How to speed up allergy recovery

Suffering from allergies can be a misery. Sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion can make it difficult to go about your day. If you're looking for ways to speed up your allergy recovery, here are a few tips.
How to Speed Up Your Allergy Recovery
Identify and Eliminate Triggers
The first and arguably most important step in speeding up allergy recovery is to pinpoint and eliminate the allergens triggering your symptoms. This might involve keeping a detailed allergy diary, noting down foods eaten, environments visited, and any subsequent reactions. Consider consulting with an allergist to undergo allergy testing (skin prick test or blood test) for a definitive diagnosis. Once identified, take steps to minimize exposure. If it's pollen, stay indoors on high-pollen days, use air purifiers with HEPA filters, and change clothes after being outside. For food allergies, carefully read labels and avoid cross-contamination. Identifying and removing the source of the allergen is crucial for faster recovery.
Optimize Your Medications
Following your doctor's advice on medication is key. Antihistamines can quickly alleviate symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids are often prescribed for more severe allergies to reduce inflammation. Remember to take your medication as directed and don't hesitate to discuss any side effects or lack of effectiveness with your physician. They might adjust your dosage or prescribe a different medication to better manage your allergies and accelerate recovery. Don't self-medicate – consult a professional.
Employ Natural Remedies
While not a replacement for medical advice or medication, certain natural remedies can provide additional support and potentially ease allergy symptoms. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse out irritants from your nasal passages. A neti pot (following proper hygiene protocols) can also achieve this. Some people find relief with local honey (from your region), although this is not scientifically proven for all allergies. Quercetin, a natural antioxidant, shows some promise in reducing inflammation, but more research is needed. It’s vital to remember that these remedies should be used in conjunction with, not instead of, your prescribed medication.
Improve Your Indoor Air Quality
Even when allergens are outside, you can significantly reduce your exposure indoors. Regularly clean your home, paying special attention to dusting and vacuuming. Use allergen-impermeable covers on your mattresses, pillows, and bedding. Consider investing in an air purifier with a HEPA filter to remove allergens from the air you breathe. Keeping your home clean and the air fresh can create a sanctuary from allergens and facilitate quicker recovery.
Manage Stress Levels
Believe it or not, stress can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Chronic stress weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to allergic reactions and prolonging recovery time. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Adequate sleep is also essential for immune function and overall well-being, contributing to faster allergy recovery. Finding ways to manage stress can significantly impact your body's ability to fight off allergens and heal.
| Strategy | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Identify & Eliminate Triggers | Allergy testing, diary tracking, environmental modifications | Reduces allergen exposure, speeds healing |
| Optimize Medications | Follow doctor's advice, discuss side effects | Effective symptom relief, faster recovery |
| Natural Remedies | Saline spray, neti pot, local honey (use cautiously) | Complementary support, symptom management |
| Improve Indoor Air Quality | Cleaning, air purifiers, allergen-impermeable covers | Minimizes indoor allergen exposure |
| Manage Stress | Yoga, meditation, sufficient sleep | Boosts immune function, reduces symptom severity |
How to Speed Up Your Allergy Recovery
Identify and Eliminate Triggers
The first and arguably most important step in speeding up allergy recovery is to pinpoint and eliminate the allergens triggering your symptoms. This might involve keeping a detailed allergy diary, noting down foods eaten, environments visited, and any subsequent reactions. Consider consulting with an allergist to undergo allergy testing (skin prick test or blood test) for a definitive diagnosis. Once identified, take steps to minimize exposure. If it's pollen, stay indoors on high-pollen days, use air purifiers with HEPA filters, and change clothes after being outside. For food allergies, carefully read labels and avoid cross-contamination. Identifying and removing the source of the allergen is crucial for faster recovery.
Optimize Your Medications
Following your doctor's advice on medication is key. Antihistamines can quickly alleviate symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion. Nasal corticosteroids are often prescribed for more severe allergies to reduce inflammation. Remember to take your medication as directed and don't hesitate to discuss any side effects or lack of effectiveness with your physician. They might adjust your dosage or prescribe a different medication to better manage your allergies and accelerate recovery. Don't self-medicate – consult a professional.
