on Immune System | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Inflammation can trigger an overactive immune response. Nutrients support immune regulation. | Anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
| Stress | Chronic stress weakens the immune system and can cause overreaction. | Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, and exercise. |
| Sleep | Lack of sleep weakens the immune system. | 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. |
| Lifestyle | Exercise, weight management, alcohol and smoking avoidance are crucial. | Healthy habits contribute to balanced immune function. |
| Supplements/Herbs | Some may modulate immune response, but consult a doctor first. | Only use under medical supervision. |
Naturally Suppressing an Overactive Immune System
It's crucial to understand that intentionally suppressing your immune system is generally not recommended. A healthy immune system is vital for fighting off infections and diseases. However, in certain situations, like autoimmune disorders where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, or following an organ transplant to prevent rejection, managing an overactive immune response might be necessary. The following information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health regimen, especially if you suspect an immune system issue.
Dietary Changes to Modulate Immune Response
Certain dietary choices can influence immune function. Reducing inflammatory foods like processed foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats is often advised. Instead, focus on an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health. Specifically, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish) and antioxidants (like berries and leafy greens) may help to moderate immune responses. It's also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. However, drastic dietary changes should always be discussed with a doctor or registered dietitian.
Stress Management Techniques for Immune Regulation
Chronic stress can significantly impact the immune system, potentially leading to an overactive response. Practicing stress-reduction techniques is crucial. This could include regular exercise, mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature. These activities help to lower cortisol levels (a stress hormone) and promote a sense of calm, which can contribute to a more balanced immune response. Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is essential for long-term immune health.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements (Consult a Doctor First!)
Some herbal remedies and supplements are traditionally used to modulate immune function. However, it's vital to consult a doctor before using any of these, as they can interact with medications or have side effects. Examples include turmeric (curcumin), ginger, and certain types of mushrooms. These have shown promise in preliminary studies, but more research is needed. Self-treating can be risky, so professional guidance is paramount.
Sleep Hygiene and Immune Function
Sufficient sleep is essential for a healthy immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool. Lack of sleep can weaken the immune system and make it more prone to overreacting.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Immune System Support
Beyond diet and stress management, other lifestyle changes can impact immune function. Regular exercise strengthens the immune system, but avoid overtraining. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the immune system. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking are also crucial steps. These healthy habits can contribute to a more balanced and effective immune system.
| Factor | Impact on Immune System | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Inflammation can trigger an overactive immune response. Nutrients support immune regulation. | Anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
| Stress | Chronic stress weakens the immune system and can cause overreaction. | Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, and exercise. |
| Sleep | Lack of sleep weakens the immune system. | 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. |
| Lifestyle | Exercise, weight management, alcohol and smoking avoidance are crucial. | Healthy habits contribute to balanced immune function. |
| Supplements/Herbs | Some may modulate immune response, but consult a doctor first. | Only use under medical supervision. |
Which foods decrease immunity?

Which Foods Decrease Immunity?
Processed Foods
Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars, while being low in essential nutrients. These foods can contribute to inflammation in the body, which can suppress immune function. The high sugar content can also disrupt the gut microbiome, further weakening immunity. Excessive consumption disrupts the delicate balance of gut bacteria crucial for immune system health. Avoid processed foods as much as possible.
- High in unhealthy fats: These fats contribute to inflammation.
- High in sodium: This can lead to water retention and increased blood pressure, negatively impacting overall health and immune function.
- Low in essential nutrients: Lack of vitamins and minerals hinders immune cell production and function.
Foods High in Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated and trans fats are found in many processed foods, fried foods, and baked goods. These fats have been linked to increased inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can impair the immune system's ability to function effectively. Limiting saturated and trans fats is crucial for optimal immune function. They contribute to a variety of health issues, including cardiovascular disease, which further weakens the immune system.
- Increased inflammation: This hinders immune cell activity.
- Impaired immune response: Inflammation makes it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Contribution to chronic diseases: These diseases further compromise immune function.
