How long do allergies last

Allergies, a common affliction, can bring about a range of unpleasant symptoms that can disrupt daily life. From the itchy eyes and runny nose of hay fever to the potentially life-threatening reactions of anaphylaxis, the impact of allergies can be significant. One of the most pressing questions for allergy sufferers is: how long do allergies last?
How Long Do Allergy Symptoms Typically Last?
The duration of allergy symptoms varies greatly depending on several factors. It's not a one-size-fits-all answer. While some people experience short-lived symptoms, others may suffer for weeks or even months. The key factors determining how long your allergies last include the type of allergen, your individual sensitivity, and the level of exposure to the allergen.
Seasonal Allergies (Hay Fever)
Seasonal allergies, triggered by pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds, typically last for several weeks during the pollen season. For example, tree pollen allergies usually start in early spring, while grass pollen allergies peak in late spring and summer. Weed pollen allergies often appear in late summer and early fall. Symptoms often subside once the pollen count decreases significantly. The duration can vary from person to person and year to year, depending on weather patterns and pollen levels.
Indoor Allergies
Allergies to indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mold can last year-round. Because you're constantly exposed to these allergens in your home, your symptoms can persist unless steps are taken to minimize exposure. The severity of your symptoms might fluctuate, depending on how well you control allergens in your environment. Regular cleaning and the use of air filters can significantly reduce symptom duration.
Food Allergies
The duration of a food allergy reaction is quite variable. A mild reaction might only last for a few hours, while a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms usually start soon after eating the allergenic food, and depending on the severity and management, they might resolve relatively quickly with appropriate treatment or persist if untreated.
Medication Allergy
Reactions to medications can range from mild to severe. Mild reactions might only last a few days after the medication is discontinued. However, severe reactions can be more prolonged and may require hospitalization. It is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance for severe medication reactions.
Environmental Allergies
Allergies to environmental factors such as pollen, mold spores, and insect stings can vary in duration. For example, a reaction to an insect sting might last for a few hours or days, depending on the severity of the reaction. Pollen allergies, as discussed earlier, will last through the pollen season. Similarly, mold allergies might persist as long as there's exposure to the mold spores. The duration often hinges on reducing or eliminating exposure to the triggering allergens.
| Allergy Type | Typical Duration | Factors Affecting Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonal Allergies | Several weeks during pollen season | Pollen levels, weather patterns, individual sensitivity |
| Indoor Allergies | Year-round | Level of allergen exposure, environmental control measures |
| Food Allergies | Variable, from hours to days | Severity of reaction, treatment received |
| Medication Allergies | Variable, from days to weeks, or longer in severe cases | Severity of reaction, type of medication, prompt medical attention |
| Environmental Allergies (e.g., insect stings) | Variable, hours to days | Severity of reaction, treatment received |
How Long Do Allergy Symptoms Typically Last?
The duration of allergy symptoms varies greatly depending on several factors. It's not a one-size-fits-all answer. While some people experience short-lived symptoms, others may suffer for weeks or even months. The key factors determining how long your allergies last include the type of allergen, your individual sensitivity, and the level of exposure to the allergen.
Seasonal Allergies (Hay Fever)
Seasonal allergies, triggered by pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds, typically last for several weeks during the pollen season. For example, tree pollen allergies usually start in early spring, while grass pollen allergies peak in late spring and summer. Weed pollen allergies often appear in late summer and early fall. Symptoms often subside once the pollen count decreases significantly. The duration can vary from person to person and year to year, depending on weather patterns and pollen levels.
Indoor Allergies
Allergies to indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mold can last year-round. Because you're constantly exposed to these allergens in your home, your symptoms can persist unless steps are taken to minimize exposure. The severity of your symptoms might fluctuate, depending on how well you control allergens in your environment. Regular cleaning and the use of air filters can significantly reduce symptom duration.
Food Allergies
The duration of a food allergy reaction is quite variable. A mild reaction might only last for a few hours, while a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms usually start soon after eating the allergenic food, and depending on the severity and management, they might resolve relatively quickly with appropriate treatment or persist if untreated.
Medication Allergy
Reactions to medications can range from mild to severe. Mild reactions might only last a few days after the medication is discontinued. However, severe reactions can be more prolonged and may require hospitalization. It is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance for severe medication reactions.