Employ Natural Remedies
While not a replacement for medical advice or medication, certain natural remedies can provide additional support and potentially ease allergy symptoms. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse out irritants from your nasal passages. A neti pot (following proper hygiene protocols) can also achieve this. Some people find relief with local honey (from your region), although this is not scientifically proven for all allergies. Quercetin, a natural antioxidant, shows some promise in reducing inflammation, but more research is needed. It’s vital to remember that these remedies should be used in conjunction with, not instead of, your prescribed medication.
Improve Your Indoor Air Quality
Even when allergens are outside, you can significantly reduce your exposure indoors. Regularly clean your home, paying special attention to dusting and vacuuming. Use allergen-impermeable covers on your mattresses, pillows, and bedding. Consider investing in an air purifier with a HEPA filter to remove allergens from the air you breathe. Keeping your home clean and the air fresh can create a sanctuary from allergens and facilitate quicker recovery.
Manage Stress Levels
Believe it or not, stress can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Chronic stress weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to allergic reactions and prolonging recovery time. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Adequate sleep is also essential for immune function and overall well-being, contributing to faster allergy recovery. Finding ways to manage stress can significantly impact your body's ability to fight off allergens and heal.
| Strategy | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Identify & Eliminate Triggers | Allergy testing, diary tracking, environmental modifications | Reduces allergen exposure, speeds healing |
| Optimize Medications | Follow doctor's advice, discuss side effects | Effective symptom relief, faster recovery |
| Natural Remedies | Saline spray, neti pot, local honey (use cautiously) | Complementary support, symptom management |
| Improve Indoor Air Quality | Cleaning, air purifiers, allergen-impermeable covers | Minimizes indoor allergen exposure |
| Manage Stress | Yoga, meditation, sufficient sleep | Boosts immune function, reduces symptom severity |
How can I make my allergic reaction go away faster?
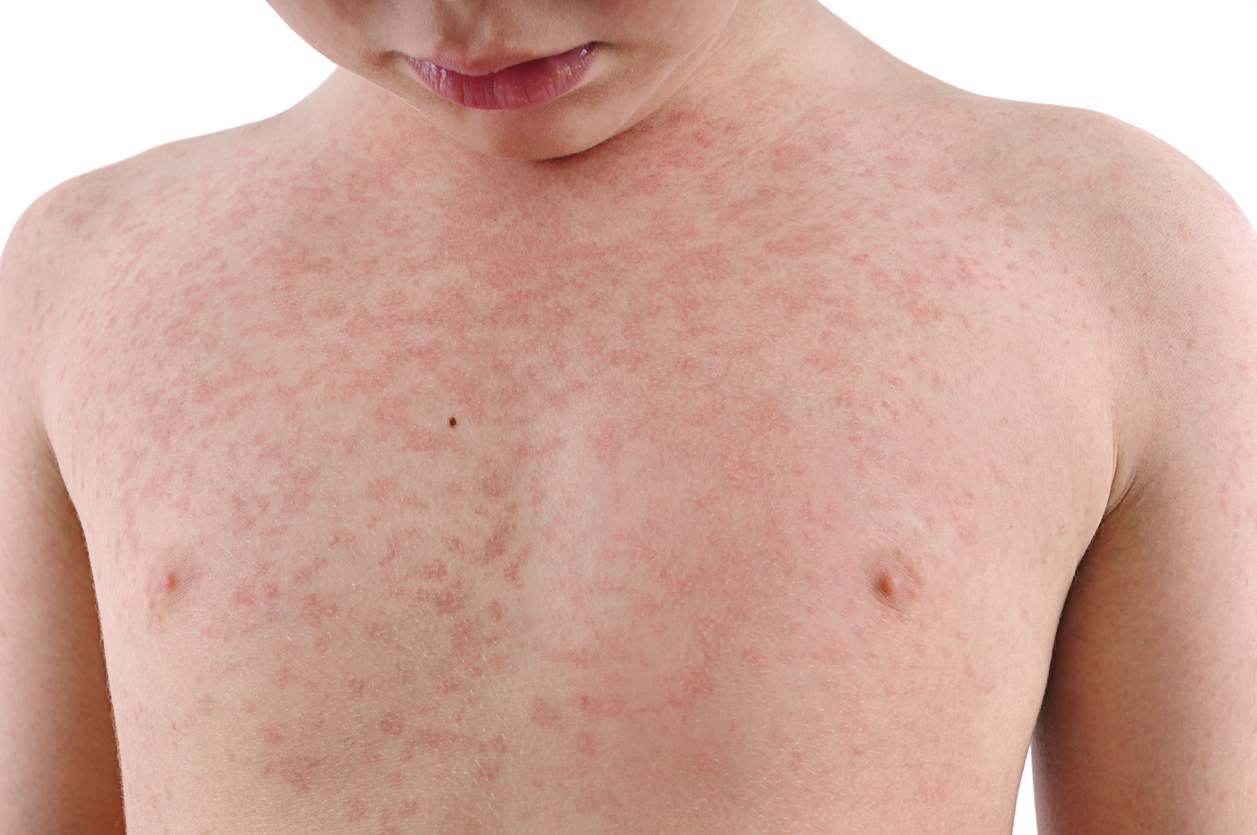
There's no single answer to how to make an allergic reaction go away faster, as the severity and type of reaction vary greatly. Treatment depends entirely on the allergen and the individual's reaction. Always seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness. This response focuses on managing milder reactions while emphasizing the crucial need for professional medical help when necessary.
Identify and Remove the Allergen
