What allergy medicine is best

In the realm of allergy sufferers, finding the most effective allergy medicine can be a constant quest. Whether you're battling sneezing fits, itchy eyes, or a stuffy nose, the search for relief can be daunting amidst the multitude of options available. From over-the-counter tablets to prescription medications, the question of "What allergy medicine is best?" lingers in the minds of countless individuals seeking solace from their relentless symptoms.
Finding the Best Allergy Medicine for You
There's no single "best" allergy medicine, as the ideal choice depends heavily on individual factors like the type of allergy, severity of symptoms, other health conditions, and personal preferences. What works wonders for one person might be ineffective or even cause side effects for another. It's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs. They can help you understand the root cause of your allergies and recommend the safest and most effective medication.
Understanding Different Allergy Medications
Allergy medications generally fall into two main categories: antihistamines and decongestants. Antihistamines work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction, which causes symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose. Decongestants help to relieve stuffiness by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages. Some medications combine both antihistamines and decongestants. There are also other types of allergy medications, such as mast cell stabilizers (like cromolyn sodium) and leukotriene inhibitors (like montelukast), which are often used for long-term allergy control or for more severe cases.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) vs. Prescription Medications
Many effective allergy medications are available over-the-counter (OTC), including various antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine) and decongestants (like pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine). However, for more severe allergies or if OTC medications aren't providing sufficient relief, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as stronger antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids. Prescription medications can often offer more targeted relief and may be necessary for individuals with chronic or severe allergies.
Choosing the Right Antihistamine
Several antihistamines are available, each with its own profile of effectiveness and side effects. First-generation antihistamines (like diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine) are often more sedating but can provide rapid relief. Second-generation antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine) are generally less sedating and can be taken daily for long-term allergy management. The best choice depends on your individual tolerance for drowsiness and your need for long-acting relief.
Considering Nasal Sprays and Other Treatments
Besides oral medications, nasal sprays can be highly effective for treating allergy symptoms. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse allergens from the nasal passages, while nasal corticosteroid sprays (like fluticasone and mometasone) are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can reduce nasal inflammation and congestion. Other treatment options include eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis (eye allergy), and immunotherapy (allergy shots) for long-term allergy management in severe cases. Your doctor can discuss the suitability of these options based on your specific allergy needs.
Side Effects and Interactions
It's essential to be aware of potential side effects associated with allergy medications. Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, headache, and upset stomach. Some medications may interact with other drugs, so it's crucial to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications and supplements you are taking. Always read the label carefully and follow the dosage instructions precisely.
| Medication Type | Examples | Common Side Effects | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-generation antihistamines | Diphenhydramine, Chlorpheniramine | Drowsiness, dry mouth | Rapid relief, inexpensive | Sedating, may cause other side effects |
| Second-generation antihistamines | Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine | Less sedating | Less drowsiness, long-lasting relief | May be more expensive |
| Decongestants | Pseudoephedrine, Phenylephrine | Increased blood pressure, insomnia | Effective for nasal congestion | Can cause nervousness and sleep problems |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Fluticasone, Mometasone | Nosebleeds, irritation | Powerful anti-inflammatory effects | Takes several days to work fully |
Finding the Best Allergy Medicine for You
There's no single "best" allergy medicine, as the ideal choice depends heavily on individual factors like the type of allergy, severity of symptoms, other health conditions, and personal preferences. What works wonders for one person might be ineffective or even cause side effects for another. It's crucial to consult a doctor or allergist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs. They can help you understand the root cause of your allergies and recommend the safest and most effective medication.
Understanding Different Allergy Medications
Allergy medications generally fall into two main categories: antihistamines and decongestants. Antihistamines work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction, which causes symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose. Decongestants help to relieve stuffiness by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages. Some medications combine both antihistamines and decongestants. There are also other types of allergy medications, such as mast cell stabilizers (like cromolyn sodium) and leukotriene inhibitors (like montelukast), which are often used for long-term allergy control or for more severe cases.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) vs. Prescription Medications
Many effective allergy medications are available over-the-counter (OTC), including various antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine) and decongestants (like pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine). However, for more severe allergies or if OTC medications aren't providing sufficient relief, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as stronger antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids. Prescription medications can often offer more targeted relief and may be necessary for individuals with chronic or severe allergies.
