How to deal with allergies

Allergies are a common ailment that can affect people of all ages. They can be caused by a variety of triggers, including pollen, dust, pet dander, and certain foods. While there is no cure for allergies, there are a number of things you can do to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. In this article, we'll provide you with some tips on how to deal with allergies. We'll discuss how to identify your triggers, avoid exposure, and use medications to relieve your symptoms. We'll also provide some tips on how to make your home more allergy-friendly.
How to Effectively Manage Your Allergies
Identifying Your Allergy Triggers
The first step in dealing with allergies is pinpointing what's causing your reaction. This might involve keeping a detailed diary of your symptoms and what you ate, touched, or were exposed to in the preceding hours or days. Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, certain foods (like peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish), and insect stings. If you suspect an allergy, it's crucial to consult an allergist for proper diagnosis. They can perform skin prick tests or blood tests to confirm your allergies and determine the severity of your reactions. Accurate identification is essential for effective management.
Medication Management for Allergies
Several medications can help manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, available over-the-counter or by prescription, are commonly used to relieve sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help clear nasal congestion. For more severe allergies, your doctor might prescribe corticosteroids (either nasal sprays or oral medications) to reduce inflammation. Leukotriene modifiers are another option for preventing allergy symptoms. It’s vital to follow your doctor's instructions carefully when taking any allergy medication and to discuss any side effects you experience. Self-treating can be dangerous, so professional guidance is recommended.
Environmental Controls for Allergy Reduction
Minimizing your exposure to allergens is key to managing your allergies. This involves making changes to your home environment. For dust mite allergies, use allergy-proof bedding, wash bedding weekly in hot water, and regularly clean carpets and furniture. For pet allergies, keep pets out of bedrooms and frequently clean pet bedding. If you have pollen allergies, try to stay indoors on high-pollen days, and use air conditioning. Regular cleaning and the use of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can significantly reduce indoor allergens.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For some individuals with moderate to severe allergies, immunotherapy, or allergy shots, may be an option. This involves gradually introducing increasing amounts of the allergen into your system to build up tolerance. Over time, this can significantly reduce your allergic reaction to the specific allergen. Immunotherapy is a long-term commitment, often requiring multiple injections over several years, but it can provide lasting relief for many people. It's essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your allergist before considering this treatment.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Certain lifestyle adjustments can help you manage your allergies more effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, strengthens your immune system and can help reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also be beneficial, as stress can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Knowing your triggers and practicing preventative measures are vital for successful allergy management. Pay attention to weather forecasts for pollen counts and adjust your activities accordingly.
| Allergy Type | Common Triggers | Common Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seasonal Allergies (Hay Fever) | Pollen (trees, grasses, weeds) | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, decongestants |
| Food Allergies | Peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, shellfish | Hives, swelling, itching, digestive problems, anaphylaxis | Avoidance, epinephrine (EpiPen), antihistamines |
| Pet Allergies | Pet dander, saliva | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Avoidance, antihistamines, immunotherapy |
| Dust Mite Allergies | Dust mites (in bedding, carpets) | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Encasement of bedding, regular cleaning, antihistamines |
How to Effectively Manage Your Allergies
Identifying Your Allergy Triggers
The first step in dealing with allergies is pinpointing what's causing your reaction. This might involve keeping a detailed diary of your symptoms and what you ate, touched, or were exposed to in the preceding hours or days. Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, certain foods (like peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish), and insect stings. If you suspect an allergy, it's crucial to consult an allergist for proper diagnosis. They can perform skin prick tests or blood tests to confirm your allergies and determine the severity of your reactions. Accurate identification is essential for effective management.
Medication Management for Allergies
Several medications can help manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, available over-the-counter or by prescription, are commonly used to relieve sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help clear nasal congestion. For more severe allergies, your doctor might prescribe corticosteroids (either nasal sprays or oral medications) to reduce inflammation. Leukotriene modifiers are another option for preventing allergy symptoms. It’s vital to follow your doctor's instructions carefully when taking any allergy medication and to discuss any side effects you experience. Self-treating can be dangerous, so professional guidance is recommended.
