Is eating 10 eggs a day bad

In the realm of health and nutrition, eggs have long held a controversial place. Some extol their nutritional benefits, while others raise concerns about their potential risks. One question that has sparked considerable debate is whether consuming 10 eggs per day is harmful or beneficial. This article will delve into the evidence-based research to explore the potential impacts of such high egg intake on various health parameters. We will examine both the potential advantages and disadvantages, providing a comprehensive analysis of the available scientific knowledge to answer the question: 'Is eating 10 eggs a day bad?'
Is Eating 10 Eggs a Day Really That Bad?
The question of whether eating 10 eggs a day is harmful is complex and doesn't have a simple yes or no answer. It depends heavily on several individual factors, including your overall diet, health status, and activity level. While eggs are a nutritional powerhouse packed with protein, vitamins, and minerals, consuming such a large quantity daily could potentially lead to negative consequences. Let's break down the potential benefits and drawbacks.
Cholesterol Concerns: The Egg and Heart Health Debate
For many years, eggs have carried a reputation for being high in cholesterol, leading to concerns about increased risk of heart disease. However, current research suggests a more nuanced view. While eggs do contain cholesterol, dietary cholesterol's effect on blood cholesterol levels is less significant than previously thought. Your body's own cholesterol production is a much more influential factor. However, consuming 10 eggs daily might still contribute to a high overall cholesterol intake, especially if combined with other cholesterol-rich foods. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or high cholesterol should consult their doctor before dramatically increasing their egg consumption.
Nutrient Overload: Too Much of a Good Thing?
Eggs are packed with essential nutrients like protein, vitamin D, choline, and various minerals. While these are beneficial, consuming 10 eggs a day could lead to a nutrient imbalance and potential toxicity from excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals. For instance, excessive vitamin D can lead to hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by high blood calcium levels. Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial to avoid these potential problems.
Protein Intake and Kidney Function
A diet high in protein, like one including 10 eggs a day, could potentially stress the kidneys, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. The kidneys work to filter waste products from protein metabolism, and excessive protein intake can overburden this system. While healthy individuals might tolerate this, those with kidney issues should exercise caution and consult their doctor.
Saturated Fat and Weight Management
Eggs, especially the yolk, contain saturated fat. While saturated fat is not as demonized as it once was, consuming large quantities can still contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of certain health problems. 10 eggs a day represents a significant amount of saturated fat, which needs to be considered in the context of your overall dietary fat intake and calorie goals. If not balanced with adequate exercise and a calorie deficit, this could contribute to weight gain.
Individual Variations and Underlying Health Conditions
It's crucial to remember that individual responses to diet vary greatly. What might be tolerated by one person could be problematic for another. Pre-existing health conditions like kidney disease, high cholesterol, or diabetes can significantly impact how your body processes the nutrients in 10 eggs daily. Always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes, particularly if you have any health concerns.
| Factor | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | Minimal impact on blood cholesterol for healthy individuals | Potential contribution to high cholesterol for susceptible individuals |
| Protein | High protein intake supports muscle building and satiety | Potential strain on kidneys, especially in those with pre-existing conditions |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich source of essential nutrients | Risk of nutrient overload and toxicity from excessive intake |
| Saturated Fat | Provides energy | Potential contribution to weight gain and increased risk of certain health problems |
Is Eating 10 Eggs a Day Really That Bad?
The question of whether eating 10 eggs a day is harmful is complex and doesn't have a simple yes or no answer. It depends heavily on several individual factors, including your overall diet, health status, and activity level. While eggs are a nutritional powerhouse packed with protein, vitamins, and minerals, consuming such a large quantity daily could potentially lead to negative consequences. Let's break down the potential benefits and drawbacks.
Cholesterol Concerns: The Egg and Heart Health Debate
For many years, eggs have carried a reputation for being high in cholesterol, leading to concerns about increased risk of heart disease. However, current research suggests a more nuanced view. While eggs do contain cholesterol, dietary cholesterol's effect on blood cholesterol levels is less significant than previously thought. Your body's own cholesterol production is a much more influential factor. However, consuming 10 eggs daily might still contribute to a high overall cholesterol intake, especially if combined with other cholesterol-rich foods. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or high cholesterol should consult their doctor before dramatically increasing their egg consumption.
Nutrient Overload: Too Much of a Good Thing?