The first and most important step is to identify and remove the source of the allergic reaction. This could be anything from pollen and pet dander to food or medication. Once you've pinpointed the allergen, immediately remove yourself from its presence. This can dramatically slow down or even prevent further reaction progression. For example, if you're having a reaction to peanuts, immediately avoid any further contact with peanut products.
- Identify the trigger: Pay close attention to what you've recently touched, eaten, or been exposed to.
- Remove the source: Get away from the allergen completely.
- Wash thoroughly: If the allergen is on your skin, wash the affected area with soap and water.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can help relieve many allergy symptoms. These medications work by blocking histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction. Follow the dosage instructions carefully, and remember that some antihistamines can cause drowsiness. In some cases, a topical antihistamine cream or ointment may be more effective for skin reactions.
- Oral antihistamines: Take as directed for itching, hives, and sneezing.
- Topical antihistamines: Apply to skin rashes for localized relief.
- Decongestants (pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine): Can be helpful for nasal congestion but are not appropriate for all individuals.
Cold Compresses
Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and itching associated with allergic reactions like hives or insect bites. The cold helps constrict blood vessels, reducing inflammation. Ensure the compress is clean and wrapped in a soft cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Apply cold compresses: For 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Use a clean cloth: Avoid direct ice contact with the skin.
- Reapply as needed: For continuous relief of itching and swelling.
Hydrocortisone Cream
For mild skin reactions such as hives or rashes, a 1% hydrocortisone cream can provide relief. This topical corticosteroid reduces inflammation and itching. Apply a thin layer to the affected area as directed on the packaging. Avoid using it on large areas of the body without consulting a doctor.
- Apply a thin layer: Do not overapply.
- Use as directed: Follow the instructions on the packaging carefully.
- Do not use on broken skin: Consult a doctor for more severe skin conditions.
Seek Medical Attention
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms indicating a severe allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat (anaphylaxis). Your doctor can provide appropriate treatment, which might include epinephrine (adrenaline) injections. Even if your symptoms seem mild initially, if they persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical advice.
- Call emergency services immediately: In case of severe allergic reaction symptoms.
- Consult a doctor or allergist: For diagnosis and a personalized management plan.
- Follow up on treatment: Even after initial symptom relief.
How to quickly recover from allergies?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural-allergy-remedies-89245_final-afc2c7d8000b4df183653b6b2af84f41.jpg)
How to Quickly Recover from Allergies?