Foods High in Added Sugar
Excessive sugar consumption, particularly added sugars found in sugary drinks, desserts, and processed foods, can significantly impair immune function. High sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, which in turn can suppress the activity of immune cells. Additionally, sugar can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, further compromising immune defenses. Reducing added sugar intake is essential for a robust immune system.
- Insulin resistance: This reduces the effectiveness of immune cells.
- Gut microbiome disruption: An imbalance of gut bacteria weakens immunity.
- Increased inflammation: High sugar levels contribute to chronic inflammation.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can suppress the immune system, reducing the body's ability to fight off infections. Excessive alcohol consumption interferes with various immune cell functions and can increase the risk of infections. Moderate alcohol consumption, or abstaining altogether, is recommended for optimal immune function. Alcohol also depletes essential nutrients needed for immune function.
- Immune cell suppression: Alcohol directly inhibits the activity of immune cells.
- Increased susceptibility to infection: This makes the body more vulnerable to pathogens.
- Nutrient depletion: Alcohol interferes with nutrient absorption.
Refined Grains
Refined grains, such as white bread, white rice, and pastries, are often low in fiber and essential nutrients. These foods can lead to blood sugar spikes and crashes, weakening the immune system. The lack of fiber also impacts the gut microbiome, which plays a critical role in immune regulation. Choosing whole grains over refined grains is vital for immune support. Whole grains provide sustained energy and beneficial fiber.
- Blood sugar fluctuations: These fluctuations negatively impact immune function.
- Low fiber content: Fiber is essential for a healthy gut microbiome.
- Nutrient deficiency: Refined grains lack several crucial vitamins and minerals.
How do you reset your immune system?

There's no single button to "reset" your immune system. The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that constantly adapts and changes. The concept of a "reset" is more accurately described as supporting and optimizing its function, allowing it to work more effectively. This involves making lifestyle changes to reduce stress, improve sleep, and optimize nutrition, thereby promoting a healthier overall state. It's crucial to understand that significant immune dysfunction should always be addressed by consulting a medical professional. Self-treating can be dangerous and may delay proper diagnosis and treatment.
Supporting Your Immune System Through Diet
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in immune function. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants crucial for immune cell development and activity. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats minimizes inflammation, a factor that can negatively impact the immune system. Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods is key to building a strong immune foundation.
- Increase intake of fruits and vegetables: They are packed with vitamins C, A, and E, along with antioxidants.
- Choose lean protein sources: Chicken, fish, beans, and lentils support immune cell production.
- Limit processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats: These contribute to inflammation.
The Importance of Sleep for Immune Health
Sleep is not merely a time for rest; it's a critical period for immune system repair and regeneration. During sleep, your body produces cytokines, which are proteins that help regulate inflammation and fight infection. Chronic sleep deprivation weakens your immune response, making you more susceptible to illness. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support your immune system.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Optimize your sleep environment for darkness and quiet.
Stress Management Techniques for Immune Support
Chronic stress significantly impairs immune function. The body releases stress hormones like cortisol, which can suppress the immune system's ability to fight off infections. Employing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can help regulate cortisol levels and improve immune resilience.
- Practice mindfulness meditation daily.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Connect with supportive friends and family.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Immune Enhancement
Regular moderate-intensity exercise boosts immune function by increasing circulation, reducing inflammation, and improving the efficiency of immune cells. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week. However, avoid overtraining, as excessive exercise can have the opposite effect and weaken the immune system. Finding a balance is key.
- Include cardiovascular exercise like brisk walking, jogging, or swimming.
- Incorporate strength training exercises two to three times a week.
- Listen to your body and rest when needed.
Hydration and its Impact on Immune Function
Water is essential for various bodily functions, including immune responses. Dehydration can impair immune cell activity and reduce the body's ability to fight off infections. Staying properly hydrated ensures efficient transport of immune cells and nutrients throughout the body. Consume enough water to maintain good hydration throughout the day.
- Carry a water bottle and sip throughout the day.
