How to reverse allergies

Do you suffer from allergies that make your life miserable? Sneezing, itchy eyes, and a runny nose can be debilitating, but what if there was a way to reverse them? While there is no known cure for allergies, there are a number of things you can do to reduce your symptoms and improve your quality of life. In this article, we will explore some of the most effective ways to reverse allergies and get your life back on track.
How to Potentially Reverse or Manage Allergic Reactions
It's crucial to understand that while completely reversing allergies is not always possible with current medical knowledge, significant progress can be made in managing symptoms and potentially reducing their severity. Many approaches focus on building immune tolerance and reducing the body's overreaction to allergens. The methods outlined below should be discussed with your doctor before implementation, as they may not be suitable for everyone, and some may interact with existing medications.
1. Identify and Avoid Allergens
The first step in managing allergies is accurate identification of your triggers. This often involves allergy testing (skin prick tests or blood tests) to determine specific allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods. Once identified, diligent avoidance becomes critical. This means minimizing exposure to the allergen as much as possible. For example, if you're allergic to dust mites, regular cleaning, using allergen-proof bedding, and maintaining low humidity are key. Avoiding specific foods requires careful label reading and potential dietary changes.
2. Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots or Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT))
Immunotherapy involves gradually introducing small amounts of the allergen to your body over time, aiming to build tolerance. Allergy shots (subcutaneous immunotherapy) are administered by a healthcare professional, while sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) involves placing drops or tablets containing the allergen under the tongue. Both methods work by gradually desensitizing your immune system to the allergen, reducing the severity of reactions. It's a long-term process, often requiring multiple years of treatment.
3. Dietary Changes and Supplements
Certain dietary changes may help manage allergy symptoms. Eliminating inflammatory foods, such as processed foods, sugar, and certain fats, can potentially reduce overall inflammation in the body, which might lessen allergic reactions. Some believe that specific supplements, like quercetin or vitamin C, may have anti-inflammatory properties and help support the immune system. However, more research is needed to confirm their efficacy in allergy management, and it is crucial to discuss these supplements with your doctor before starting them. Self-treating with supplements can be risky.
4. Lifestyle Modifications for Allergy Relief
Several lifestyle changes can help manage allergies. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can all contribute to a stronger immune system and potentially reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through a diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics may also play a role in immune regulation. These lifestyle adjustments often support overall health, which can improve allergy management.
5. Medications for Allergy Symptom Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines reduce inflammation and itching, while decongestants help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids can be prescribed for more severe cases, and in emergencies, epinephrine (EpiPen) is a life-saving medication for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). It's important to use these medications as directed by a doctor and to be aware of potential side effects.
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergen Avoidance | Identifying and avoiding triggers. | Highly effective for preventing reactions. | Requires diligent effort and may not be fully achievable. |
| Immunotherapy | Gradually introducing allergens to build tolerance. | Can significantly reduce allergy symptoms or even lead to remission. | Requires long-term commitment and potential for side effects. |
| Dietary Changes | Modifying diet to reduce inflammation. | May help reduce symptom severity in some individuals. | Requires careful planning and may not be effective for all. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Improving overall health through exercise, sleep, and stress management. | Supports immune system health and may lessen reactions. | Requires commitment to healthy habits. |
| Medications | Using antihistamines, decongestants, or corticosteroids. | Effective for symptom relief. | Potential for side effects; epinephrine is crucial for anaphylaxis. |
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YftK98fJWiA%26pp%3DygUSI3Blcm1hbmVudGx5YXRob21l
How to Potentially Reverse or Manage Allergic Reactions
It's crucial to understand that while completely reversing allergies is not always possible with current medical knowledge, significant progress can be made in managing symptoms and potentially reducing their severity. Many approaches focus on building immune tolerance and reducing the body's overreaction to allergens. The methods outlined below should be discussed with your doctor before implementation, as they may not be suitable for everyone, and some may interact with existing medications.
1. Identify and Avoid Allergens
The first step in managing allergies is accurate identification of your triggers. This often involves allergy testing (skin prick tests or blood tests) to determine specific allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods. Once identified, diligent avoidance becomes critical. This means minimizing exposure to the allergen as much as possible. For example, if you're allergic to dust mites, regular cleaning, using allergen-proof bedding, and maintaining low humidity are key. Avoiding specific foods requires careful label reading and potential dietary changes.
2. Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots or Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT))
Immunotherapy involves gradually introducing small amounts of the allergen to your body over time, aiming to build tolerance. Allergy shots (subcutaneous immunotherapy) are administered by a healthcare professional, while sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) involves placing drops or tablets containing the allergen under the tongue. Both methods work by gradually desensitizing your immune system to the allergen, reducing the severity of reactions. It's a long-term process, often requiring multiple years of treatment.
3. Dietary Changes and Supplements
Certain dietary changes may help manage allergy symptoms. Eliminating inflammatory foods, such as processed foods, sugar, and certain fats, can potentially reduce overall inflammation in the body, which might lessen allergic reactions. Some believe that specific supplements, like quercetin or vitamin C, may have anti-inflammatory properties and help support the immune system. However, more research is needed to confirm their efficacy in allergy management, and it is crucial to discuss these supplements with your doctor before starting them. Self-treating with supplements can be risky.
4. Lifestyle Modifications for Allergy Relief
Several lifestyle changes can help manage allergies. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can all contribute to a stronger immune system and potentially reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through a diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics may also play a role in immune regulation. These lifestyle adjustments often support overall health, which can improve allergy management.
5. Medications for Allergy Symptom Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines reduce inflammation and itching, while decongestants help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids can be prescribed for more severe cases, and in emergencies, epinephrine (EpiPen) is a life-saving medication for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). It's important to use these medications as directed by a doctor and to be aware of potential side effects.
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergen Avoidance | Identifying and avoiding triggers. | Highly effective for preventing reactions. | Requires diligent effort and may not be fully achievable. |
| Immunotherapy | Gradually introducing allergens to build tolerance. | Can significantly reduce allergy symptoms or even lead to remission. | Requires long-term commitment and potential for side effects. |
| Dietary Changes | Modifying diet to reduce inflammation. | May help reduce symptom severity in some individuals. | Requires careful planning and may not be effective for all. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Improving overall health through exercise, sleep, and stress management. | Supports immune system health and may lessen reactions. | Requires commitment to healthy habits. |
| Medications | Using antihistamines, decongestants, or corticosteroids. | Effective for symptom relief. | Potential for side effects; epinephrine is crucial for anaphylaxis. |
How can I reverse my allergies naturally?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural-allergy-remedies-89245_final-afc2c7d8000b4df183653b6b2af84f41.jpg)
How Can I Reverse My Allergies Naturally?
There's no guaranteed "cure" for allergies, and what works for one person may not work for another. However, several natural approaches may help reduce allergy symptoms and potentially lessen their severity over time. It's crucial to understand that these methods are not a replacement for medical advice, and you should always consult with a doctor or allergist before making significant changes to your healthcare routine, especially if you have severe allergies. Self-treating can be dangerous.
Dietary Changes to Reduce Allergic Reactions
Modifying your diet can significantly impact your allergy symptoms. Eliminating common allergens like dairy, gluten, soy, eggs, nuts, and shellfish can reduce inflammation and improve gut health, a crucial factor in allergy management. Focus on incorporating anti-inflammatory foods instead. A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is key. Working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can be extremely beneficial in creating a personalized plan.
- Eliminate common allergens: Identify and remove foods you suspect trigger your allergies from your diet.
- Increase anti-inflammatory foods: Consume foods rich in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and turmeric.
- Improve gut health: Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt (if tolerated) and kefir to support beneficial gut bacteria.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements for Allergy Relief
Certain herbs and supplements are traditionally used to alleviate allergy symptoms. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional before using these, especially if you're taking other medications, as interactions can occur. Some commonly discussed options include quercetin (a potent antioxidant), bromelain (an enzyme from pineapple), and stinging nettle. Remember that these are not FDA-approved treatments for allergies.
- Quercetin: A flavonoid with anti-inflammatory properties.
- Bromelain: May help reduce inflammation and improve immune function.
- Stinging Nettle: Traditionally used to reduce allergy symptoms, but more research is needed.