Environmental Controls for Allergy Reduction
Minimizing your exposure to allergens is key to managing your allergies. This involves making changes to your home environment. For dust mite allergies, use allergy-proof bedding, wash bedding weekly in hot water, and regularly clean carpets and furniture. For pet allergies, keep pets out of bedrooms and frequently clean pet bedding. If you have pollen allergies, try to stay indoors on high-pollen days, and use air conditioning. Regular cleaning and the use of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can significantly reduce indoor allergens.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For some individuals with moderate to severe allergies, immunotherapy, or allergy shots, may be an option. This involves gradually introducing increasing amounts of the allergen into your system to build up tolerance. Over time, this can significantly reduce your allergic reaction to the specific allergen. Immunotherapy is a long-term commitment, often requiring multiple injections over several years, but it can provide lasting relief for many people. It's essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your allergist before considering this treatment.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Certain lifestyle adjustments can help you manage your allergies more effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, strengthens your immune system and can help reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also be beneficial, as stress can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Knowing your triggers and practicing preventative measures are vital for successful allergy management. Pay attention to weather forecasts for pollen counts and adjust your activities accordingly.
| Allergy Type | Common Triggers | Common Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seasonal Allergies (Hay Fever) | Pollen (trees, grasses, weeds) | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, decongestants |
| Food Allergies | Peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, shellfish | Hives, swelling, itching, digestive problems, anaphylaxis | Avoidance, epinephrine (EpiPen), antihistamines |
| Pet Allergies | Pet dander, saliva | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Avoidance, antihistamines, immunotherapy |
| Dust Mite Allergies | Dust mites (in bedding, carpets) | Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion | Encasement of bedding, regular cleaning, antihistamines |
How do people cope with allergies?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural-allergy-remedies-89245_final-afc2c7d8000b4df183653b6b2af84f41.jpg)
People cope with allergies in a variety of ways, depending on the severity and type of allergy. Management often involves a combination of strategies aimed at avoiding allergens and managing symptoms when exposure occurs. The approach is highly individualized and requires close collaboration with a doctor or allergist to develop a personalized plan.
Allergen Avoidance
Avoiding allergens is the cornerstone of allergy management. This can be challenging, as allergens are ubiquitous in the environment. However, diligent avoidance can significantly reduce symptom severity. Identifying and eliminating specific triggers is key. This may involve changes to lifestyle, home environment, and diet.
- Detailed allergen identification: Skin prick tests, blood tests, and elimination diets can pinpoint specific triggers.
- Environmental control: Regular cleaning, using hypoallergenic bedding, air purifiers with HEPA filters, and avoiding exposure to pet dander or mold.
- Dietary changes: Eliminating allergenic foods from the diet, carefully reading food labels, and being aware of cross-contamination risks.
Medication
Various medications are available to manage allergy symptoms. These range from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications, each addressing different aspects of allergic responses. Choosing the right medication depends on the severity and type of allergy and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Antihistamines: These are commonly used to relieve sneezing, itching, runny nose, and watery eyes.
- Decongestants: These help relieve nasal congestion.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These are more potent anti-inflammatory medications delivered via nasal spray, effective for reducing nasal inflammation.
- Leukotriene modifiers: These are oral medications that can reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
- Epinephrine (EpiPen): This is a life-saving medication for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis).
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For individuals with moderate to severe allergies, immunotherapy (allergy shots) can be a highly effective long-term treatment. This therapy involves gradually exposing the body to increasing amounts of the allergen to build tolerance and reduce the allergic response. It’s a long-term commitment but can lead to significant symptom improvement or even remission.
- Subcutaneous Immunotherapy (SCIT): Injections administered by a healthcare professional.
- Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT): Tablets or drops placed under the tongue.
- Requires consistent treatment: Regular visits to an allergist are necessary.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Beyond medical interventions, lifestyle changes can support allergy management. Proactive steps, such as stress reduction techniques and regular exercise, can improve overall health and potentially lessen the impact of allergies. Paying attention to environmental conditions can also help individuals prepare and mitigate allergic reactions.