Choosing the Right Antihistamine
Several antihistamines are available, each with its own profile of effectiveness and side effects. First-generation antihistamines (like diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine) are often more sedating but can provide rapid relief. Second-generation antihistamines (like cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine) are generally less sedating and can be taken daily for long-term allergy management. The best choice depends on your individual tolerance for drowsiness and your need for long-acting relief.
Considering Nasal Sprays and Other Treatments
Besides oral medications, nasal sprays can be highly effective for treating allergy symptoms. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse allergens from the nasal passages, while nasal corticosteroid sprays (like fluticasone and mometasone) are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can reduce nasal inflammation and congestion. Other treatment options include eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis (eye allergy), and immunotherapy (allergy shots) for long-term allergy management in severe cases. Your doctor can discuss the suitability of these options based on your specific allergy needs.
Side Effects and Interactions
It's essential to be aware of potential side effects associated with allergy medications. Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, headache, and upset stomach. Some medications may interact with other drugs, so it's crucial to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications and supplements you are taking. Always read the label carefully and follow the dosage instructions precisely.
| Medication Type | Examples | Common Side Effects | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-generation antihistamines | Diphenhydramine, Chlorpheniramine | Drowsiness, dry mouth | Rapid relief, inexpensive | Sedating, may cause other side effects |
| Second-generation antihistamines | Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine | Less sedating | Less drowsiness, long-lasting relief | May be more expensive |
| Decongestants | Pseudoephedrine, Phenylephrine | Increased blood pressure, insomnia | Effective for nasal congestion | Can cause nervousness and sleep problems |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Fluticasone, Mometasone | Nosebleeds, irritation | Powerful anti-inflammatory effects | Takes several days to work fully |
What is the most effective anti-allergy medicine?
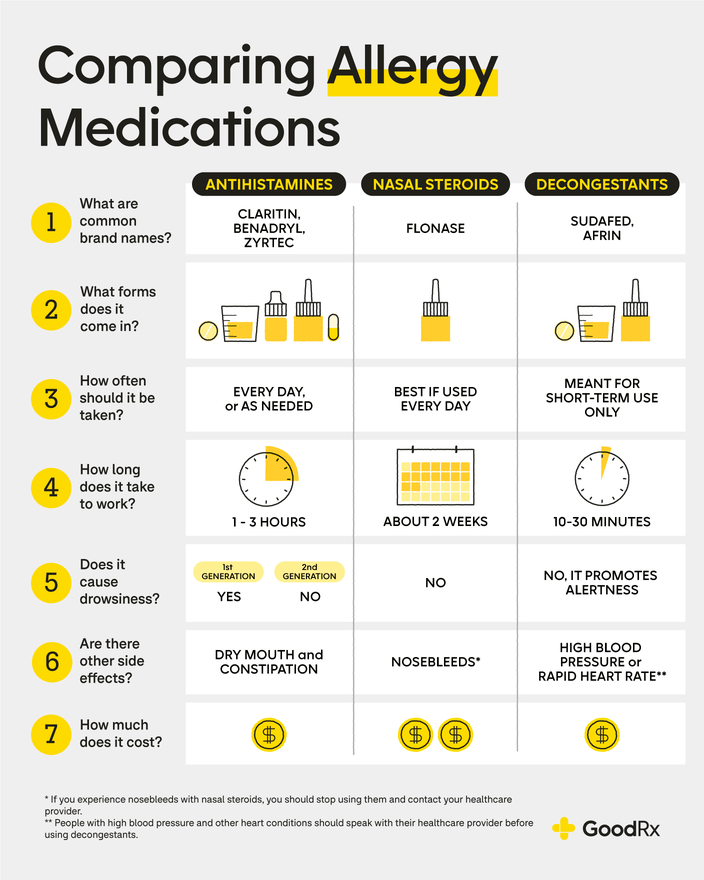
There is no single "most effective" anti-allergy medicine, as the best choice depends heavily on the individual, the specific allergen, and the severity of the allergic reaction. Effectiveness also varies from person to person. What works well for one individual may be ineffective for another. The choice often involves a combination of factors and potentially multiple medications.
