How to clear allergies from lungs

If you're struggling with allergies that seem to be affecting your lungs, causing coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, you're not alone. Millions of people suffer from allergies that can irritate and inflame the delicate tissues of the lungs. The good news is that there are effective ways to clear allergies from your lungs and get back to breathing easy. This article will explore a range of strategies to help you manage your allergies and improve your lung health.
How to Alleviate Allergy Symptoms Affecting Your Lungs
It's important to understand that you cannot completely "clear" allergies from your lungs. Allergies are an immune system response, and you can't eliminate that response entirely. However, you can significantly reduce allergy symptoms and their impact on your lungs. The goal is to manage your allergies effectively to minimize inflammation and discomfort. This involves a multifaceted approach combining lifestyle changes, medication, and potentially, allergy immunotherapy.
Identify and Avoid Allergens
The first step in managing lung allergy symptoms is identifying your specific allergens. Common culprits include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, can help pinpoint the exact allergens triggering your reactions. Once identified, actively avoid these allergens whenever possible. This might involve using air purifiers with HEPA filters, regularly cleaning your home, choosing hypoallergenic bedding, and avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons. Regularly cleaning your home, especially bedding and carpets, significantly reduces the concentration of dust mites and other allergens.
Medication Management
Several medications can effectively manage lung allergy symptoms. Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, can help reduce sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants, like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, can alleviate nasal congestion. For more severe symptoms, your doctor might prescribe inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in your airways. These medications are very effective in controlling asthma, a common consequence of lung allergies. In some cases, leukotriene modifiers or mast cell stabilizers may be recommended. Remember to always follow your doctor's instructions and consult them before starting any new medication.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Lung Health
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve lung health and minimize allergy symptoms. Regular exercise strengthens your lungs and overall immune system. However, it's crucial to exercise during times of lower pollen counts and to use appropriate allergy control measures before and after each workout. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can also boost your immunity. Quitting smoking is crucial as smoking significantly worsens lung health and increases the severity of allergies.
Allergy Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For individuals with severe or persistent allergies, allergy immunotherapy might be an option. This involves receiving regular injections of small amounts of your specific allergens over a period of time. The goal is to gradually desensitize your immune system to these allergens, reducing your allergic reaction. While it takes time, immunotherapy can offer long-term relief from allergy symptoms, often leading to a significant reduction in medication needs. Consult your allergist to determine if this is a suitable option for you.
Proper Hydration and Humidification
Staying well-hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier to clear from your lungs. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is vital. Using a humidifier, especially during dry seasons or in heated environments, can add moisture to the air, preventing your nasal passages and lungs from drying out and becoming irritated. This is particularly helpful in reducing the severity of symptoms. Maintaining the right humidity level can reduce irritation and promote better lung function.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Allergen Avoidance | Identifying and minimizing exposure to specific allergens. | Highly effective for preventing symptoms. |
| Medication | Antihistamines, decongestants, corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers. | Effective in managing symptoms, severity varies depending on medication and individual. |
| Immunotherapy | Allergy shots to desensitize the immune system. | Long-term relief, requires commitment, can significantly reduce medication. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Exercise, diet, smoking cessation, hydration. | Supports overall health and improves immune function, indirectly managing symptoms. |
| Humidification | Adding moisture to the air to soothe irritated airways. | Helpful in reducing dryness and irritation in the respiratory tract. |
How to Alleviate Allergy Symptoms Affecting Your Lungs
It's important to understand that you cannot completely "clear" allergies from your lungs. Allergies are an immune system response, and you can't eliminate that response entirely. However, you can significantly reduce allergy symptoms and their impact on your lungs. The goal is to manage your allergies effectively to minimize inflammation and discomfort. This involves a multifaceted approach combining lifestyle changes, medication, and potentially, allergy immunotherapy.
Identify and Avoid Allergens
The first step in managing lung allergy symptoms is identifying your specific allergens. Common culprits include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, can help pinpoint the exact allergens triggering your reactions. Once identified, actively avoid these allergens whenever possible. This might involve using air purifiers with HEPA filters, regularly cleaning your home, choosing hypoallergenic bedding, and avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons. Regularly cleaning your home, especially bedding and carpets, significantly reduces the concentration of dust mites and other allergens.