Environmental Allergies
Allergies to environmental factors such as pollen, mold spores, and insect stings can vary in duration. For example, a reaction to an insect sting might last for a few hours or days, depending on the severity of the reaction. Pollen allergies, as discussed earlier, will last through the pollen season. Similarly, mold allergies might persist as long as there's exposure to the mold spores. The duration often hinges on reducing or eliminating exposure to the triggering allergens.
| Allergy Type | Typical Duration | Factors Affecting Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonal Allergies | Several weeks during pollen season | Pollen levels, weather patterns, individual sensitivity |
| Indoor Allergies | Year-round | Level of allergen exposure, environmental control measures |
| Food Allergies | Variable, from hours to days | Severity of reaction, treatment received |
| Medication Allergies | Variable, from days to weeks, or longer in severe cases | Severity of reaction, type of medication, prompt medical attention |
| Environmental Allergies (e.g., insect stings) | Variable, hours to days | Severity of reaction, treatment received |
How long does it take for allergies to go away?

There's no single answer to how long allergies last. The duration depends on several factors, including the type of allergy, the allergen's presence, and the individual's immune response. Seasonal allergies, like hay fever, typically last only as long as the allergen (pollen, for example) is prevalent in the environment. This usually means several weeks or months during pollen season. Food allergies, on the other hand, are lifelong conditions, meaning symptoms can appear anytime the trigger food is consumed. Pet allergies also tend to be persistent as long as exposure to the pet continues. Some allergies might even resolve themselves over time, especially in children, but this is not guaranteed. The severity of symptoms also varies, with some people experiencing mild symptoms while others have severe reactions requiring medical attention.
Factors Influencing Allergy Duration
Several elements affect how long allergy symptoms persist. Exposure to the allergen is paramount. The more exposure, the longer the symptoms might last. Similarly, the allergen's potency matters; some allergens trigger stronger responses than others. Individual immune system response also plays a significant role; some people have more robust reactions than others. Finally, treatment effectiveness – whether medication is used, and how effective it is – influences symptom duration. Ignoring the allergy can lead to prolonged or worsening symptoms.
- Allergen Exposure: Frequent or prolonged exposure to an allergen extends the duration of symptoms.
- Allergen Potency: Highly potent allergens elicit more intense and longer-lasting reactions.
- Immune System Response: Individual immune systems vary in sensitivity and responsiveness to allergens.
Seasonal Allergies and Their Duration
Seasonal allergies, often triggered by pollen, are characterized by their cyclical nature. Their duration is directly tied to the pollination season in a given geographic area. Tree pollen typically causes allergies in early spring, grass pollen in late spring and summer, and weed pollen in late summer and fall. The length of these seasons varies based on location and climate. In areas with longer pollen seasons, allergy symptoms will persist longer.
- Pollen Type: Different pollens have different seasons, leading to varying durations of allergies.
- Geographic Location: Climate and geographic location influence the length of pollen seasons.
- Climate Change: Shifting climate patterns can extend pollen seasons, leading to longer allergy durations.
Allergy Medication and Symptom Duration
Appropriate allergy medication can significantly impact the length and severity of allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, decongestants, and corticosteroids can effectively alleviate symptoms, shortening their overall duration. However, medication only manages symptoms; it doesn't cure the underlying allergy. Consistent medication use, as prescribed by a doctor, is crucial for effective management and potentially shorter symptom duration. The specific medication and dosage depend on the allergy type and severity.
- Antihistamines: Reduce allergic reactions by blocking histamine.
- Decongestants: Relieve nasal congestion associated with allergies.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation in the airways and nasal passages.
Perennial Allergies: A Lifelong Concern?
Perennial allergies, unlike seasonal ones, persist throughout the year. These allergies are typically triggered by indoor allergens such as pet dander, dust mites, and mold. Because these allergens are often present continuously in the environment, symptoms can last indefinitely unless effective allergen control measures are implemented in the home. For instance, regular cleaning and the use of air purifiers can help mitigate exposure and reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and reducing exposure.
- Indoor Allergens: Pet dander, dust mites, and mold are common triggers of perennial allergies.
- Allergen Control: Reducing exposure through cleaning and air purifiers helps manage symptoms.
- Symptom Management: Medications and other treatments are crucial for managing the ongoing symptoms.
Children's Allergies: Potential for Resolution?
While some allergies persist throughout life, some children's allergies, particularly to milk, eggs, or soy, can resolve themselves over time. This often occurs in early childhood, but there's no guarantee. Factors influencing resolution are poorly understood, but a strong genetic predisposition might play a role. Regular checkups with an allergist are essential for monitoring the child's allergies and determining the need for continued treatment or re-evaluation. Growth and development could potentially alter the immune system's response to allergens.