Identify and Eliminate the Allergen
The fastest way to recover from an allergic reaction is to remove yourself from contact with the allergen. This might seem obvious, but it's crucial. If you've touched something that caused a reaction, wash your hands thoroughly. If you're experiencing respiratory symptoms from airborne allergens like pollen, move indoors and close windows. Identifying the specific allergen is also important for long-term management. Keeping a detailed allergy diary can help pinpoint triggers. Knowing your triggers allows for proactive avoidance, preventing future reactions.
- Identify the source: Pollen, pet dander, food, medication, insect stings, etc.
- Remove yourself from contact with the allergen immediately.
- Keep a detailed diary to track potential triggers and reactions.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide significant relief from allergy symptoms. Antihistamines, like cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), or loratadine (Claritin), can effectively reduce sneezing, itching, runny nose, and hives. Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, can help relieve nasal congestion. Always follow the dosage instructions on the packaging and consult a pharmacist or doctor if you have any concerns or pre-existing conditions. Remember that some OTC medications can cause drowsiness.
- Antihistamines: Block histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction.
- Decongestants: Shrink swollen blood vessels in the nasal passages.
- Nasal sprays (saline or steroid): Help clear nasal passages and reduce inflammation.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Several home remedies can complement OTC medications. A warm shower or bath can help soothe itchy skin. Saline nasal rinse can clear nasal passages of irritants. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids is vital, especially during allergy season. Avoiding known allergens as much as possible is crucial for long-term management. Consider air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove allergens from your indoor environment.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water.
- Warm showers/baths: Soothe itchy skin.
- Saline nasal rinse: Clear nasal passages.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most allergic reactions are manageable with OTC medications and home remedies, some require immediate medical attention. Seek medical help immediately if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat (anaphylaxis). These symptoms indicate a severe allergic reaction that requires emergency treatment. Even if symptoms seem mild, consulting a doctor can help determine the best course of action and rule out other conditions.
- Difficulty breathing: Wheezing, shortness of breath.
- Severe swelling: Angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, or tongue).
- Anaphylaxis: Life-threatening allergic reaction.
Long-Term Allergy Management
For persistent or recurring allergies, a doctor may recommend long-term management strategies. This could include allergy testing to identify specific triggers, immunotherapy (allergy shots), or prescription medications like nasal corticosteroids or leukotriene inhibitors. Regular check-ups with an allergist or immunologist are crucial for developing a personalized management plan. This plan may involve medication, avoidance strategies, and other therapies to minimize allergy symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Allergy testing: Identify specific allergens.
- Immunotherapy: Allergy shots to desensitize to allergens.
- Prescription medications: Nasal corticosteroids, leukotriene inhibitors.
How do you flush allergies out of your system?
There's no single method to instantly "flush" allergies out of your system. Allergies are a complex immune response, and while you can manage symptoms and reduce exposure to allergens, you can't completely eliminate the underlying sensitivity. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing future reactions. The best approach depends on the specific allergen and the severity of your symptoms. However, several strategies can help alleviate allergy symptoms and improve your overall health.
Identify and Avoid Allergens
This is the cornerstone of allergy management. Identifying your specific allergens is crucial. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, and certain foods. Once identified, minimizing exposure is key. This might involve: using air purifiers, regular house cleaning, avoiding certain foods, or using medications to manage symptoms during exposure. Accurate identification often requires allergy testing by a medical professional.
- Keep a detailed allergy diary: Note when symptoms occur and what you were exposed to.
- Undergo allergy testing: Skin prick tests or blood tests can help identify specific allergens.
- Work with an allergist: They can create a personalized plan to manage your allergies.
Medication
Various medications can effectively manage allergy symptoms. These are not cures, but they can significantly reduce discomfort and improve quality of life. Antihistamines block histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction, relieving symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants can help clear nasal passages. Nasal corticosteroids are effective for reducing nasal inflammation. Some people benefit from immunotherapy (allergy shots), a long-term treatment that aims to desensitize the body to allergens.
- Over-the-counter antihistamines: Cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine.