Medication Management
Several medications can effectively manage lung allergy symptoms. Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, can help reduce sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants, like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, can alleviate nasal congestion. For more severe symptoms, your doctor might prescribe inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in your airways. These medications are very effective in controlling asthma, a common consequence of lung allergies. In some cases, leukotriene modifiers or mast cell stabilizers may be recommended. Remember to always follow your doctor's instructions and consult them before starting any new medication.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Lung Health
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve lung health and minimize allergy symptoms. Regular exercise strengthens your lungs and overall immune system. However, it's crucial to exercise during times of lower pollen counts and to use appropriate allergy control measures before and after each workout. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can also boost your immunity. Quitting smoking is crucial as smoking significantly worsens lung health and increases the severity of allergies.
Allergy Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For individuals with severe or persistent allergies, allergy immunotherapy might be an option. This involves receiving regular injections of small amounts of your specific allergens over a period of time. The goal is to gradually desensitize your immune system to these allergens, reducing your allergic reaction. While it takes time, immunotherapy can offer long-term relief from allergy symptoms, often leading to a significant reduction in medication needs. Consult your allergist to determine if this is a suitable option for you.
Proper Hydration and Humidification
Staying well-hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier to clear from your lungs. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is vital. Using a humidifier, especially during dry seasons or in heated environments, can add moisture to the air, preventing your nasal passages and lungs from drying out and becoming irritated. This is particularly helpful in reducing the severity of symptoms. Maintaining the right humidity level can reduce irritation and promote better lung function.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Allergen Avoidance | Identifying and minimizing exposure to specific allergens. | Highly effective for preventing symptoms. |
| Medication | Antihistamines, decongestants, corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers. | Effective in managing symptoms, severity varies depending on medication and individual. |
| Immunotherapy | Allergy shots to desensitize the immune system. | Long-term relief, requires commitment, can significantly reduce medication. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Exercise, diet, smoking cessation, hydration. | Supports overall health and improves immune function, indirectly managing symptoms. |
| Humidification | Adding moisture to the air to soothe irritated airways. | Helpful in reducing dryness and irritation in the respiratory tract. |
How do you get rid of allergens in your lungs?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/respiratory-allergies-symptoms-causes-and-treatment-5206183-5205177-final-7af9eb5916eb4a8dacf8b9bd516cad85.jpg)
Unfortunately, you can't directly "get rid" of allergens already lodged in your lungs. Once an allergen like pollen, dust mite feces, or pet dander is inhaled and reaches the lungs, the body's immune system is primarily responsible for dealing with it. The goal isn't to remove the allergen itself, but to manage the body's reaction to it and minimize its impact. This involves reducing inflammation and mitigating symptoms.
Managing Allergic Reactions
The body's response to allergens in the lungs often manifests as inflammation. This inflammation is the source of many allergy symptoms. Managing this inflammatory response is key. This involves treating the symptoms and preventing future exposure.
- Medication: Antihistamines, corticosteroids (inhaled or oral), and leukotriene modifiers can reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Lifestyle changes: Avoiding triggers is crucial. This could involve using air purifiers, regularly cleaning your home, and managing pet exposure.
- Immunotherapy: Allergy shots (subcutaneous immunotherapy) or sublingual immunotherapy (tablets) can help desensitize the body to specific allergens over time, gradually reducing the allergic reaction.
Avoiding Allergen Exposure
Preventing further allergen exposure is critical to reducing the burden on your lungs. Minimizing contact with allergens is the most effective way to lessen the severity and frequency of allergic reactions. This requires a proactive approach to identifying and avoiding triggers.
- Identify triggers: Through allergy testing, determine your specific allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, etc.).
- Home environment control: Regularly clean your home, use dust mite-proof covers for bedding, and invest in high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters for your air conditioning and heating systems.
- Outdoor precautions: Check pollen counts before going outside, and stay indoors on high-pollen days. Shower and change clothes after spending time outdoors.
Using Medications to Control Symptoms
A variety of medications can help manage the symptoms of lung allergies. Choosing the right medication and using it correctly can significantly improve your quality of life. Your doctor can guide you on the best approach based on your specific situation.
- Over-the-counter medications: Antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or loratadine (Claritin) can help relieve sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
- Prescription medications: For more severe allergies, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications like inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in the lungs.
- Combination therapies: Some medications combine antihistamines and decongestants for broader symptom relief.
Improving Lung Function
While you can't remove allergens already in the lungs, you can support overall lung health to improve your ability to manage and cope with allergic reactions. Improving lung function through healthy habits can help minimize the effects of allergies.