- Stress management: Stress can worsen allergy symptoms; techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
- Regular exercise: Improves overall health and may indirectly reduce the severity of allergy symptoms.
- Monitoring pollen counts and air quality: This enables individuals to plan activities accordingly and minimize exposure to allergens.
Emergency Preparedness
For individuals with severe allergies, particularly those at risk of anaphylaxis, emergency preparedness is crucial. This involves carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) at all times and having a plan in place for managing a severe reaction. Knowing how and when to use an epinephrine auto-injector is essential. Family members and close contacts should also be trained in how to recognize and respond to anaphylaxis.
- Carrying an EpiPen or similar auto-injector: This should always be accessible and readily available.
- Having a personalized emergency action plan: This includes contact information for emergency services and healthcare providers.
- Educating family and friends: Ensuring those around you know how to recognize and respond to an anaphylactic reaction.
How bad can allergies make you feel?
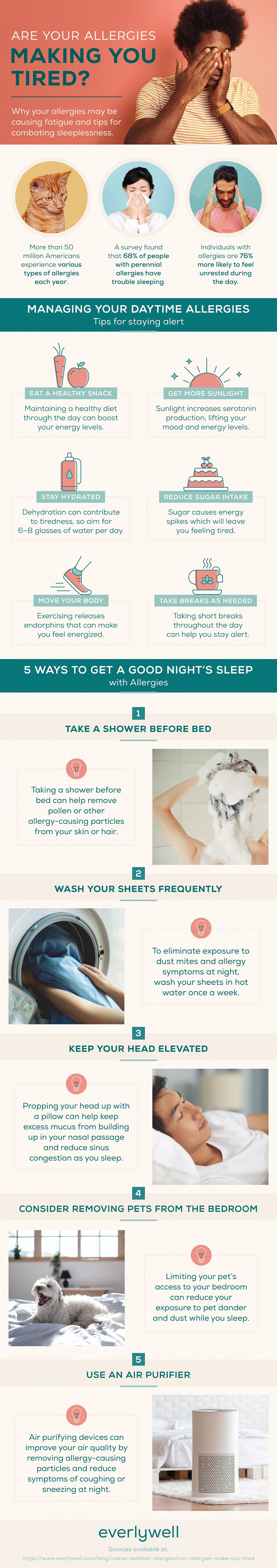
How Bad Can Allergies Make You Feel?
The severity of allergic reactions can vary dramatically from person to person. Some individuals experience mild discomfort, while others face debilitating symptoms that significantly impact their daily lives. The intensity of symptoms depends on several factors, including the allergen, the amount of exposure, and the individual's sensitivity. Allergic reactions range from annoying nuisances to life-threatening emergencies. It's crucial to understand the spectrum of allergic reactions to effectively manage them.
Mild Allergic Reactions
Mild allergic reactions are typically characterized by manageable symptoms that rarely require medical intervention. These symptoms are often bothersome but don't significantly interfere with daily activities. Examples include sneezing, a runny nose, itchy eyes, and mild skin rashes. While unpleasant, these symptoms usually respond well to over-the-counter medications.
- Sneezing fits: Frequent, uncontrollable sneezing can be disruptive but generally resolves without intervention.
- Itchy, watery eyes: Eye irritation can be relieved with artificial tears or antihistamine eye drops.
- Runny nose and congestion: Nasal congestion can be treated with saline sprays or decongestants.
Moderate Allergic Reactions
Moderate allergic reactions involve more intense symptoms that significantly impact daily functioning. These reactions often require medical attention for symptom management, and might necessitate stronger medications. These symptoms could lead to lost productivity or impaired quality of life.
- Significant nasal congestion: Severe stuffiness can make it difficult to breathe, sleep, or concentrate.
- Severe itching and rash: Intense skin irritation, possibly leading to skin breakdown, requires topical or oral medications.