Types of Anti-Allergy Medications
Anti-allergy medications are broadly categorized into several types, each targeting different aspects of the allergic response. Antihistamines block the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants constrict blood vessels in the nasal passages, relieving stuffiness. Leukotriene modifiers block the action of leukotrienes, inflammatory chemicals involved in allergy symptoms. Corticosteroids (both nasal sprays and oral) reduce inflammation in the airways and nasal passages. Immunotherapy (allergy shots) aims to gradually desensitize the body to specific allergens over time.
- Antihistamines: Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine (Allegra, Zyrtec, Claritin)
- Decongestants: Pseudoephedrine, Phenylephrine
- Leukotriene Modifiers: Montelukast (Singulair)
- Corticosteroids: Fluticasone (Flonase), Budesonide (Rhinocort)
- Immunotherapy: Allergen-specific immunotherapy
Over-the-Counter vs. Prescription Medications
Many effective anti-allergy medications are available over-the-counter (OTC), such as antihistamines and some decongestants. However, for more severe allergies or persistent symptoms, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications like leukotriene modifiers, higher-dose corticosteroids, or immunotherapy. Self-treating severe allergies can be dangerous, so it's crucial to seek medical advice if symptoms are significant or don't improve with OTC medications. A doctor can also determine the underlying cause of the allergy and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
- OTC medications are generally safer for mild allergies.
- Prescription medications offer stronger relief for more severe allergies.
- A doctor can diagnose the allergy and prescribe the most appropriate treatment.
Considering Individual Needs and Allergies
The most effective anti-allergy medicine is highly personalized. Factors like the type of allergy (e.g., seasonal allergies, pet allergies, food allergies), the severity of symptoms, and the presence of other medical conditions all influence the choice of medication. Some individuals may experience side effects from certain medications, such as drowsiness with some antihistamines. A doctor can help determine the best course of action based on an individual's specific circumstances and medical history.
- Age and overall health are important considerations.
- Potential drug interactions with other medications need to be considered.
- Individual responses to medications vary widely.
Importance of Allergy Testing and Diagnosis
Before starting any anti-allergy medication, accurate diagnosis is crucial. Allergy testing can identify specific allergens triggering the reaction. This information guides the choice of medication and allows for personalized treatment plans. For instance, immunotherapy is highly effective for specific allergies but requires an accurate diagnosis. Knowing the specific allergen(s) causing the problem can be invaluable for effective management.
- Skin prick tests are commonly used to identify allergens.
- Blood tests can measure specific IgE antibodies to allergens.
- Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Managing allergies often requires a long-term approach. This may include regular medication use during allergy seasons, avoidance of triggers whenever possible, and possibly immunotherapy. Lifestyle modifications, such as using air purifiers, washing bedding frequently, and avoiding known triggers, can significantly reduce symptom severity. Regular check-ups with an allergist or doctor can help monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Lifestyle changes can significantly reduce exposure to allergens.
- Immunotherapy offers long-term allergy relief for certain individuals.
- Regular monitoring with a healthcare professional is vital for long-term allergy management.
Is Claritin or Zyrtec better for allergies?

There's no single "better" allergy medication between Claritin (loratadine) and Zyrtec (cetirizine). The optimal choice depends heavily on individual factors like the severity of your allergies, your personal response to each medication, and any potential side effects. Both are effective antihistamines, meaning they block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your body in response to allergens. This blockage reduces allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, runny nose, and watery eyes. However, they differ slightly in their mechanisms and potential side effects.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms
Claritin contains loratadine, a non-sedating antihistamine that works by blocking histamine receptors in your body. This means it prevents histamine from causing allergy symptoms. Zyrtec, on the other hand, contains cetirizine, another antihistamine that also blocks histamine receptors but can potentially have slightly more sedative effects for some individuals. The key difference lies in how long each drug remains active in your system. Loratadine tends to last longer (up to 24 hours), while Cetirizine is also long-acting, but potentially with slightly more variation in individual responses.