Lifestyle Modifications for Allergy Management
Making lifestyle changes can significantly support your body in managing allergies. Regular exercise helps boost your immune system and reduce inflammation. Managing stress is also crucial, as stress can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Getting enough sleep is vital for immune function, and ensuring good air quality in your home (using air purifiers, for example) can minimize exposure to allergens.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Environmental Control to Minimize Allergen Exposure
Minimizing your exposure to allergens is a cornerstone of managing allergies. Regularly cleaning your home, especially bedding and carpets, helps remove dust mites. Using air purifiers with HEPA filters can significantly reduce airborne allergens like pollen and pet dander. Keeping windows closed during peak pollen seasons is also essential.
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum and dust frequently, wash bedding in hot water weekly.
- Air Purifiers: Use HEPA filters to remove airborne allergens.
- Window Management: Keep windows closed during high pollen counts.
Immunotherapy and Other Medical Interventions
While focusing on natural methods, it's crucial to understand that immunotherapy (allergy shots) and other medical interventions are often necessary for severe allergies. These approaches aim to desensitize your immune system to specific allergens and should be discussed and managed by your allergist. Don't neglect professional medical advice when dealing with serious allergic reactions.
- Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy): A gradual process to desensitize to allergens.
- Medication: Antihistamines, decongestants, and other medications can help manage symptoms.
- Regular Checkups: Consistent monitoring with an allergist is essential.
Can an allergy be reversed?
Can an Allergy Be Reversed?
Whether an allergy can be reversed is a complex question with no simple yes or no answer. While it's generally not possible to completely eliminate the underlying immune response that causes an allergic reaction, significant improvement and even remission are possible in some cases, depending on the type of allergy and the individual. There's currently no single method guaranteed to reverse allergies, and success rates vary considerably. Approaches focus on managing symptoms, desensitizing the immune system, or identifying and avoiding triggers. The possibility of reversal depends heavily on factors like the allergen's nature, the severity of the allergy, and the individual's immune system response.
What are the common types of allergy treatments?
Allergy treatments aim to manage symptoms and, in some cases, desensitize the immune system. These treatments don't necessarily "reverse" the allergy, but they can significantly reduce its impact on a person's life. Common treatments include:
- Medication: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine (for severe reactions) are frequently used to manage allergy symptoms.
- Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots): This involves gradually introducing increasing amounts of the allergen to build tolerance over time. It's considered the most effective way to achieve long-term relief for some allergies.
- Avoidance Strategies: Identifying and eliminating or minimizing exposure to specific allergens is crucial in managing allergies. This can involve changes to diet, environment, or lifestyle.
Can food allergies be reversed?
Food allergies are generally considered more challenging to reverse than other types of allergies. While spontaneous remission can occur, especially in early childhood, it's not predictable. There is ongoing research exploring various methods to induce tolerance, but currently, no established method guarantees reversal of food allergies. Strategies focus on symptom management, careful avoidance, and potentially, future immunotherapy approaches that are still under development.
- Oral Immunotherapy (OIT): This involves gradually increasing the amount of the allergen consumed under medical supervision.
- Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT): This involves placing the allergen under the tongue.
- Avoidance is key: Strict avoidance of the allergenic food is crucial to prevent allergic reactions.
What about environmental allergies (pollen, dust mites, etc.)?
Environmental allergies may show more potential for improvement or even remission than food allergies. Immunotherapy, particularly allergy shots, has demonstrated success in reducing symptoms and increasing tolerance to environmental allergens in many individuals. However, it's not a guaranteed reversal, and maintaining the benefits often requires continued treatment or careful avoidance strategies.
- Allergy shots: Repeated injections of diluted allergens can build tolerance.
- Medication: Antihistamines, nasal sprays, and other medications effectively manage symptoms.
- Environmental control: Reducing exposure through air purifiers, frequent cleaning, and other measures can lessen symptoms.
Is there a role for lifestyle changes in reversing allergies?
While lifestyle changes alone cannot reverse an allergy, they play a crucial role in managing symptoms and overall health. A healthy lifestyle can support the immune system and help reduce the severity of allergic reactions. These changes can be particularly beneficial when combined with other treatment approaches.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports immune function.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances the immune system and can reduce inflammation.
- Stress management: Reducing stress levels can improve immune health and potentially reduce allergy symptoms.
What is the future of allergy reversal research?
Research into allergy reversal continues to progress, with scientists exploring new avenues such as targeted immunotherapies, microbiome manipulation, and novel drug delivery methods. While a complete cure for all allergies remains elusive, the potential for improved treatments and even reversal in specific cases is promising. These advances may offer more effective and personalized approaches to allergy management in the future.