Eggs are packed with essential nutrients like protein, vitamin D, choline, and various minerals. While these are beneficial, consuming 10 eggs a day could lead to a nutrient imbalance and potential toxicity from excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals. For instance, excessive vitamin D can lead to hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by high blood calcium levels. Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial to avoid these potential problems.
Protein Intake and Kidney Function
A diet high in protein, like one including 10 eggs a day, could potentially stress the kidneys, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. The kidneys work to filter waste products from protein metabolism, and excessive protein intake can overburden this system. While healthy individuals might tolerate this, those with kidney issues should exercise caution and consult their doctor.
Saturated Fat and Weight Management
Eggs, especially the yolk, contain saturated fat. While saturated fat is not as demonized as it once was, consuming large quantities can still contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of certain health problems. 10 eggs a day represents a significant amount of saturated fat, which needs to be considered in the context of your overall dietary fat intake and calorie goals. If not balanced with adequate exercise and a calorie deficit, this could contribute to weight gain.
Individual Variations and Underlying Health Conditions
It's crucial to remember that individual responses to diet vary greatly. What might be tolerated by one person could be problematic for another. Pre-existing health conditions like kidney disease, high cholesterol, or diabetes can significantly impact how your body processes the nutrients in 10 eggs daily. Always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes, particularly if you have any health concerns.
| Factor | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | Minimal impact on blood cholesterol for healthy individuals | Potential contribution to high cholesterol for susceptible individuals |
| Protein | High protein intake supports muscle building and satiety | Potential strain on kidneys, especially in those with pre-existing conditions |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich source of essential nutrients | Risk of nutrient overload and toxicity from excessive intake |
| Saturated Fat | Provides energy | Potential contribution to weight gain and increased risk of certain health problems |
What happens if we eat 10 eggs a day?

What Happens if We Eat 10 Eggs a Day?
Consuming 10 eggs daily significantly exceeds the recommended dietary intake of eggs for most individuals. The consequences depend on various factors including overall diet, individual health, and pre-existing conditions. While eggs offer nutritional benefits like protein and certain vitamins, such a high intake can lead to several potential adverse effects. The most significant risk is an excessive cholesterol intake, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease. Other potential issues stem from the high saturated fat content and the risk of nutrient imbalances due to over-reliance on eggs as a primary food source. The body can only process a limited amount of cholesterol and nutrients efficiently; excess intake can overwhelm these systems and lead to various health problems.
Cholesterol Levels and Heart Health
Eating 10 eggs a day will dramatically increase your cholesterol intake. Each egg contains approximately 186mg of cholesterol. Consuming ten would result in 1860mg, far exceeding the recommended daily intake. This substantial increase in dietary cholesterol can significantly raise LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels, increasing your risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and other cardiovascular problems. This risk is amplified for individuals already predisposed to high cholesterol or heart disease.
- Increased LDL cholesterol: This contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow.
- Elevated risk of heart disease: Higher LDL cholesterol levels are a major risk factor for heart attacks and strokes.
- Potential for increased blood pressure: High cholesterol can contribute to hypertension.
Nutrient Imbalances and Deficiencies
Relying heavily on eggs as a primary food source for 10 eggs a day can lead to nutrient imbalances. While eggs provide some vitamins and minerals, they lack others crucial for a balanced diet. This could result in deficiencies of essential nutrients not found in abundance in eggs. Overconsumption can also hinder the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals from other foods you might eat. A diet centered around eggs may lack fiber, certain vitamins and minerals found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Vitamin C deficiency: Eggs are not a significant source of Vitamin C.
- Fiber deficiency: A lack of fiber can lead to digestive problems like constipation.
- Potential for other micronutrient deficiencies: A varied diet is necessary to obtain all essential micronutrients.
Digestive Issues
Consuming such a large quantity of eggs daily can overwhelm your digestive system. Some individuals may experience digestive upset, such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation. The high protein content can also place a strain on the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering metabolic waste products. This can be particularly concerning for people with pre-existing kidney issues.
- Bloating and gas: Due to the high protein and fat content.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Depending on individual tolerance and gut microbiome.
- Strain on the kidneys: Increased metabolic workload can stress kidney function.