- Persistent coughing and wheezing: These respiratory symptoms can indicate airway irritation and warrant medical evaluation.
Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention. It's characterized by a rapid onset of symptoms that can affect multiple body systems. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency that demands immediate treatment with epinephrine (adrenaline) and emergency medical services.
- Difficulty breathing and wheezing: Airway constriction can lead to respiratory failure.
- Swelling of the throat and tongue: Swelling in the airway can obstruct breathing.
- Low blood pressure and shock: A drastic drop in blood pressure can be life-threatening.
Impact on Daily Life
Even mild allergies can disrupt daily routines. The constant sneezing, itching, and congestion can affect sleep, concentration, and productivity at work or school. More severe allergies can completely incapacitate individuals, limiting their ability to participate in social activities, exercise, and engage in their usual daily tasks. Proper allergy management is essential for maintaining quality of life.
- Sleep disturbances: Nighttime allergy symptoms can significantly impact sleep quality.
- Reduced productivity: Symptoms can impair concentration and focus during work or study.
- Social limitations: Symptoms can cause avoidance of social gatherings or activities.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Allergies
Untreated allergies can have significant long-term consequences for health. Chronic inflammation related to allergies can contribute to other health problems, such as asthma, sinusitis, and ear infections. In addition to affecting physical health, the continuous discomfort and limitations caused by allergies can negatively affect mental health and overall well-being.
- Development of asthma: Untreated allergic rhinitis can increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Chronic sinusitis: Persistent inflammation can lead to chronic sinus infections.
- Increased risk of ear infections: Allergies can contribute to fluid buildup in the ears.
How do I treat my allergy at home?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural-allergy-remedies-89245_final-afc2c7d8000b4df183653b6b2af84f41.jpg)
How Do I Treat My Allergy at Home?
Treating allergies at home focuses on managing symptoms and avoiding triggers. The severity of your allergies and the specific allergen will dictate the best course of action. It's crucial to remember that home remedies are for symptom relief and may not address the underlying cause. If your symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsening, you should always seek professional medical advice. A doctor can properly diagnose your allergies and recommend appropriate treatment options, potentially including medication.
Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
The most effective home treatment for allergies is to identify and avoid your triggers. This can involve keeping a detailed allergy diary to track your symptoms and their correlation with specific environmental factors. Once you identify the allergen, you can take steps to minimize your exposure. For instance, if you're allergic to dust mites, you might need to regularly clean your home, use hypoallergenic bedding, and consider air purifiers. Careful identification and avoidance are often the cornerstone of effective allergy management.
- Keep a detailed diary to track symptoms and potential triggers.
- Conduct thorough home cleaning, focusing on dust removal.
- Invest in hypoallergenic bedding and consider using air purifiers.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Numerous over-the-counter (OTC) medications can help manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, available in various forms like tablets, capsules, and liquids, are commonly used to relieve sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion, but prolonged use should be avoided due to potential side effects. Nasal corticosteroids, available as nasal sprays, are also effective in reducing nasal inflammation. Always follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions or concerns about using OTC medications.
- Choose from various antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine, loratadine, diphenhydramine).
- Use decongestants sparingly to avoid potential side effects.
- Consider nasal corticosteroid sprays for effective nasal inflammation reduction.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
Several home remedies can provide temporary relief from allergy symptoms. A saline nasal rinse can help clear nasal passages and remove irritants. Warm compresses applied to the eyes can alleviate itching. Honey, while not scientifically proven for all allergies, is sometimes used to soothe a cough or sore throat associated with seasonal allergies. Note that these remedies are generally for mild symptom relief and may not work for everyone.
- Use a neti pot or saline spray to rinse nasal passages.
- Apply warm compresses to reduce eye itching and inflammation.
- Consider honey to soothe a cough or sore throat (consult with your doctor first).