- Novel immunotherapies: Research is exploring more targeted and efficient ways to modify immune responses.
- Microbiome manipulation: Investigating the role of gut bacteria in allergic reactions may lead to new treatment strategies.
- Gene therapy: Emerging research explores the possibility of genetically modifying immune cells to prevent allergic reactions.
How do you flush allergies out of your system?
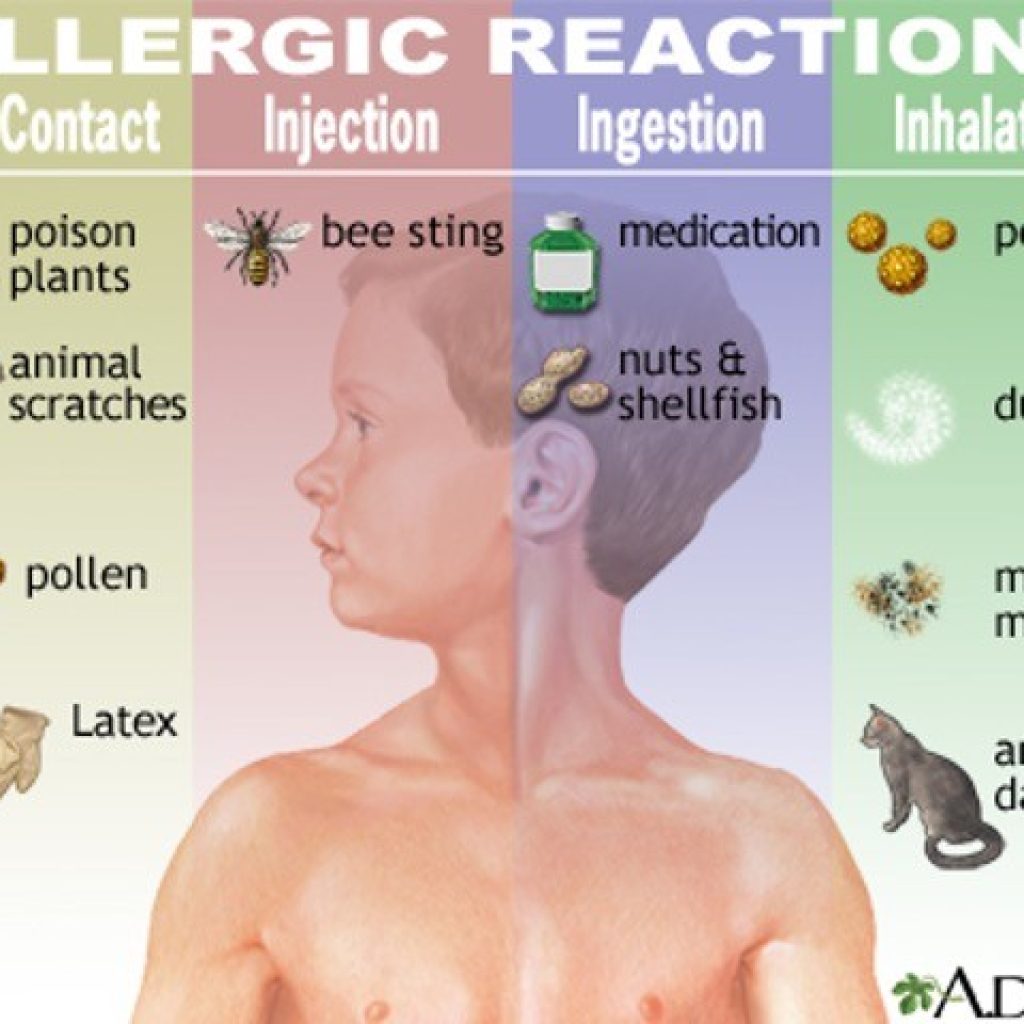
There's no single method to "flush" allergies out of your system. Allergies are a result of your immune system overreacting to a harmless substance (allergen). While you can't completely eliminate this response, you can manage your symptoms and reduce the severity of your allergic reactions through various strategies. These strategies focus on minimizing exposure to allergens and managing your body's reaction to them, rather than literally flushing them out.
Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
The most effective way to manage allergies is to identify and avoid the substances that trigger your reactions. This requires careful observation and possibly allergy testing. Keeping a detailed allergy diary can help you pinpoint potential triggers. Once identified, avoiding these triggers is crucial.
- Keep a detailed diary noting times of reactions, possible exposures, and symptoms.
- Undergo allergy testing to get a definitive list of allergens.
- Avoid known allergens diligently. This might involve changes to your diet, environment, or lifestyle.
Managing Symptoms with Medication
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. Antihistamines block the effects of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants help relieve nasal congestion. For more severe allergies, your doctor might prescribe stronger medications such as corticosteroids or immunotherapy.
- Antihistamines are available in various forms (oral, nasal spray, eye drops).
- Decongestants provide temporary relief from nasal congestion.
- Corticosteroids (prescription) reduce inflammation in the airways and sinuses.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots) gradually desensitizes your immune system to allergens over time.
Lifestyle Changes for Allergy Relief
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact your allergy symptoms. Maintaining good hygiene helps reduce exposure to allergens. Regular showering and changing clothes after being outdoors can remove pollen and other allergens from your body and hair. A clean home, particularly keeping your bedroom allergen-free, is crucial. Also, consider using air purifiers with HEPA filters to reduce airborne allergens.
- Regular showering helps wash away allergens.
- Changing clothes after being outdoors minimizes allergen exposure.
- Cleaning your home regularly reduces allergen buildup.
- Using air purifiers with HEPA filters removes airborne allergens.
Dietary Considerations for Allergies
While diet won't "flush" allergies, eliminating certain foods can help manage symptoms, especially if you have food allergies. Some people find that reducing foods high in histamine, such as aged cheese, fermented foods, or certain fish, can ease their allergy symptoms. Consulting a registered dietitian or allergist can help you create a personalized dietary plan that addresses your specific needs and allergies.
- Identify and eliminate food allergens from your diet.
- Consider reducing histamine-rich foods, but consult a professional first.
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice
It's crucial to consult with a doctor or allergist for proper diagnosis and management of your allergies. They can perform allergy tests to identify your specific triggers, recommend appropriate medications, and provide personalized advice on managing your condition. Ignoring allergies or attempting self-treatment with unproven methods can be risky and potentially worsen your condition. A healthcare professional can create a safe and effective plan tailored to your individual needs.
- Schedule an appointment with an allergist or doctor.
- Discuss your symptoms and medical history thoroughly.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations for treatment and management.
What to do if I ate something I'm allergic to?

Eating something you're allergic to can trigger a range of reactions, from mild discomfort to a life-threatening emergency. The severity of your reaction depends on several factors, including the type of allergen, the amount consumed, and your individual sensitivity. Immediate action is crucial, and the steps you take will vary depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Identifying the Allergen and Severity of Reaction
The first step is to identify what you ate that caused the reaction. This information is vital for future avoidance and for informing medical professionals. Assess the severity of your symptoms. Mild reactions might include itching, hives, or mild digestive upset. More severe reactions can involve difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat (angioedema), dizziness, or loss of consciousness. Knowing the severity guides your next steps.
- Keep a food diary to track what you consume and note any subsequent reactions.
- Carefully read food labels to check for potential allergens.
- If you suspect cross-contamination in a restaurant setting, inform the staff.
Administering Epinephrine (if applicable)
If you have a history of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), you should have an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen or Auvi-Q) readily available. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that can counteract the effects of a severe allergic reaction. If you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, or dizziness, administer epinephrine immediately, then call emergency services (911 in the US).
- Follow the instructions provided with your auto-injector precisely.
- Even if symptoms improve after administering epinephrine, seek immediate medical attention as reactions can recur.
- Inform emergency medical personnel about the allergen and the epinephrine administration.
Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
Call emergency services (911 in the US, or your local equivalent) immediately if you experience any severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. Even if you have administered epinephrine, emergency medical personnel can provide further support and monitor your condition. Do not attempt to drive yourself to the hospital.
- Clearly explain your symptoms to the dispatcher.
- Provide information about the allergen you consumed.
- Follow the dispatcher's instructions carefully.
Managing Mild Allergic Reactions
For mild allergic reactions, such as mild itching or hives, over-the-counter antihistamines (like diphenhydramine or cetirizine) can often provide relief. However, if symptoms worsen or do not improve within a reasonable time, seek medical attention. Monitor your symptoms closely for any signs of escalation.