Weight Gain
Ten eggs a day represents a significant caloric intake. Eggs, while nutritious, are also calorie-dense. Consistent consumption at this level could lead to weight gain, especially if not balanced with sufficient physical activity and a controlled overall calorie intake. This surplus of calories can be stored as fat, resulting in an increase in body weight and associated health risks.
- High caloric density: Eggs provide a substantial number of calories per serving.
- Potential for weight gain: Increased calorie intake exceeding expenditure.
- Increased risk of obesity-related diseases: Weight gain increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease and other conditions.
Other Potential Risks
Beyond cholesterol, heart health, and digestive issues, other potential concerns include the risk of vitamin and mineral imbalances, allergic reactions (although rare), and the potential for increased risk of certain cancers, although research on this is ongoing and not definitive. The impact will be highly individualized and dependent on many factors like genetics, health status and overall lifestyle.
- Increased risk of certain cancers (limited evidence): Some studies have suggested potential links, requiring further research.
- Allergic reactions: While uncommon, some individuals are allergic to eggs.
- Nutrient toxicity: Consuming excess amounts of certain nutrients can be harmful.
What happens if you eat 12 eggs a day?

What Happens If You Eat 12 Eggs a Day?
Consuming 12 eggs daily significantly exceeds the recommended intake for most individuals. The consequences depend on various factors like your overall diet, activity level, pre-existing health conditions, and the type of eggs consumed (e.g., free-range, organic). However, several potential negative impacts are likely.
High Cholesterol Levels
Eggs are a good source of protein and nutrients, but they are also relatively high in cholesterol. Eating 12 eggs daily would drastically increase your cholesterol intake, potentially leading to high blood cholesterol levels. This can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. High cholesterol may not directly cause noticeable symptoms initially but poses a long-term health risk.
- Increased LDL ("bad") cholesterol: This type of cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Elevated risk of cardiovascular disease: High LDL cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart attacks and strokes.
- Potential need for medication: If cholesterol levels become dangerously high, medication may be necessary to manage it.
Nutrient Imbalance
While eggs provide some essential nutrients, relying solely on them for a substantial portion of your daily caloric intake can lead to nutritional deficiencies. Your diet would lack the variety of vitamins, minerals, and fiber found in other food groups like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This imbalance can negatively impact your overall health and well-being.
- Lack of fiber: Eggs lack fiber, crucial for digestive health and preventing constipation.
- Insufficient vitamins and minerals: Many essential vitamins and minerals found in fruits and vegetables would be missing.
- Potential for fatigue and weakness: Nutrient deficiencies can manifest as fatigue, weakness, and impaired immune function.
Digestive Issues
Consuming such a large quantity of eggs can overburden your digestive system, leading to various problems. Some people may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating, stomach cramps, nausea, or diarrhea. The high protein content, in particular, can be difficult for some individuals to digest in such large amounts.
- Bloating and gas: Difficulty digesting the large amount of protein.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Imbalance in gut flora and lack of fiber.
- Stomach pain and discomfort: Overburdening of the digestive system.
Weight Gain
Eggs are relatively high in calories, and consuming 12 per day will significantly increase your daily calorie intake. This surplus of calories, unless balanced with a very low-calorie intake from other food sources and a high level of physical activity, is likely to result in weight gain.
- Calorie surplus: 12 eggs contain a substantial number of calories.
- Increased body fat: Excess calories are stored as fat.
- Potential for obesity-related health issues: Weight gain increases the risk of various health problems.
Increased Risk of Certain Diseases
While the link between egg consumption and certain diseases is complex and not fully understood, consuming such a high quantity may increase the risk of some conditions beyond heart disease. The high saturated fat and cholesterol content, combined with the potential for nutrient imbalances, may contribute to an increased risk of some cancers and other chronic illnesses.
- Certain types of cancer: Some studies suggest a link between high cholesterol and certain cancers.
- Type 2 diabetes: High saturated fat intake can contribute to insulin resistance.
- Kidney stones: High protein intake may increase the risk of kidney stones in some individuals.
How many eggs is too much in a day?