- Loratadine (Claritin): Generally considered non-sedating, offering longer-lasting relief (up to 24 hours).
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec): Can cause drowsiness in some individuals, also generally long-lasting (up to 24 hours) but may have more variation in individual duration.
- Both are effective for relieving common allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, runny nose, and watery eyes.
Side Effects
Both Claritin and Zyrtec can cause side effects, although they are generally well-tolerated. Common side effects for both include drowsiness, dry mouth, fatigue, and headache. However, the frequency and severity of these side effects can vary significantly between individuals. Some people might find one medication more tolerable than the other. It's crucial to pay attention to how your body reacts to each medication and to report any unusual side effects to your doctor.
- Drowsiness: More likely with Zyrtec, though less common with both.
- Dry Mouth: A common side effect for both medications.
- Headache: Can occur with both, though often mild and temporary.
Dosage and Administration
Both Claritin and Zyrtec are available as tablets, capsules, and liquid formulations. The recommended dosage for adults is typically one tablet or capsule per day, but you should always follow the instructions on the label or as advised by your doctor or pharmacist. For children, the dosage will vary depending on age and weight. It's vital to consult a healthcare professional before giving either medication to a child.
- Adult dosage is typically one tablet daily for both.
- Children's dosage varies by age and weight; consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- Always follow the label instructions precisely.
Cost and Availability
Both Claritin and Zyrtec are widely available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription. The cost can vary depending on the pharmacy, the dosage, and whether or not you have insurance coverage. Generic versions of both medications are also available and are typically more affordable. You can compare prices at different pharmacies to find the best deal.
- Available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription.
- Generic versions are usually more cost-effective.
- Prices can vary based on pharmacy, insurance, and dosage.
Interactions with Other Medications
Both Claritin and Zyrtec can interact with other medications, so it's important to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you are taking. This is especially crucial if you are taking medications for other conditions, such as blood pressure or heart problems. They may need to adjust your dosage or recommend an alternative allergy medication to avoid potential interactions.
- Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you're using.
- Potential interactions with other drugs, especially those for heart conditions or blood pressure.
- Your doctor can help manage potential interactions and suggest appropriate adjustments.
What medicine is best for allergies?

There is no single "best" medicine for allergies, as the ideal treatment depends on the severity and type of allergy, as well as individual factors like age and other health conditions. The best approach often involves a combination of strategies and may require consultation with a doctor or allergist to determine the most appropriate course of action. However, several types of medications are commonly used to manage allergy symptoms.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are the most common over-the-counter (OTC) medications used to treat allergy symptoms. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body in response to allergens. This reduces symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and hives. First-generation antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), are effective but can cause drowsiness. Second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin), are generally less sedating. Choosing between them depends on individual sensitivity and tolerance to side effects.
- First-generation antihistamines: Often more effective at treating some symptoms but more likely to cause drowsiness.
- Second-generation antihistamines: Typically less sedating and longer-lasting, but might be less effective for some individuals.
- Consider non-drowsy options if you need to remain alert during the day.
Decongestants
Decongestants help relieve nasal congestion by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages. They are available as nasal sprays (like oxymetazoline or phenylephrine) or oral medications (like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine). While effective for short-term relief, prolonged use of nasal decongestant sprays can lead to rebound congestion, making congestion worse. Oral decongestants can raise blood pressure, so they're not suitable for everyone.
- Nasal sprays provide quick relief but should be used for only a short period to prevent rebound congestion.
- Oral decongestants offer longer-lasting relief, but can interact with other medications and have cardiovascular effects.
- Consult a doctor before using decongestants if you have high blood pressure or other underlying health issues.
Corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids, like fluticasone (Flonase), mometasone (Nasonex), and budesonide (Rhinocort), are highly effective in treating allergic rhinitis (hay fever). They are available as nasal sprays and work by reducing inflammation in the nasal passages. They are not immediate-acting, requiring several days to weeks for full effectiveness, but are generally very safe for long-term use when prescribed by a doctor.
- Effective for long-term management of allergy symptoms, especially nasal congestion and inflammation.