- Breathing exercises: Controlled breathing techniques can help improve lung capacity and alleviate some symptoms like shortness of breath.
- Regular exercise: Cardiovascular exercise, when tolerated, can strengthen the lungs and improve overall health.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking significantly damages lung health and exacerbates allergic reactions. Quitting is essential for protecting lung function.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice
Consulting with a doctor or allergist is paramount for managing lung allergies effectively. They can diagnose the specific allergens you're sensitive to, recommend appropriate treatments, and monitor your condition. They are best equipped to handle individual circumstances.
- Allergy testing: Skin prick tests or blood tests can identify specific allergens causing your symptoms.
- Personalized treatment plan: Your doctor can create a tailored plan based on your individual needs and allergies.
- Regular checkups: Monitoring your condition and making adjustments to your treatment plan as needed is essential.
What are the symptoms of allergies in the lungs?
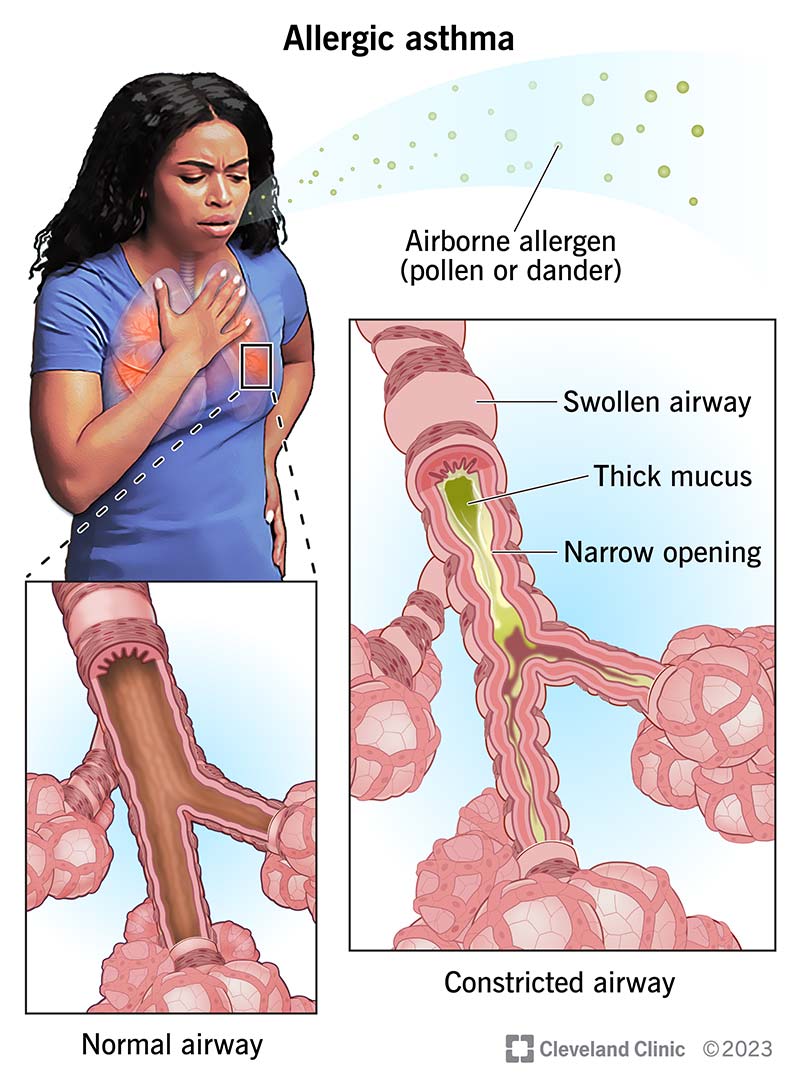
Allergic reactions in the lungs, often stemming from inhaled allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores, manifest in various ways. The severity can range from mild discomfort to a life-threatening condition. Symptoms can overlap with other respiratory illnesses, making accurate diagnosis crucial.
Wheezing and Coughing
Wheezing, a whistling sound during breathing, is a common sign of airway narrowing due to inflammation and mucus build-up. This is often accompanied by a persistent cough, which may be dry or produce mucus. The cough can be particularly bothersome at night or in the early morning. The severity of wheezing and coughing can vary significantly depending on the allergen exposure and individual sensitivity.
- Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound heard during exhalation, indicating constricted airways.