Managing Allergic Reactions
Knowing how to manage an allergic reaction is essential. Mild reactions, such as sneezing, runny nose, and itching, can often be managed with home remedies and OTC medications. However, severe reactions (anaphylaxis), characterized by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and dizziness, require immediate medical attention. If you suspect anaphylaxis, call emergency services immediately. Having an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) readily available is crucial for individuals with severe allergies.
- Keep a detailed plan for managing mild allergy reactions.
- Know the symptoms of anaphylaxis and seek immediate medical attention if necessary.
- If prescribed, have an epinephrine auto-injector readily available and know how to use it.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving your home's indoor air quality can significantly reduce allergy symptoms. This involves regular cleaning and dusting to remove allergens like dust mites and pet dander. Using air purifiers with HEPA filters can help remove airborne particles from the air. Regularly changing air filters in your heating and air conditioning system is also important. Keeping humidity levels in check (ideally around 30-50%) can help reduce mold growth, a common allergen. Preventing allergen buildup is a proactive approach to allergy management.
- Regularly dust and vacuum your home.
- Use air purifiers with HEPA filters.
- Change air filters regularly and control indoor humidity.
Can I stop being allergic to pollen?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Preventing-and-Treating-Seasonal-Allergies_Danie-Drankwalter_Final-884166d09ac94425ad7e7a3b68a14249.jpg)
Can I Stop Being Allergic to Pollen?
Unfortunately, there's no cure for pollen allergies. While you can't completely stop being allergic, you can significantly manage and reduce your symptoms. The allergic response is driven by your immune system's mistaken identification of pollen as a threat. This leads to the production of IgE antibodies, which trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals, resulting in allergy symptoms. While you cannot change your genetic predisposition, you can take steps to lessen the severity of your reaction.
Can I outgrow my pollen allergies?
It's possible, though not guaranteed. Children are more likely to outgrow allergies, particularly to pollen. Some people find that their allergies lessen in severity with age. However, it’s unpredictable, and many adults continue to experience pollen allergies throughout their lives. The likelihood of outgrowing allergies depends on several factors, including the type of allergen and individual genetic makeup.
- Age of onset: Allergies developing in childhood are more likely to be outgrown.
- Type of allergen: Allergies to certain pollens are more likely to resolve than others.
- Genetic factors: Family history and individual immune system responses play a role.
What treatments can help manage my pollen allergies?
Several effective treatments can significantly reduce the impact of pollen allergies. These approaches aim to either prevent the allergic reaction or manage its symptoms. Medication is crucial, but lifestyle changes can also prove beneficial. Combining different strategies often yields the best results.
- Antihistamines: These over-the-counter or prescription medications block histamine, reducing allergy symptoms.
- Decongestants: These help relieve nasal congestion caused by inflammation.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These prescription nasal sprays reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): This involves gradually exposing your body to increasing amounts of pollen to desensitize your immune system.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce pollen allergy symptoms?
Yes, significantly. Proactive steps to limit exposure to pollen can dramatically reduce symptoms. These changes may require adjustments to your daily routines, but the benefits are often worthwhile. Combining these strategies with medical treatments will likely provide the most effective relief.
- Monitor pollen counts: Stay informed about daily pollen levels to plan activities accordingly.
- Stay indoors on high-pollen days: Limit outdoor exposure during peak pollen times (usually morning and early evening).
- Use air conditioning: Keep windows closed and use air conditioning to filter pollen from the air.
- Shower and change clothes after being outdoors: This removes pollen from your hair and skin.
What are the long-term effects of untreated pollen allergies?
Untreated pollen allergies can lead to a variety of complications, impacting both your immediate health and your long-term well-being. Ignoring symptoms can lead to a worsening of allergy conditions and the development of related issues. It is crucial to seek appropriate medical advice and treatment.
- Chronic sinusitis: Persistent inflammation of the sinuses.
- Asthma exacerbations: Worsening of asthma symptoms, potentially leading to severe respiratory problems.
- Sleep disturbances: Nighttime allergy symptoms can interfere with sleep quality.
- Reduced quality of life: Constant allergy symptoms can impact daily activities, productivity, and overall well-being.
Are there any natural remedies for pollen allergies?