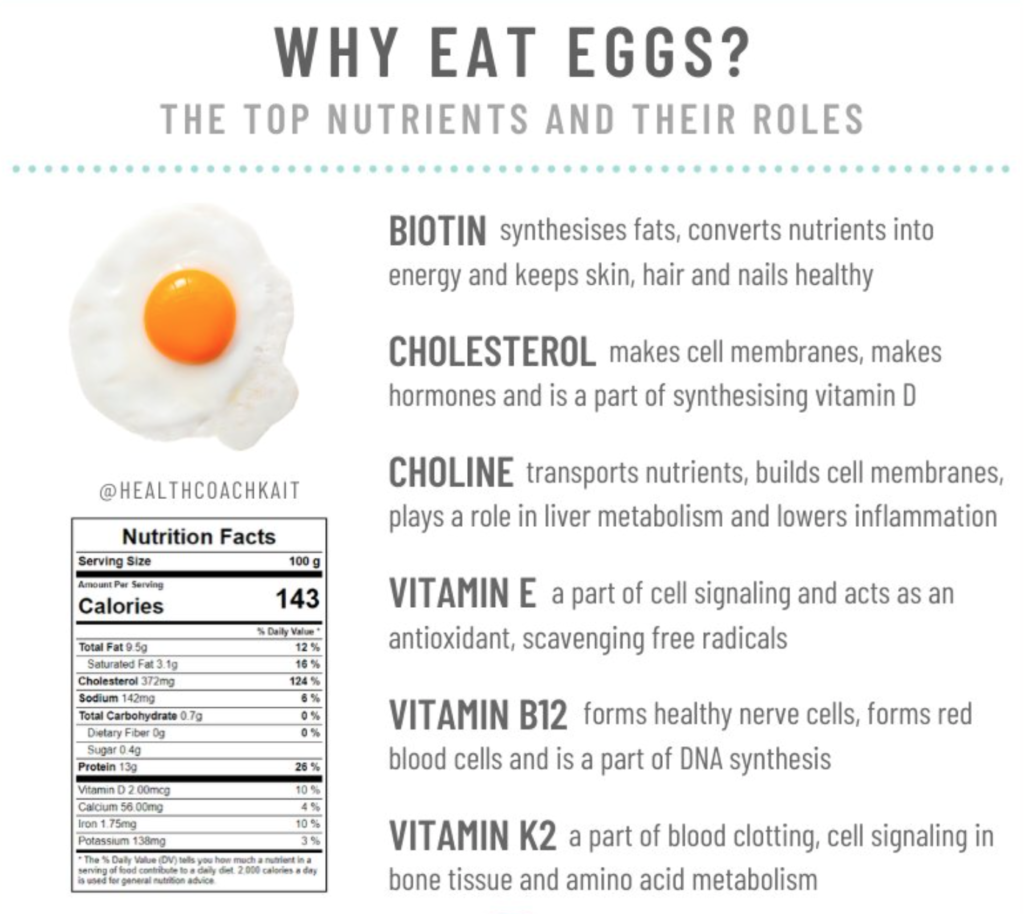
There's no single answer to how many eggs are too many in a day. The ideal number depends on several individual factors, including overall diet, health conditions, activity level, and personal goals. While some people might tolerate several eggs daily without issue, others might experience negative consequences even with one. Generally, most health organizations don't recommend exceeding more than one or two whole eggs per day, focusing on incorporating eggs as part of a balanced diet. However, this is a guideline, not a strict limit.
Cholesterol Concerns and Egg Consumption
For many years, eggs were demonized due to their cholesterol content. However, current research indicates that dietary cholesterol has a less significant impact on blood cholesterol levels than previously thought. While eggs do contain cholesterol, the impact on individual cholesterol levels varies greatly. Factors like genetics, saturated fat intake, and overall dietary pattern play a much larger role. It's crucial to consider your personal cholesterol levels and discuss egg consumption with your doctor, particularly if you have high cholesterol or a family history of heart disease.
- Consult your doctor before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
- Focus on overall dietary cholesterol intake, not just eggs. Limit saturated and trans fats for better cholesterol management.
- Regular blood tests can monitor your cholesterol levels and help determine the appropriate egg intake for you.
Egg Consumption and Heart Health
The relationship between egg consumption and heart health is complex and not fully understood. While some studies suggest a correlation between high egg intake and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, other studies find no such link or even a positive association with certain heart health markers. The type of fat consumed alongside the eggs is critical; consuming eggs with saturated or trans fats might negatively impact heart health more than consuming them with healthier fats like olive oil or unsaturated fats.
- Prioritize consuming eggs with healthy fats instead of unhealthy ones to maximize health benefits.