- Coughing can be dry or produce clear or white mucus.
- Night-time or early morning coughing is a common symptom.
Shortness of Breath and Chest Tightness
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) and a feeling of chest tightness are indicators that the airways are significantly constricted, reducing airflow into the lungs. This can make even simple activities like breathing or talking difficult. The sensation of chest tightness can feel like a pressure or squeezing in the chest. Severe cases can lead to difficulty breathing at rest.
- Difficulty breathing, even at rest, is a sign of airway constriction.
- Chest tightness may feel like pressure or a squeezing sensation.
- Shortness of breath can range from mild discomfort to a severe, life-threatening condition.
Increased Mucus Production
Allergic reactions in the lungs often lead to an increase in mucus production. This mucus can be clear, white, or sometimes yellow-tinged. Excessive mucus can further clog the airways, worsening the symptoms of wheezing and coughing and contributing to shortness of breath. The mucus can also be thicker and more difficult to clear than normal.
- Mucus may be clear, white, or slightly yellow.
- Increased mucus production can further obstruct airways.
- The mucus may be thicker and harder to expel than usual.
Frequent Respiratory Infections
Individuals with lung allergies are often more susceptible to frequent respiratory infections like bronchitis or pneumonia. Inflamed and irritated airways are more vulnerable to viral and bacterial infections. The constant inflammation from allergies weakens the lungs’ ability to fight off infections.
- Allergies can weaken the lungs’ immune defenses.
- Increased susceptibility to colds, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
- Infections may be more severe and prolonged.
Asthma-like Symptoms
In many cases, allergic reactions in the lungs mimic the symptoms of asthma. This includes wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. While not all individuals with lung allergies develop asthma, the overlapping symptoms can make it challenging to distinguish between the two conditions. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is essential.
- Wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath are common in both asthma and lung allergies.
- Chest tightness is another symptom that overlaps with asthma.
- A doctor's diagnosis is essential to distinguish between lung allergies and asthma.
How to cure lung allergy?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/respiratory-allergies-symptoms-causes-and-treatment-5206183-5205177-final-7af9eb5916eb4a8dacf8b9bd516cad85.jpg)
How to Cure Lung Allergy?
There is no known cure for lung allergies (allergic asthma or other allergic lung conditions), but symptoms can be effectively managed and controlled to allow for a near-normal life. The goal of treatment is to reduce the frequency and severity of allergic reactions. This involves identifying and avoiding allergens, using medications to control symptoms, and in some cases, undergoing immunotherapy. It's crucial to remember that what works for one person may not work for another, and finding the right approach often requires collaboration with an allergist or pulmonologist.
Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
Identifying the specific allergens triggering your lung allergy is the first step toward effective management. Common culprits include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and cockroaches. Allergy testing (skin prick test or blood test) can help pinpoint these triggers. Once identified, avoiding these allergens as much as possible is key. This might involve:
- Regularly cleaning your home, using allergen-proof covers for mattresses and pillows, and employing a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter vacuum cleaner.
- Avoiding exposure to pets, or at least keeping them out of bedrooms and regularly grooming them.
- Minimizing exposure to pollen during peak seasons by staying indoors when pollen counts are high, using air conditioning, and changing clothes after being outside.
Medication for Symptom Control
Several medications can effectively manage lung allergy symptoms. These are often used in combination to address different aspects of the allergic response. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Inhalers (Bronchodilators): These quickly relieve symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath by relaxing the muscles around the airways. Examples include albuterol and levalbuterol.
- Inhalers (Corticosteroids): These reduce inflammation in the airways, preventing future attacks and reducing the severity of symptoms. Examples include fluticasone and budesonide.
- Oral medications: For severe cases or when inhalers aren't sufficient, oral corticosteroids (like prednisone) may be prescribed for a short period to reduce inflammation. Other oral medications such as leukotriene modifiers (e.g., montelukast, zafirlukast) can also be effective.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For some individuals with persistent allergic reactions, immunotherapy may be considered. This involves gradually introducing increasing amounts of the allergen into the body to desensitize the immune system. Immunotherapy aims to reduce the severity of allergic responses over time, potentially improving long-term symptom control.
- Immunotherapy typically involves a series of injections administered by a healthcare professional over several months or years.
- It's not suitable for everyone and carries potential risks, making it crucial to discuss its suitability with an allergist.