- Age-Related Changes: The immune system's response can change with age and development.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition influences the likelihood of allergy resolution.
- Allergy Testing: Regular testing is crucial for monitoring allergy changes in children.
What gets rid of allergies fast?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Preventing-and-Treating-Seasonal-Allergies_Danie-Drankwalter_Final-884166d09ac94425ad7e7a3b68a14249.jpg)
What Gets Rid of Allergies Fast?
There's no single magic bullet to eliminate allergies instantly. Allergic reactions are complex, and what works quickly for one person might not work for another, or might only offer temporary relief. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing future reactions. The speed of relief depends on the severity of the allergy, the allergen, and the chosen treatment method. Immediate relief often requires medications, while longer-term solutions involve identifying and avoiding triggers or undergoing immunotherapy.
Over-the-Counter Medications for Fast Allergy Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide relatively quick relief from allergy symptoms. These are often the first line of defense for many people experiencing mild to moderate allergic reactions. Antihistamines, like cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin), block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction. Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) or phenylephrine, can help relieve stuffiness by shrinking swollen blood vessels in the nasal passages. However, it's crucial to follow dosage instructions and be aware of potential side effects.
- Antihistamines: These medications target histamine, reducing itching, sneezing, and runny nose. They often provide relief within 30-60 minutes.
- Decongestants: These help clear nasal passages, but overuse can lead to rebound congestion.
- Combination medications: Many OTC products combine antihistamines and decongestants for broader symptom relief.
Prescription Medications for Faster and Stronger Allergy Relief
For more severe allergies or when OTC medications are insufficient, a doctor might prescribe stronger medications. Prescription antihistamines are available for more intense symptoms and can provide longer-lasting relief. Nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase) or mometasone (Nasonex), are inhaled steroids that reduce inflammation in the nasal passages. Leukotriene modifiers, like montelukast (Singulair), block the action of leukotrienes, inflammatory chemicals involved in allergic reactions. These often require a prescription and can take a few days to show full effect, but they can be highly effective in reducing allergy symptoms.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and are very effective for nasal congestion and sneezing.
- Oral corticosteroids: (e.g., prednisone) are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs but are usually only prescribed for short-term use due to potential side effects.
- Leukotriene modifiers: These prevent the production of leukotrienes, reducing inflammation and improving lung function in those with asthma triggered by allergies.
Home Remedies for Quick Allergy Symptom Relief
While not as fast-acting as medication, some home remedies can offer temporary relief from mild allergy symptoms. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can help thin mucus, making it easier to clear your nasal passages. Using a saline nasal spray or rinse can also help flush out allergens and irritants. Applying a cool compress to itchy eyes or skin can provide soothing relief. Avoiding known allergens is crucial, but it is not always easily done.
- Saline rinse: Helps cleanse nasal passages of allergens and irritants.
- Cool compress: Soothes itchy eyes and skin.
- Hydration: Thinning mucus to ease congestion.
Emergency Treatments for Severe Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, and a rapid drop in blood pressure. Epinephrine (adrenaline), administered via an auto-injector like an EpiPen, is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis. It's crucial to seek immediate medical help even after administering epinephrine, as additional treatment may be necessary.
- Epinephrine auto-injectors (EpiPen): These deliver a dose of epinephrine to counteract the effects of anaphylaxis.
- Emergency medical services: Call emergency services immediately if experiencing symptoms of anaphylaxis.
- Hospitalization: Further treatment and monitoring are typically needed after anaphylaxis.
Allergy Testing and Immunotherapy for Long-Term Solutions
While not providing immediate relief, allergy testing can identify specific triggers and pave the way for long-term management. Allergy skin tests or blood tests pinpoint allergens causing reactions. Immunotherapy (allergy shots), involves gradually exposing you to increasing doses of allergens over time to desensitize your immune system. This is a long-term process but can significantly reduce allergy symptoms over time. This is a preventive approach that does not provide fast relief but helps build tolerance to allergens over several months or years.
- Skin prick test: A quick and relatively inexpensive way to identify allergens.
- Blood test (RAST): Measures the level of specific IgE antibodies in your blood.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): A long-term treatment to desensitize the immune system to allergens.
Am I sick or is it allergies?