- Follow the dosage instructions on the antihistamine packaging.
- Avoid scratching hives to prevent further irritation.
- If symptoms persist or worsen, contact a doctor or allergist.
Preventing Future Allergic Reactions
Once you've recovered, take steps to prevent future reactions. This includes accurately identifying your allergen, carefully reading food labels, informing restaurants about your allergy, and carrying your epinephrine auto-injector at all times. Consider allergy testing to get a comprehensive understanding of your allergies and develop a personalized avoidance plan. Regular communication with your doctor or allergist is crucial for managing your condition.
- Create a detailed list of foods and ingredients you must avoid.
- Inform family members, friends, and caregivers about your allergies.
- Carry an allergy alert medical bracelet or necklace.
Can allergies be reversed completely?
Unfortunately, there's no guaranteed method to completely reverse allergies. While some people experience a spontaneous remission, meaning their allergy symptoms disappear over time without intervention, this isn't predictable or reliable. The underlying immune system response that causes allergies is complex and deeply ingrained. Current treatments primarily focus on managing symptoms and reducing the severity of allergic reactions, rather than eradicating the allergy itself. Immunotherapy, such as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT), works by gradually introducing small amounts of the allergen to desensitize the immune system. While this can significantly reduce symptoms and even lead to a decrease in allergy severity over time, it doesn't necessarily "reverse" the allergy completely. The body still recognizes the allergen, but the reaction is lessened. Other approaches, like dietary changes and avoiding triggers, can help manage symptoms but don't eliminate the underlying allergic response. Therefore, while significant improvement is possible, complete reversal remains elusive for the vast majority of individuals.
What are the most effective treatments for reversing or managing allergies?
While complete reversal is unlikely, several treatments effectively manage and often significantly reduce allergic reactions. Immunotherapy is a cornerstone of allergy management, particularly for allergies to things like pollen, dust mites, and certain foods. Allergy shots involve gradual injections of increasing allergen doses, desensitizing the immune system. Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) uses drops or tablets placed under the tongue, offering a more convenient alternative. Both methods aim to alter the immune response over time. Beyond immunotherapy, medication plays a vital role. Antihistamines help relieve symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose. Decongestants address nasal congestion, while leukotriene modifiers and nasal corticosteroids are useful for more severe cases. Lifestyle changes are also crucial. Avoiding known allergens, such as maintaining a dust-free environment or following a strict elimination diet, can substantially minimize exposure and symptoms. Environmental control methods, such as HEPA filters and regular cleaning, further help reduce allergen levels in the home. Finally, for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), carrying and knowing how to use an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is essential.
Are there any natural remedies to reverse allergies?
While some natural remedies might offer mild symptom relief, there's no scientific evidence to support the claim that they can reverse allergies. Many people explore options like acupuncture, herbal remedies, or dietary supplements. However, the effectiveness of these approaches varies greatly, and results are often anecdotal rather than based on robust clinical trials. It's crucial to remember that these methods shouldn't replace conventional medical treatments, especially for severe allergies. Some natural remedies can even interact negatively with prescription medications. Always consult with a doctor or allergist before trying any alternative therapies, particularly if you're already taking medication for your allergies. While some individuals might find relief from certain natural approaches for managing mild symptoms, it's vital to prioritize medically proven treatments for effective allergy management, especially for those with severe reactions.
Can a change in diet reverse allergies?
A change in diet can help manage allergy symptoms by eliminating trigger foods, but it's unlikely to reverse an allergy completely. For food allergies, avoiding the specific allergen is essential to prevent reactions. Elimination diets, guided by an allergist or registered dietitian, can help identify trigger foods and manage symptoms. However, simply removing the allergen doesn't change the underlying immune response that causes the allergy. Once the allergen is reintroduced, the allergic reaction will likely occur again. While a well-planned diet can contribute to overall health and potentially improve tolerance to certain foods, it doesn't fundamentally alter the body's allergic response. It's crucial to collaborate with healthcare professionals to develop a safe and effective dietary plan that addresses individual needs and prevents dangerous reactions. Therefore, while dietary changes are a valuable tool in managing food allergies, they are not a cure or a means of reversing the allergy itself.

Deja una respuesta