- Prescription medications: Stronger antihistamines, nasal sprays, leukotriene inhibitors.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): A long-term treatment to reduce sensitivity to allergens.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can contribute to better allergy management. Regular cleaning to remove dust mites and other allergens from your home environment is essential. Maintaining a clean diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits and vegetables, and reducing processed foods, can also support your immune system. Regular exercise strengthens the immune system, although vigorous exercise outdoors during high pollen counts should be avoided.
- Regular vacuuming and dusting: Use a HEPA filter vacuum.
- Washing bedding frequently: Use hot water to kill dust mites.
- Air purifiers with HEPA filters: Can reduce airborne allergens.
Natural Remedies
Some people find relief from allergy symptoms using natural remedies. These are often complementary therapies and should not replace medical advice or prescription medications. Examples include local honey (thought to offer some desensitization), certain herbal remedies (like nettle), and acupuncture. However, the effectiveness of these methods is not consistently proven, and it’s important to discuss them with your doctor before trying them.
- Local honey: May offer mild relief, but efficacy is not definitively proven.
- Herbal remedies: Consult a healthcare professional before use.
- Acupuncture: Some individuals find it helpful for managing allergy symptoms.
Hydration and Diet
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health and can help thin mucus, which can improve symptoms associated with allergies. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients to support a healthy immune system. While no specific foods "flush" allergies, a healthy diet supports the body's natural ability to manage inflammation. Avoid known food allergens if you have food allergies.
- Drink plenty of water: Aids in thinning mucus.
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Eliminate trigger foods: If you have food allergies, avoid those foods entirely.
Does drinking water help with allergies?

Drinking enough water can be beneficial for overall health, and while it won't directly cure allergies, it may help manage some allergy symptoms indirectly. Dehydration can worsen allergy symptoms, as it can thicken mucus, making it harder to clear from your sinuses. This can lead to increased congestion and irritation. Staying well-hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier to expel irritants. However, it's crucial to understand that water alone is not a treatment for allergies. It's a supportive measure that can improve your body's ability to cope with allergy symptoms.
How Hydration Impacts Mucus Production
The body uses water to produce mucus, a vital substance that traps allergens and other irritants in the nasal passages. When you're dehydrated, your mucus becomes thicker and stickier. This makes it harder for your body to remove allergens effectively, leading to increased congestion and the worsening of allergy symptoms like runny nose and sinus pressure. Adequate hydration thins the mucus, facilitating its removal and alleviating these symptoms.
- Thicker mucus traps allergens more effectively, leading to prolonged irritation.
- Thin mucus allows for easier expulsion of irritants and allergens.
- Dehydration contributes to thicker mucus and increased allergy symptoms.
The Role of Water in Immune Function
Your immune system relies on proper hydration to function optimally. Water helps transport immune cells throughout your body, enabling them to effectively combat allergens and other invaders. When dehydrated, your immune system may not be as efficient, potentially making you more susceptible to the effects of allergens. While water won't directly neutralize allergens, supporting your immune system through hydration is crucial for managing allergy responses.
- Proper hydration supports efficient immune cell transportation.
- Dehydration can compromise immune system function.
- A strong immune system is vital for effectively managing allergy responses.
Water and Inflammation
Allergies often involve inflammation in the respiratory system and other areas of the body. Chronic dehydration can exacerbate inflammation, potentially worsening allergy symptoms. While water doesn't directly reduce inflammation related to allergies, maintaining sufficient hydration helps to support the body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes. It’s part of overall healthy body function which supports reducing inflammation.
- Inflammation is a key component of allergic responses.
- Dehydration can intensify inflammation.
- Hydration supports the body's natural inflammatory processes.
Water as a Complement to Allergy Treatment
Drinking enough water shouldn't replace prescribed allergy medications or other treatments. It works best as a supporting measure alongside other strategies for managing allergy symptoms. For instance, it can be beneficial in conjunction with antihistamines or nasal sprays. Using water to help manage allergy symptoms is part of a more holistic approach to allergy management.
- Water is not a replacement for prescribed allergy medications.
- Water complements other allergy treatments.
- A holistic approach to allergy management includes hydration.