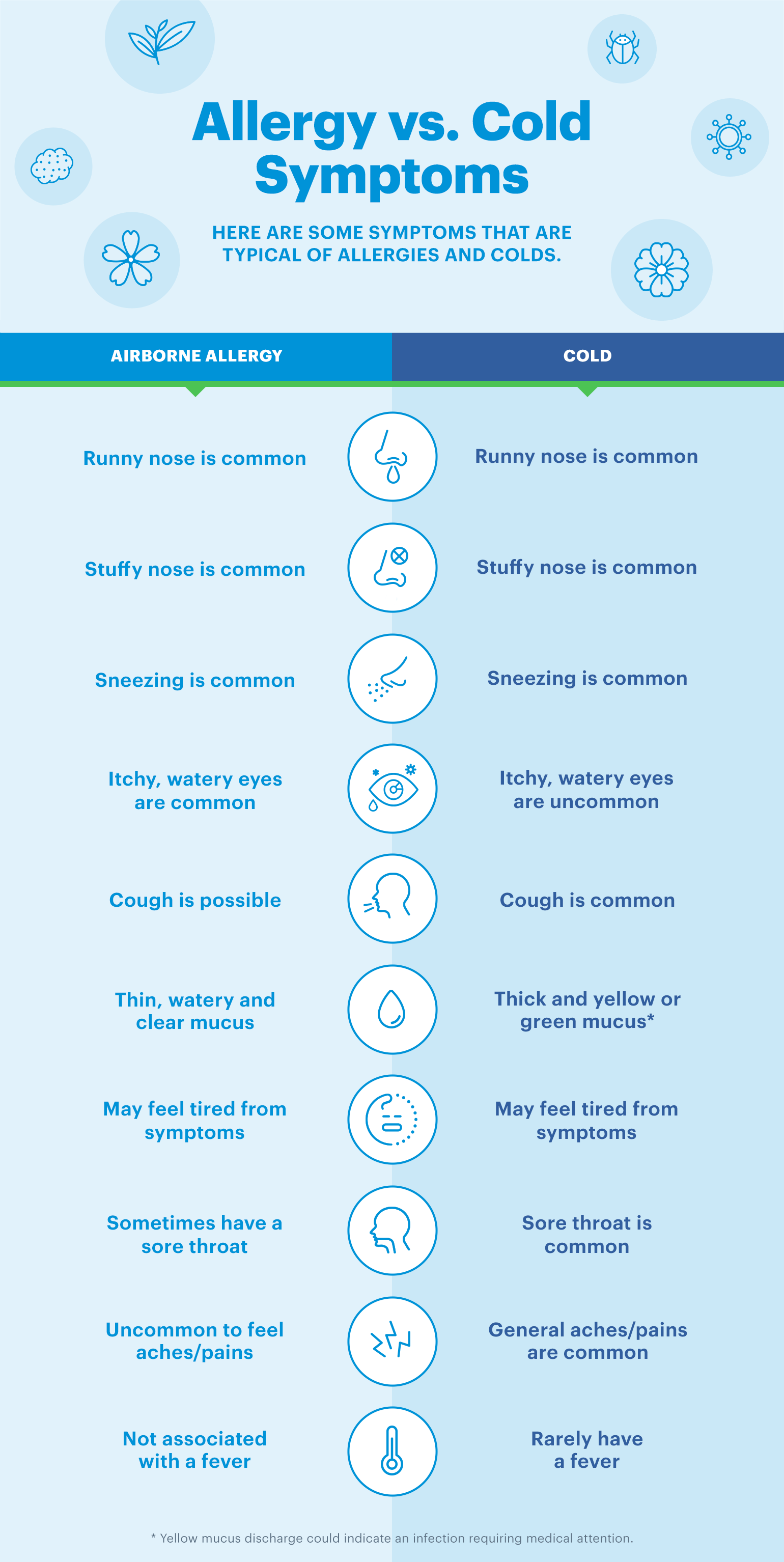
Differentiating between a sickness and allergies can be challenging because they share some similar symptoms. However, key distinctions exist. Several factors need consideration, such as the nature and duration of your symptoms, your medical history, and exposure to potential allergens. A doctor's examination is often necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Symptom Duration and Onset
The duration and onset of your symptoms are crucial. Allergies typically present with symptoms that are predictable and associated with exposure to a specific allergen. For example, seasonal allergies manifest during specific pollen seasons. A sudden onset of severe symptoms, such as high fever, body aches, or significant fatigue, is more indicative of an illness. Conversely, allergy symptoms tend to develop gradually and persist as long as you're exposed to the allergen.