While some natural remedies may offer mild relief for some individuals, there's no scientific evidence that they can cure or completely eliminate pollen allergies. They might help manage some symptoms, but they shouldn't replace medical advice or prescribed treatments. Always consult with your doctor before trying any new remedies, especially if you are taking other medications.
- Local honey: Some believe consuming local honey may desensitize the body to local pollen, but the evidence is limited.
- Quercetin: This antioxidant is thought by some to reduce inflammation, but more research is needed.
- Nettle leaf extract: Some studies suggest it might help reduce allergy symptoms, but further research is necessary.
What are the common symptoms of allergies?
Allergic reactions manifest in diverse ways, depending on the allergen and the individual's sensitivity. Some of the most common symptoms include sneezing, a runny or congested nose (rhinitis), itchy, watery eyes (conjunctivitis), and an itchy throat or cough. More severe reactions can involve skin symptoms like hives (urticaria), eczema, or rashes. Breathing difficulties, such as wheezing or shortness of breath, can indicate a more serious allergic reaction, particularly if it affects the airways (asthma). Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps can also occur, often in food allergies. The severity of symptoms varies widely; some people experience mild discomfort, while others suffer debilitating effects. It's crucial to identify the trigger and consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management, especially if symptoms are severe or worsening. Early intervention and proper treatment can significantly improve quality of life and prevent serious complications.
How can I identify my allergens?
Identifying your allergens is a crucial first step in managing your allergies. This process often involves a combination of methods. Firstly, keeping a detailed allergy diary is highly recommended. Note down when symptoms occur, what you ate, where you were, and what you were exposed to. This can help identify patterns and potential triggers. Secondly, an allergy test conducted by a doctor or allergist is incredibly helpful. These tests often include a skin prick test, which involves pricking the skin with small amounts of potential allergens to observe for reactions, or a blood test that measures the levels of allergy-specific antibodies (IgE). These tests can help identify specific allergens like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or certain foods. Thirdly, elimination diets can be used under medical supervision, particularly for suspected food allergies. This involves temporarily removing suspected foods from your diet to observe if symptoms improve. However, this should always be done with the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid nutritional deficiencies. Finally, consulting with an allergist, a specialist in allergy and immunology, is vital for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
What are the treatment options for allergies?
Treatment for allergies aims to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Options range from simple avoidance strategies to more complex medical interventions. Avoiding allergens is the cornerstone of allergy management. This could involve staying indoors during high pollen counts, using dust mite covers on bedding, avoiding known food allergens, or removing pets from the home if they're triggering your allergies. Over-the-counter medications, such as antihistamines (for relieving itching, sneezing, and runny nose) and nasal corticosteroids (for reducing nasal inflammation), can effectively manage symptoms. Prescription medications, including stronger antihistamines, leukotriene inhibitors (for asthma), or immunotherapy (allergy shots), might be necessary for more severe allergies. Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, involves gradually exposing the body to increasing amounts of the allergen to desensitize the immune system over time. This can offer long-term relief for many allergies. For severe allergic reactions, like anaphylaxis, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is essential for immediate treatment. It's always vital to consult an allergist or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate and safe treatment plan based on your specific needs and allergy profile.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for an allergic reaction?
While many allergic reactions are manageable with over-the-counter medications or home remedies, some require immediate medical attention. Seek immediate medical help if you experience symptoms of anaphylaxis, a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. These symptoms can include difficulty breathing or wheezing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, dizziness or lightheadedness, rapid heartbeat, rash or hives, nausea or vomiting, and a sudden drop in blood pressure. Also, seek immediate medical attention if your allergic symptoms are worsening rapidly, if you're having trouble breathing or swallowing, if your symptoms are not responding to usual treatments, or if you suspect a severe allergic reaction. Do not hesitate to call emergency services (911 or your local equivalent) if you suspect anaphylaxis or a severe allergic reaction. Prompt medical intervention can be life-saving in these situations. Early recognition and treatment are key to preventing serious complications.
Deja una respuesta