Misconceptions About Water and Allergies
It's important to understand that water alone cannot cure or eliminate allergies. It's a supportive measure, not a treatment. Many believe drinking water can directly flush out allergens, but this isn't entirely accurate. Water primarily helps to thin mucus and support overall bodily functions that aid in managing the symptoms. It's crucial to manage expectations and rely on proper medical advice for allergy management.
- Water does not directly flush out allergens.
- Water primarily aids in symptom management.
- It's crucial to follow medical advice for effective allergy management.
How long does it typically take for allergy symptoms to improve after starting treatment?
The time it takes for allergy symptoms to improve after starting treatment varies significantly depending on several factors. These factors include the severity of your allergies, the specific allergen causing your reaction, the type of treatment you're using, and your overall health. For example, someone with mild seasonal allergies might experience noticeable relief within a few days of starting an over-the-counter antihistamine. However, individuals with more severe allergies, such as those with asthma triggered by allergies, might require several weeks or even months of treatment, potentially including prescription medications and allergy shots, to achieve significant improvement. Consistency in taking your medication as prescribed is crucial. Missing doses can significantly delay recovery. It’s also important to note that some treatments, like immunotherapy, work by gradually building tolerance, meaning that improvement may be gradual and not immediate. If you're not seeing improvement after a reasonable amount of time (this timeframe should be discussed with your doctor), it's important to follow up with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan. They may need to modify your medication, recommend additional treatments, or investigate other possible underlying conditions. Remember, patience is key, but proactive communication with your doctor is essential for optimal results.
What are some home remedies to speed up allergy recovery?
While home remedies can't replace medical treatment for severe allergies, they can offer supportive relief and potentially accelerate recovery when used in conjunction with prescribed medications. Keeping your home clean is crucial; regular vacuuming, dusting, and washing of bedding can significantly reduce allergen exposure. Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in your home and car can also trap airborne allergens. Showering before bed can remove allergens that have accumulated on your skin throughout the day. Rinsing your nasal passages with a saline solution can help clear out irritants and allergens. Staying hydrated is important, as dehydration can exacerbate allergy symptoms. Some people find relief from applying a cool compress to itchy eyes or skin. Over-the-counter remedies like saline nasal sprays, lubricating eye drops, and antihistamine creams can provide additional relief. However, it’s vital to consult your doctor before using any home remedies, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications, to avoid potential interactions or complications. While these home remedies can be helpful in managing symptoms, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice and treatment, particularly if your allergies are severe or persistent.
Are there any foods or drinks that can help alleviate allergy symptoms?
While no specific food or drink can magically cure allergies, certain foods and drinks can help alleviate symptoms or support the immune system. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and dark chocolate, can help reduce inflammation, a key component of allergic reactions. Foods high in Vitamin C, like citrus fruits and bell peppers, can strengthen the immune system and aid in recovery. Staying hydrated with plenty of water is crucial, as dehydration can worsen allergy symptoms. Some people find that certain foods, such as those rich in quercetin (like onions and apples), may offer some antihistamine properties, although further research is needed to confirm their effectiveness. However, it's essential to remember that individual responses vary, and what helps one person might not help another. Furthermore, it's important to be mindful of potential food allergies and avoid any foods known to trigger reactions. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is generally recommended for overall health and may indirectly support allergy recovery by boosting the immune system. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice, especially if you have specific concerns or underlying health conditions.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for allergy symptoms?
While many allergy symptoms can be managed at home, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if your symptoms indicate a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate emergency treatment. Signs of anaphylaxis include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, hives, rapid pulse, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. Do not hesitate to call emergency services (911 in the US) if you experience any of these symptoms. Additionally, you should seek medical attention if your allergy symptoms are severe and unresponsive to over-the-counter medications. This might include persistent and severe coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or difficulty breathing. If your allergy symptoms significantly impact your daily life, making it difficult to work, sleep, or participate in normal activities, you should consult your doctor to discuss possible treatment options. Similarly, if you experience any new or worsening symptoms, it's best to seek medical advice to rule out any other underlying conditions or complications. Early intervention and proper diagnosis are crucial for effective allergy management and prevention of potentially serious complications.
Deja una respuesta