- Consider the overall nutritional context of your diet. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can offset any potential negative impacts of higher egg consumption.
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve heart health, regardless of egg intake.
Protein Intake from Eggs
Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein. One large egg provides roughly 6 grams of protein, crucial for muscle growth and repair, satiety, and overall health. However, it's essential to balance protein intake with other dietary needs, ensuring sufficient intake of carbohydrates, healthy fats, and micronutrients. Excessive protein intake from any source, including eggs, can have negative consequences.
- Don't rely solely on eggs for protein; include a variety of protein sources in your diet.
- Consider your individual protein needs based on factors like age, activity level, and body composition.
- Excessive protein intake can strain the kidneys and lead to dehydration; ensure adequate water consumption.
Individual Tolerance and Dietary Preferences
Individual responses to egg consumption vary significantly. Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as bloating or gas, with even a single egg, while others may consume multiple eggs daily without any problems. Pay attention to your body's signals; if you experience any digestive discomfort after consuming eggs, reduce your intake. Personal dietary preferences also play a vital role; you should incorporate eggs into your diet only if you enjoy them and they fit your overall culinary preferences.
- Listen to your body. If eggs cause discomfort, reduce your consumption or avoid them altogether.
- Choose egg preparation methods that you enjoy to promote consistent consumption of eggs as part of a healthy diet.
- Don't feel pressured to eat eggs if you don't enjoy them or experience negative effects.
Other Nutritional Considerations Beyond Cholesterol
While cholesterol is often the main concern regarding egg consumption, eggs are also a good source of other nutrients, including choline, vitamin D, and several B vitamins. A balanced diet should prioritize a wide array of nutritious foods, not just focusing on individual nutrients like those found in eggs. Therefore, eggs should be considered part of a balanced diet, rather than a primary source of any specific nutrient.
- Focus on consuming a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Supplementing with specific vitamins and minerals might be necessary depending on individual dietary needs and deficiencies.
- Consider the overall nutritional profile of your diet and how eggs fit into your balanced eating plan.
Can bodybuilders eat 10 eggs a day?

Whether a bodybuilder can eat 10 eggs a day depends on several factors and isn't a universally applicable "yes" or "no." There's no inherent danger in consuming that many eggs, but it's crucial to consider individual needs, dietary goals, and potential health implications.
Egg Nutritional Profile
Eggs are a fantastic source of protein, crucial for muscle growth and repair. They also provide essential nutrients like choline, vitamin D, and various minerals. However, 10 eggs represent a significant caloric intake and a high concentration of cholesterol. While dietary cholesterol's impact on blood cholesterol is less significant than previously thought, it’s still a factor to consider.
- High protein content: Excellent for muscle building and repair.
- Essential nutrients: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and choline.
- High cholesterol: Should be monitored, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Caloric Intake and Macronutrient Balance
Ten eggs constitute a substantial number of calories, likely exceeding the daily needs for many individuals, even bodybuilders. This could lead to unwanted weight gain if not factored into their overall calorie budget. It is vital to ensure a balanced macronutrient profile – adequate protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates – to support both muscle growth and overall health. Simply focusing on protein without considering the other macronutrients is detrimental.
- High calorie count: Can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with other dietary choices.
- Macronutrient balance: Essential to support both muscle growth and overall well-being.
- Calorie deficit or surplus: 10 eggs should be integrated into a well-planned dietary strategy considering the individual's goals.
Individual Dietary Needs and Goals
A bodybuilder's specific dietary requirements vary greatly depending on factors such as training intensity, body weight, goals (muscle gain, fat loss, maintenance), and overall health. What works for one individual might not work for another. Consulting a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist is highly recommended to personalize a diet plan tailored to specific needs and objectives. This professional can help determine if 10 eggs a day are appropriate within the broader dietary context.
- Training intensity: Influences calorie and macronutrient needs.
- Body weight and composition: Dictates caloric requirements and macronutrient ratios.
- Individual goals: Muscle gain, fat loss, or maintenance influence dietary strategies.
Potential Health Risks and Considerations
While eggs offer many benefits, excessive consumption can present some risks. The high cholesterol content should be considered, especially for individuals with high cholesterol levels or a family history of heart disease. Additionally, consuming a monotonous diet high in eggs could lead to nutrient deficiencies if other food groups are neglected. Gut health is also a factor to consider as excessive egg consumption can, for some individuals, cause digestive discomfort.