- While not a cure, it can significantly reduce the need for other medications.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a supportive role in managing lung allergies. Certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly minimize symptoms and improve overall well-being:
- Regular exercise strengthens the lungs and improves respiratory function.
- Quitting smoking is crucial as smoking significantly worsens lung conditions.
- Managing stress, as stress can trigger or exacerbate allergy symptoms. Techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be helpful.
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Regular monitoring and check-ups with your doctor or allergist are essential for managing lung allergies effectively. This allows for early detection of any worsening symptoms, adjustments to medication, and overall assessment of the effectiveness of your treatment plan.
- Keep a detailed record of your symptoms, including frequency, severity, and triggers.
- Attend regular check-ups to discuss your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Don't hesitate to contact your doctor immediately if you experience a significant worsening of your symptoms.
How long do lung allergies last?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/respiratory-allergies-symptoms-causes-and-treatment-5206183-5205177-final-7af9eb5916eb4a8dacf8b9bd516cad85.jpg)
How Long Do Lung Allergies Last?
The duration of lung allergy symptoms, often associated with conditions like asthma and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), varies greatly depending on several factors. There isn't a single answer to how long they last because it's highly individual and influenced by the specific allergen, the severity of the allergic response, and the effectiveness of treatment. Some people experience symptoms only during specific seasons when certain pollens are prevalent, while others may have persistent symptoms year-round. The duration can range from a few hours to several weeks or even months, with some experiencing chronic symptoms requiring ongoing management. Triggers like exposure to dust mites, pet dander, or mold can exacerbate symptoms, potentially prolonging their duration. Similarly, the level of exposure to allergens impacts how long the symptoms will last. A brief exposure may cause short-lived symptoms, while continuous exposure can cause longer-lasting effects. Effective treatment, including medications like inhalers and allergy shots, plays a crucial role in controlling and shortening the duration of lung allergy symptoms.
Factors Influencing the Duration of Lung Allergy Symptoms
Many factors contribute to how long your lung allergy symptoms last. These include the type of allergen you're exposed to, the level of exposure, your overall health, and the effectiveness of your treatment plan. Seasonal allergies, for example, will typically only last for the pollen season, whereas allergies to pet dander might persist year-round depending on the level of exposure. Similarly, if you have a history of severe allergic reactions, your symptoms are likely to last longer than someone with a milder response. The potency and appropriate use of medications also influence the symptom duration.
- Type of allergen: Pollen allergies are typically seasonal, while dust mite allergies are year-round.
- Exposure level: High exposure leads to longer-lasting symptoms.
- Individual health: Underlying conditions can influence symptom duration.
Seasonal vs. Year-Round Lung Allergies
Seasonal lung allergies, often triggered by pollen, typically last only during the specific season when the triggering pollen is in the air. This might be springtime for tree pollen, summer for grass pollen, or fall for weed pollen. Year-round lung allergies, however, are caused by allergens that are present throughout the year, such as dust mites, pet dander, or mold. These allergies can cause persistent symptoms unless effectively managed with medication and allergen avoidance strategies. The duration for year-round allergies is directly tied to the level of exposure to the specific allergens.
- Seasonal allergies: Symptoms are typically limited to specific seasons.
- Year-round allergies: Symptoms persist continuously throughout the year.
- Management: Effective management can significantly reduce symptom duration in both cases.
The Role of Treatment in Managing Lung Allergy Duration
Proper treatment is essential in managing the duration of lung allergy symptoms. Medications like inhalers (bronchodilators and corticosteroids) can help to quickly relieve symptoms and prevent future attacks. Allergy shots (immunotherapy) are a long-term treatment that can reduce the body's sensitivity to specific allergens, leading to a decrease in the frequency and severity of symptoms over time. Other management strategies include avoiding known allergens and maintaining good indoor air quality. The effectiveness of treatment directly correlates with a reduced symptom duration.
- Inhalers: Provide quick relief and prevent future attacks.
- Allergy shots: Long-term treatment reducing sensitivity to allergens.
- Allergen avoidance: Minimizes exposure to trigger substances.
Severe Lung Allergy Reactions and Their Duration
In cases of severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, the symptoms can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. While the acute phase of such a reaction may subside within hours with appropriate treatment, the impact on lung function can persist for a longer period. Following a severe reaction, individuals might experience lingering inflammation or bronchospasm, requiring ongoing monitoring and treatment. Delayed reactions might also occur, with symptoms appearing hours or even days after the initial exposure. These delayed reactions are important to manage.