- Allergies: Gradual onset, often predictable timing (seasonal, specific triggers).
- Illness: Sudden onset, often unpredictable.
- Consider: How long have you had symptoms? Did they start suddenly or gradually?
Type of Symptoms
The typeof symptoms can also be telling. Allergies commonly cause itchy eyes, runny nose, sneezing, and congestion. These symptoms are often accompanied by itching and are localized. Illnesses, however, can present with a wider range of symptoms, including fever, chills, body aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, and fatigue. While some illnesses might involve a runny nose, it's often accompanied by other more systemic symptoms.
- Allergies: Primarily localized symptoms (eyes, nose), itching, sneezing, runny nose.
- Illness: Can involve a broader range of symptoms, including fever, body aches, fatigue, digestive issues.
- Consider: What specific symptoms are you experiencing?
Exposure to Potential Allergens
Have you been recently exposed to potential allergens such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or certain foods? If your symptoms coincide with exposure to a known allergen, allergies are more likely. Keeping a symptom diary, noting your activities and potential allergen exposures, can be invaluable in determining the cause. This is especially important for food allergies, where the link between ingestion and symptoms is more direct.
- Allergies: Symptoms linked to specific allergen exposure.
- Illness: Symptoms not necessarily linked to a specific allergen exposure.
- Consider: Have you been around any known allergens? Keep a diary of your activities and symptoms.
Severity of Symptoms
The severity of your symptoms can also provide clues. Mild symptoms, such as mild nasal congestion and occasional sneezing, might suggest allergies, especially if they are consistent with seasonal patterns. However, more severe symptoms, such as high fever, difficulty breathing, or significant pain, usually point towards an illness requiring medical attention. Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) are a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
- Allergies: Typically mild to moderate symptoms.
- Illness: Can range from mild to severe, potentially life-threatening.
- Consider: How intense are your symptoms? Are they interfering with your daily activities?
Medical History and Other Factors
Your medical history and other factors, such as family history of allergies or illnesses, can provide additional context. If you have a known allergy, it's more likely that similar symptoms are allergy-related. Similarly, if you've recently been in contact with someone who is ill, or if you have other risk factors such as weakened immunity, illness is more probable. Other factors such as travel history, recent exposure to animals, or changes in environment should also be considered.
- Allergies: Pre-existing allergies increase the likelihood of an allergic reaction.
- Illness: Recent exposure to illness, weakened immune system, or other risk factors may indicate illness.
- Consider: Your family history, recent exposures, and overall health status.
Which month is worst for allergies?

There's no single "worst" month for allergies universally, as it heavily depends on geographical location and the specific allergens affecting a person. However, for many people in North America, spring months, particularly May, are often considered the worst due to the high pollen counts from trees, grasses, and weeds.
Different Allergy Seasons Across Regions
Allergy seasons vary significantly across the globe. In regions with temperate climates, such as much of the United States and Europe, the spring season typically brings the highest pollen counts. However, in other parts of the world with different climates and vegetation, the peak allergy season might fall in different months. For example, some areas may experience higher allergy levels during the fall due to weed pollen. The dominant plants in an area will dictate the timing of the peak allergy season.
- Spring (March-May): Tree pollen is a significant contributor to allergies in this period.
- Summer (June-August): Grass pollen becomes a primary irritant during these summer months.
- Fall (September-November): Weed pollen, like ragweed, can trigger severe allergies for many.
The Role of Tree Pollen in Spring Allergies
Many spring allergies are triggered by tree pollen, which is released in large quantities as trees begin to blossom. Different types of trees release pollen at varying times throughout the spring, extending the allergy season. The specific types of trees prevalent in an area greatly influence the severity and duration of spring allergies. Monitoring local pollen forecasts is crucial for people with tree pollen allergies.
- Oak trees
- Birch trees
- Maple trees
Grass Pollen's Impact on Summer Allergies
Grass pollen is a major allergen during the summer months. Different grass species release their pollen at various times, leading to a prolonged allergy season. The concentration of grass pollen in the air can be particularly high on windy days. Mowing lawns and other activities that disturb grass can also increase pollen levels, exacerbating symptoms for those who are sensitive.
- Timothy grass
- Ryegrass
- Bermuda grass
Weed Pollen and Fall Allergies
Ragweed is the most common culprit for fall allergies. This weed releases massive amounts of pollen, which can travel for miles on the wind. Fall allergies caused by weed pollen can overlap with other fall allergens like mold, making symptom management more complex. Knowing the predominant weeds in your area can help you anticipate the start and duration of your fall allergy season.