- Eat fruits and vegetables with high water content.
- Monitor your urine color; pale yellow indicates adequate hydration.
How to calm down your immune system?
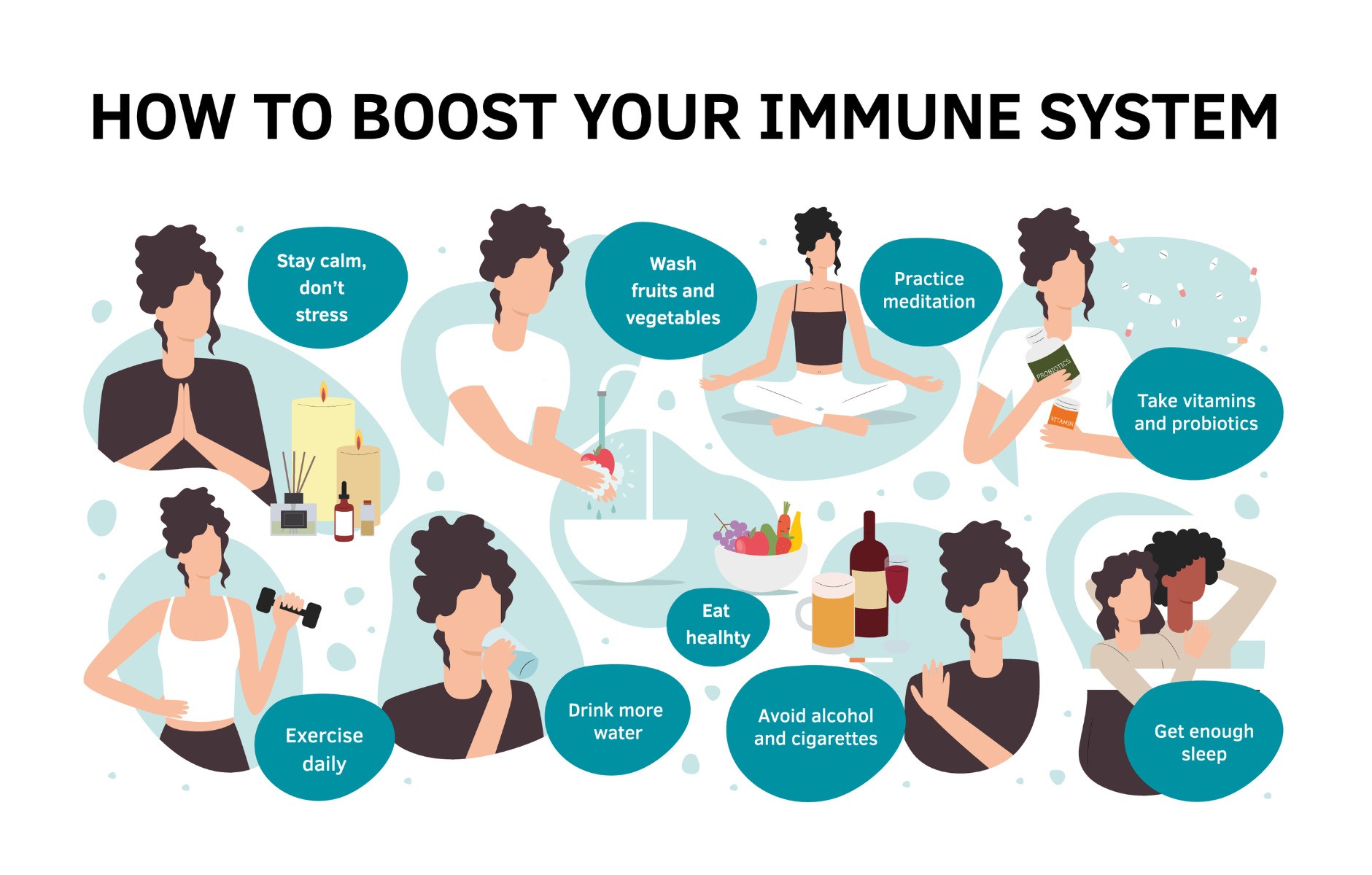
How to Calm Down Your Immune System
Calming down an overactive immune system, often associated with autoimmune diseases or chronic inflammation, requires a multifaceted approach. There's no single solution, and what works for one person might not work for another. It's crucial to work with a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan, especially if you suspect an autoimmune condition. Self-treating can be dangerous. The information below is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Immune System Overactivity
Significant lifestyle changes can profoundly impact immune regulation. Adopting a healthier lifestyle is often the cornerstone of managing an overactive immune system. This includes focusing on stress reduction techniques, improving sleep quality, and engaging in regular physical activity. These changes help regulate the body's overall inflammatory response, indirectly calming the immune system.