- Anaphylaxis: Requires immediate medical attention and can have lasting effects.
- Lingering inflammation: Can persist even after the acute phase.
- Delayed reactions: Symptoms may appear hours or days after exposure.
Impact of Co-existing Conditions
The presence of other respiratory conditions, such as asthma, can significantly influence the duration and severity of lung allergy symptoms. Individuals with asthma often experience more persistent and severe symptoms compared to those without. Similarly, other health conditions might impair the immune system or affect the body's response to allergens, potentially prolonging the duration of allergic reactions. The interplay between allergies and other medical conditions is critical in determining the overall management strategy and predicting the symptom duration.
- Asthma: Often exacerbates lung allergy symptoms.
- Other health conditions: Can impact immune response and symptom duration.
- Integrated treatment: Managing co-existing conditions is essential for optimal allergy management.
How long does it take to clear allergies from my lungs?
There's no single answer to how long it takes to clear allergy symptoms from your lungs. The duration depends on several factors, including the severity of your allergies, the allergen involved, and your body's response to treatment. A mild allergic reaction might subside within a few days with simple over-the-counter medications like antihistamines or nasal sprays. However, more severe reactions, such as those involving significant lung inflammation (like asthma triggered by allergies), could take weeks or even months to fully resolve. Consistent management of your allergies is key. This may involve avoiding triggers, using prescribed medications (such as inhaled corticosteroids or bronchodilators for asthma), and potentially undergoing allergy testing and immunotherapy to desensitize your immune system. If your symptoms are persistent or worsen, it is crucial to consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can assess the extent of the lung involvement and recommend the most appropriate course of action. Self-treating severe allergies can be dangerous, so seeking professional medical advice is essential for optimal recovery and management.
Can I clear lung allergies at home?
While you can manage some mild allergy symptoms at home, it's crucial to understand the limitations. Home remedies can offer temporary relief for some, but they're not a cure and might not be effective for everyone. Measures like increasing humidity in your home (using a humidifier) to loosen mucus and using a saline nasal spray to rinse nasal passages can help alleviate some discomfort. Over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines and decongestants can also provide temporary symptom relief, but they address the symptoms, not the underlying cause. If your symptoms are severe or persistent (e.g., difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest tightness), home remedies are insufficient. Seeking professional medical advice is vital. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the specific allergens causing your reaction, prescribe more effective medications (potentially including inhaled corticosteroids for lung inflammation), and guide you on a proper management plan. Improperly managing lung allergies at home could lead to complications and worsening symptoms.
What are the best ways to clear allergy-induced lung inflammation?
Reducing lung inflammation caused by allergies requires a multi-pronged approach, and the best methods depend on the severity of your condition and the specific allergens involved. Avoiding allergens is the cornerstone of management. This means identifying the triggers (pollen, dust mites, pet dander, etc.) and minimizing exposure. Medications play a crucial role. For mild inflammation, antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids can be effective. For more severe cases, your doctor might prescribe inhaled corticosteroids, which are delivered directly to the lungs to reduce inflammation. Bronchodilators, which relax the airways and improve breathing, are also common treatments for allergy-induced asthma. In certain situations, allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots or sublingual tablets) might be recommended. This process gradually desensitizes your immune system to the specific allergens, reducing your reaction over time. In addition to these approaches, lifestyle changes can support lung health, including maintaining a healthy diet, getting sufficient rest, exercising regularly (if your condition allows), and practicing stress management techniques. Always consult your doctor to develop a safe and personalized plan to manage your allergy-induced lung inflammation.
When should I see a doctor for lung allergies?
You should see a doctor if your allergy symptoms affect your breathing or are severe or persistent. Shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, or coughing that doesn't improve are serious signs requiring immediate medical attention. If you experience difficulty sleeping due to coughing or breathlessness, this is also a significant indication that you need professional help. Furthermore, if over-the-counter medications provide minimal or no relief, it's crucial to seek a doctor's evaluation. They can conduct appropriate tests, diagnose the underlying cause of your allergies, and recommend a tailored treatment plan. Don't hesitate to consult your doctor if your symptoms are impacting your daily life, work, or social activities. Early diagnosis and management of lung allergies are essential to prevent complications and ensure optimal lung health. Ignoring symptoms could lead to more severe respiratory problems.
Deja una respuesta