- Not for immediate relief; effects take time to develop.
- Generally safe for long-term use when used as directed and prescribed by a doctor.
Leukotriene Modifiers
Leukotriene modifiers, such as montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate), block the action of leukotrienes, substances involved in allergic inflammation. They are usually prescribed for people with asthma who also experience allergy symptoms, or for those with severe allergies who don't respond adequately to other medications. They are taken orally once daily.
- Effective for preventing allergy symptoms, particularly in those with asthma or severe allergies.
- Not for immediate relief of symptoms; effects develop over several days.
- Often used in combination with other allergy medications for optimal control.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT), involves gradually exposing the body to increasing doses of allergens to build up tolerance. It's a long-term treatment that can provide lasting relief from allergy symptoms. Immunotherapy is typically administered by an allergist and is best suited for individuals with moderate to severe allergies that don't respond adequately to other treatments.
- Long-term treatment aimed at modifying the immune system's response to allergens.
- Requires regular visits to an allergist for injections or sublingual administration.
- Can provide lasting relief from allergies but requires significant time and commitment.
Is Zyrtec or Allegra better?

Is Zyrtec or Allegra Better?
There's no single "better" medication between Zyrtec (cetirizine) and Allegra (fexofenadine). The best choice depends entirely on individual factors like your specific allergy symptoms, other medical conditions, and potential side effects. Both are effective second-generation antihistamines, meaning they are less likely to cause drowsiness than older antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl). However, they differ in their mechanisms of action and potential side effects.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Action
Zyrtec (cetirizine) and Allegra (fexofenadine) both work by blocking histamine, a chemical released by your body during an allergic reaction. However, they do so slightly differently. Cetirizine is a more potent histamine receptor blocker, meaning it's generally more effective at preventing allergy symptoms. Fexofenadine is more selective, primarily targeting peripheral histamine receptors, meaning it may be less likely to cause central nervous system side effects like drowsiness.
- Zyrtec: Blocks both peripheral and central histamine receptors.
- Allegra: Primarily blocks peripheral histamine receptors.
- Both are effective against allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itching.
Effectiveness for Different Allergy Symptoms
While both medications are generally effective for common allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes, some individuals might find one works better for their specific symptoms. Some studies suggest Zyrtec might be slightly more effective for treating certain symptoms, particularly nasal congestion, while others show no significant difference. The best way to determine which is more effective for you is through personal trial and error.
- Both are effective for sneezing, runny nose, and itchy, watery eyes.
- Zyrtec may be slightly more effective for nasal congestion in some individuals.
- Individual responses can vary; what works for one person may not work as well for another.
Side Effects
Both Zyrtec and Allegra are generally well-tolerated, but they can cause side effects. Zyrtec is more often associated with drowsiness, although this is less common than with older antihistamines. Other potential side effects for both medications include dry mouth, headache, and fatigue. It's important to note that Allegra is less likely to cause drowsiness but may be more likely to cause other side effects in some individuals.
- Zyrtec: More likely to cause drowsiness, but less common than with first-generation antihistamines.
- Allegra: Less likely to cause drowsiness, but may cause other side effects like headache or fatigue.
- Always check the medication's label for a complete list of potential side effects.
Drug Interactions
Both Zyrtec and Allegra can interact with other medications. It's crucial to inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking before starting either Zyrtec or Allegra to avoid potential interactions. Some medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver, may interact with both drugs leading to changes in efficacy or increased risk of side effects.
- Inform your doctor about all current medications and supplements.
- Drug interactions can significantly affect efficacy and side effects.
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have concerns about drug interactions.
Cost and Availability
The cost of Zyrtec and Allegra can vary depending on your location, insurance coverage, and the form of the medication (e.g., generic vs. brand name). Generic versions of both medications are generally more affordable than brand-name versions. Both medications are widely available over-the-counter and by prescription, though prescription strength may be required in some instances based on individual needs.
- Generic versions are usually cheaper than brand-name options.
- Cost can vary by location and insurance coverage.
- Both are readily available over-the-counter and by prescription.
What is the best allergy medicine for me?