- Ragweed
- Pigweed
- Lambsquarters
Mold Spores and Their Influence
While pollen is a major contributor to seasonal allergies, mold spores are another significant factor. Mold spores can be prevalent throughout the year, but often peak during certain seasons depending on rainfall and humidity. Fall, especially after periods of rain and dampness, can see a surge in mold spore counts. They can exacerbate allergies and also trigger allergic reactions independently of pollen. It's essential to consider mold spores when assessing the worst month for allergies in any given location.
- Alternaria
- Cladosporium
- Aspergillus
How long do seasonal allergies last?
Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever, are typically triggered by pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds. The duration of seasonal allergy symptoms depends heavily on the specific allergens prevalent in your region and the length of their pollen seasons. Most seasonal allergy sufferers experience symptoms for a few weeks to several months, depending on the allergen. For example, tree pollen allergies might peak in the spring, lasting several weeks, while grass pollen allergies can extend throughout the summer months. Weed pollen allergies often persist into the fall. The intensity of symptoms can also vary from person to person, with some experiencing mild symptoms and others experiencing severe ones. Factors influencing the duration include the level of pollen in the air, individual sensitivity to specific allergens, and the effectiveness of treatment methods employed. It's important to note that the symptoms may not be continuous; there might be days with less severe symptoms interspersed with periods of more intense symptoms, depending on pollen counts. Consult with an allergist or healthcare professional for personalized advice regarding the duration and management of your seasonal allergies. They can conduct tests to pinpoint the specific allergens triggering your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options to minimize their impact and duration.
How long do food allergies last?
Unlike seasonal allergies that come and go with the pollen seasons, food allergies are generally lifelong conditions. This means that once a person develops a food allergy, they are likely to remain allergic to that specific food for the rest of their lives. The severity of the allergic reaction can vary, from mild symptoms like hives or itching to severe and life-threatening reactions like anaphylaxis. Even a small amount of the offending food can trigger a reaction, and the intensity of the reaction can depend on several factors such as the amount of food consumed, the individual's sensitivity, and even the method of preparation of the food. While the underlying allergy itself is permanent, the symptoms' severity can be managed through careful avoidance of the allergenic food and the use of emergency medication like epinephrine in case of a severe reaction. It's crucial to work closely with an allergist or immunologist to develop a comprehensive management plan that includes identifying triggers, avoiding allergens, and learning how to manage reactions. It's also important to remember that food allergies are not always easy to diagnose, so a thorough evaluation by a medical professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
How long do indoor allergies last?
Indoor allergies, triggered by substances like dust mites, pet dander, mold, and cockroach allergens, can last year-round, as these allergens are typically present consistently in the indoor environment. Unlike seasonal allergies, the symptoms are not tied to specific pollen seasons, and therefore, symptoms can persist for extended periods. However, the severity of symptoms can fluctuate based on factors such as exposure levels, the effectiveness of preventative measures implemented, and environmental conditions like humidity. Higher humidity levels, for example, can exacerbate mold growth leading to more intense symptoms. Proper cleaning, regular vacuuming, air filtration systems, and maintaining low humidity levels can help to minimize exposure and mitigate symptom severity. Effective management involves identifying and controlling exposure to indoor allergens. The duration of symptoms can be significantly reduced by implementing effective control measures. Consult with an allergist or healthcare professional for personalized advice on allergy testing, specific control measures, and possible medical treatments to minimize the impact of indoor allergies and their duration.
How long do drug allergies last?
The duration of a drug allergy varies greatly depending on several factors including the specific medication, the type of allergic reaction experienced, and the individual's response. Some drug allergies may result in a short-lived reaction that resolves quickly once the drug is discontinued, perhaps only lasting a few days or weeks. However, other drug allergies can be more long-lasting or even lifelong. This is because the body's immune system may develop a persistent sensitivity to the medication, making it impossible to safely take it again in the future. The most severe type of drug allergy is anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate medical attention. In cases of milder reactions, the duration of symptoms might be shorter, and the patient may not experience lasting effects. Accurate diagnosis and meticulous management are crucial. It's important to always inform healthcare providers about any known drug allergies to prevent further exposure and avoid serious reactions. Always seek medical advice regarding any drug allergy or concerning reaction. A medical professional can provide the best guidance on managing and monitoring drug allergies and their duration.
Deja una respuesta