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sleep deprivation exacerbates inflammation.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise is beneficial, but avoid overexertion, which can increase inflammation.
Dietary Interventions for Immune System Modulation
Diet plays a critical role in immune system regulation. Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, while others possess anti-inflammatory properties. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats, is generally recommended. Specific dietary approaches, such as the Mediterranean diet, are often associated with improved immune function.
- Increase Anti-inflammatory Foods: Focus on foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish, flaxseeds), antioxidants (e.g., berries, leafy greens), and vitamins (e.g., vitamin D, vitamin C).
- Limit Pro-inflammatory Foods: Reduce consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, red meat, and saturated fats.
- Consider a Specific Diet: Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional about potentially beneficial diets like the Mediterranean diet or the elimination diet.
Supplements and Nutritional Support for Immune Balance
Some supplements may offer support in calming an overactive immune system. However, it's vital to consult a doctor before taking any supplements, as they can interact with medications or have unintended side effects. Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and curcumin, have shown promise in reducing inflammation in some studies.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Vitamin D: Plays a crucial role in immune regulation.
- Curcumin: A compound found in turmeric with anti-inflammatory properties.
Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques
Chronic stress significantly impacts the immune system. Practicing mindfulness and stress reduction techniques is crucial for long-term immune health. These practices help regulate the body's stress response, indirectly reducing inflammation and promoting immune balance. These methods help reduce the body's production of cortisol, a stress hormone that can suppress the immune system.
- Meditation: Regular meditation can help calm the mind and reduce stress hormones.
- Yoga: Combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing exercises can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Medical Interventions for Immune System Disorders
For individuals with diagnosed autoimmune diseases or other immune system disorders, medical intervention is often necessary. This can involve medications such as immunosuppressants, biologics, or corticosteroids, all of which should be prescribed and monitored by a qualified physician. These medications aim to suppress the immune system's overactivity, but they come with potential side effects and require careful monitoring.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications help suppress the immune system's activity.
- Biologics: Targeted therapies that specifically block inflammatory pathways.
- Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, often used for short-term treatment of flares.
How can I build my immune system to not get sick?

How Can I Build My Immune System to Not Get Sick?
Building a robust immune system isn't about guaranteeing you'll never get sick – exposure to pathogens is inevitable. However, a strong immune system can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of illnesses. It's a multifaceted approach involving lifestyle choices, diet, and sometimes, medical intervention. Focusing on these areas can help your body better fight off infections.
Prioritize Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for immune function. During sleep, your body produces cytokines, proteins that target infection and inflammation. Sleep deprivation weakens your immune response, making you more susceptible to illness. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment can all contribute to better sleep.
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Optimize your sleep environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in immune function. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein provides the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants your body needs to fight off infections. These nutrients support the production and activity of immune cells. Avoid excessive processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, which can weaken your immune system.
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables: They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains: Whole grains provide more fiber and nutrients.
- Include lean protein sources in your diet: Lean protein is essential for building and repairing tissues.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can significantly suppress your immune system. Stress hormones like cortisol can interfere with the function of immune cells. Practicing stress-management techniques is essential for maintaining a healthy immune response. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress can significantly improve your overall health and well-being.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps to reduce stress hormones.
- Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can help you to manage stress and improve your mental well-being.
- Spend time in nature: Studies show that spending time outdoors can reduce stress and improve mood.
Maintain Hygiene
Good hygiene practices are critical in preventing the spread of infections. Regular handwashing, especially after using the restroom and before eating, is crucial. Avoiding close contact with sick individuals and practicing respiratory etiquette (covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze) can minimize your exposure to pathogens.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water: This is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infection.
- Avoid touching your face: Germs can easily enter your body through your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces: This includes doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
Stay Hydrated
Staying properly hydrated is important for overall health and immune function. Water helps to flush out toxins from your body and supports the proper functioning of your immune system. Dehydration can impair immune cell activity, making you more vulnerable to illness. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Carry a water bottle: This will remind you to drink water regularly.
- Drink water before, during, and after exercise: Exercise can lead to dehydration.
- Eat fruits and vegetables with high water content: Watermelon, cucumbers, and spinach are good choices.
What are the best foods to boost my immune system naturally?
A healthy diet is crucial for a strong immune system. Focus on incorporating a wide variety of nutrient-rich foods. Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that fight inflammation and protect your cells. Aim for a rainbow of colors on your plate to ensure you're getting a diverse range of nutrients. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are excellent sources of vitamin A, C, and K, which are all vital for immune function. Berries are rich in antioxidants, which help combat oxidative stress and protect your cells from damage. Citrus fruits, like oranges and grapefruits, are brimming with vitamin C, a well-known immune-boosting nutrient. Don't forget about foods rich in zinc, such as nuts, seeds, and legumes, as zinc plays a crucial role in immune cell function. Garlic and ginger have potent anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Including whole grains and lean proteins completes a balanced approach, providing essential amino acids and fiber needed for overall health and immune support. Remember that moderation is key; while these foods offer significant benefits, a balanced approach is more effective than focusing on any single 'superfood'. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to personalize your dietary approach based on your individual needs and health status.
How can I improve my sleep to strengthen my immune system?
Sleep is paramount for a robust immune system. During sleep, your body releases cytokines, which are proteins that target infection and inflammation. Insufficient sleep disrupts this process, leaving you more vulnerable to illness. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, to regulate your body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body it's time to rest. This could include a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music. Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Limit exposure to screens before bed, as the blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production, a hormone that regulates sleep. Manage stress effectively, as chronic stress can significantly impact sleep quality. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine. If you consistently struggle with sleep, consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying sleep disorders or address any potential contributing factors. Prioritizing sleep is not merely about feeling rested; it's a fundamental aspect of maintaining a strong and resilient immune system.
What role does exercise play in boosting immunity naturally?
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of natural immune support. Moderate exercise boosts circulation, helping immune cells move efficiently throughout your body to combat infections. It also helps regulate stress hormones, which have a significant impact on immune function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle mass and improve overall fitness. However, it's crucial to find a balance. Overtraining can actually suppress your immune system, so listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard, especially when you're feeling unwell. Proper hydration is also essential during and after exercise. Ensure you're drinking plenty of water to support your body's functions. Remember that exercise isn't just about physical health; it's a powerful tool for strengthening your immune system naturally. Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program, particularly if you have any underlying health conditions.
Are there any natural supplements that can support my immune system?
While a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are the cornerstones of a strong immune system, some natural supplements may offer additional support. Vitamin D is crucial for immune function, and many people are deficient. Elderberry extract has shown promise in reducing the duration and severity of colds and flu. Echinacea is another herbal supplement often used to support the immune system, though more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness. Zinc, as mentioned earlier, is essential for immune cell function, and supplementation may be beneficial if you're deficient. However, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they can interact with medications or have potential side effects. Don't self-treat; supplements should be considered supportive additions to a holistic approach to immune health, not replacements for a healthy lifestyle. The effectiveness of supplements can vary significantly depending on individual factors, and the best approach is to work with a healthcare professional to determine if supplementation is appropriate and safe for you.
Deja una respuesta