There's no single "best" allergy medicine, as the ideal choice depends on several individual factors. Your specific allergy symptoms (runny nose, sneezing, itchy eyes, congestion), the severity of your allergies, your age, and any pre-existing medical conditions or medications you're taking all play a crucial role. For example, someone with mild seasonal allergies might find relief with an over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamine like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra). These are generally well-tolerated and effective for relieving sneezing, itching, and runny nose. However, individuals with more severe symptoms, or those experiencing significant nasal congestion, might require a different approach. A combination medication containing an antihistamine and a decongestant could be more suitable. These are often available OTC, but it's always wise to consult a doctor or pharmacist to determine the best combination and dosage for your specific needs. People with certain health conditions, like high blood pressure or glaucoma, may need to avoid certain decongestants. Furthermore, individuals with asthma may find that certain allergy medications exacerbate their symptoms, requiring a different approach altogether. Finally, children require different dosages and may have specific medication options appropriate for their age group. Therefore, a consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the most appropriate and safest allergy medication for your individual circumstances.
Are there any natural allergy remedies?
While there's no magic bullet for allergies, several natural remedies may provide some relief for mild symptoms. These are often best used in conjunction with, or as a complement to, traditional allergy medications rather than as a complete replacement. Saline nasal sprays can help rinse nasal passages, removing allergens and reducing congestion. Butterbur root extract has shown promise in some studies as an effective anti-inflammatory, but it's crucial to purchase it from a reputable supplier that ensures purity and safety, as it can contain liver-damaging compounds if not properly processed. Local honey, sourced from your area, is a folk remedy that some find helpful; the theory is that exposure to local pollen through honey can build some tolerance. However, scientific evidence to support this is limited. Quercetin, a plant flavonoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, has also been explored for allergy relief, but more research is needed. Finally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a balanced diet, can enhance the overall functioning of the immune system and may improve symptom management. It's essential to remember that the effectiveness of natural remedies varies significantly between individuals, and they might not be sufficient for managing severe allergies. Always consult your doctor before using natural remedies, especially if you're taking other medications, as interactions can occur.
What are the side effects of allergy medications?
Allergy medications, whether OTC or prescription, can come with side effects, although these are not experienced by everyone. Antihistamines, commonly used to combat sneezing, itching, and runny nose, can cause drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, and headache. These side effects are more frequently associated with older-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), while newer-generation antihistamines such as cetirizine (Zyrtec) and fexofenadine (Allegra) are less likely to cause drowsiness. Decongestants, used to relieve nasal congestion, may lead to nervousness, insomnia, increased heart rate, and high blood pressure, particularly with prolonged use. Nasal corticosteroids, prescribed for more severe allergic rhinitis, can cause nosebleeds, throat irritation, and, rarely, changes in the sense of smell. Leukotriene inhibitors, another type of prescription allergy medication, can sometimes cause headaches, stomach pain, and increased risk of infection. The severity and likelihood of side effects vary depending on the specific medication, dosage, and individual sensitivity. It's vital to carefully read the medication label and inform your doctor or pharmacist about any pre-existing health conditions or medications you're already taking to minimize the risk of adverse reactions. If you experience any concerning side effects, you should contact your healthcare provider immediately.
When should I see a doctor about my allergies?
You should consult a doctor if your allergy symptoms are severe, debilitating, or don't respond adequately to OTC medications. This includes situations where allergies significantly impact your daily life, such as interfering with sleep, work, or social activities. Persistent symptoms despite using over-the-counter medications warrant a doctor's visit, as they may indicate a need for stronger medication or further investigation. If you experience severe allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat (angioedema), hives, or a sudden drop in blood pressure (anaphylaxis), you need immediate medical attention. This is a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate treatment. Additionally, if your allergies appear to be worsening over time, or if you develop new allergies, a consultation with a doctor is advisable. They can perform allergy testing to identify your specific allergens and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan. Finally, children with allergies often require special attention and should be evaluated by a pediatrician to ensure they receive safe and effective treatment. Don't hesitate to seek professional medical advice if you're unsure about your allergy symptoms or need guidance on managing your condition effectively.
Deja una respuesta