- High cholesterol levels: Could exacerbate existing health conditions.
- Nutrient deficiencies: A diverse diet is crucial to avoid imbalances.
- Digestive issues: Excessive egg consumption may cause discomfort in some individuals.
Alternatives to Excessively High Egg Intake
There are alternative ways to obtain the protein and other nutrients found in eggs. Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and various dairy products provide excellent sources of protein. Incorporating a variety of protein sources into the diet is generally a healthier and more sustainable approach than relying heavily on a single food source, like eggs.
- Lean meats and poultry: Provide high-quality protein with various micronutrients.
- Fish: Offers protein and essential omega-3 fatty acids.
- Legumes and beans: Good sources of plant-based protein and fiber.
Is eating 10 eggs a day bad for my cholesterol?
Consuming 10 eggs daily could significantly impact your cholesterol levels, but the effect varies depending on individual factors. While eggs are rich in cholesterol, the impact on blood cholesterol is less dramatic than previously thought. Many studies show that for the majority of people, dietary cholesterol has a minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels. However, individuals with family history of high cholesterol or pre-existing high cholesterol should exercise caution. The cholesterol in eggs primarily affects LDL ("bad") cholesterol, but also HDL ("good") cholesterol. The net effect depends on your body's response and other dietary factors. For example, if you consume a diet high in saturated and trans fats alongside 10 eggs a day, the overall impact on your cholesterol could be negative. Conversely, if your diet is low in saturated fats and rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber, the impact might be less detrimental. It’s crucial to consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized advice based on your specific health condition and lipid profile before making significant dietary changes like this. They can help assess your risk and advise on whether this level of egg consumption is suitable for you.
Are there other health risks associated with eating so many eggs?
While eggs are a nutritious food packed with protein, vitamins, and minerals, consuming 10 a day might present several health risks beyond cholesterol. High protein intake, although generally beneficial, can strain your kidneys, especially if you have pre-existing kidney problems. Too much protein can also lead to dehydration if you don’t consume enough water. Furthermore, consuming that much of a single food source can lead to nutritional imbalances, as you might be missing out on other essential vitamins and minerals found in a varied diet. The high amount of choline in eggs, while generally beneficial, could potentially lead to unpleasant side effects like diarrhea or digestive upset in some individuals if consumed in excess. Additionally, the saturated fat content in 10 eggs could contribute to weight gain if not balanced with sufficient physical activity. Ultimately, excessive consumption of any food can be detrimental to your overall health. Diversity in your diet is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being.
What are the benefits of eating eggs, and could 10 a day offer amplified benefits?
Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues. They're also a good source of choline, important for brain health and liver function; vitamin D, crucial for bone health and immune function; and lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that protect eye health. While 10 eggs a day would provide a significant boost of these nutrients, the benefits do not necessarily increase proportionally. In fact, exceeding the recommended intake can lead to negative consequences as previously mentioned. The benefits of eggs are best realized as part of a balanced diet. Consuming a moderate number of eggs alongside a variety of other nutrient-rich foods ensures you obtain a wide range of vitamins and minerals, optimizing your health outcomes without the risks of overconsumption. Instead of aiming for such a high number of eggs daily, focus on incorporating them strategically into a diversified and healthy eating plan.
Can I eat 10 eggs a day if I'm trying to lose weight or build muscle?
While eggs are a good source of protein crucial for muscle building, consuming 10 a day won't automatically lead to significant weight loss or muscle gain. The calorie intake from 10 eggs is substantial, and if you don't adjust your overall calorie consumption accordingly, you might gain weight instead of losing it. Similarly, muscle growth requires a balanced approach involving consistent strength training alongside adequate protein intake. While 10 eggs would provide a large amount of protein, exceeding the required amount doesn't automatically translate to faster or more significant muscle growth. Furthermore, the high cholesterol and saturated fat content in 10 eggs could potentially hinder weight loss efforts. A more effective strategy for weight loss or muscle building would be to incorporate eggs into a balanced diet with a calculated calorie deficit or surplus, respectively, combined with a suitable exercise plan. Over-reliance on a single food source, even one as nutritious as eggs, is generally not recommended for achieving these fitness goals.
Deja una respuesta