What is the best drink to boost the immune system

When it comes to strengthening your immune system, what you consume plays a pivotal role. Staying hydrated is crucial, but not all liquids are created equal. Certain drinks possess exceptional properties that can bolster your body's defenses against illness. In this article, we will explore the realm of immune-boosting beverages, identifying the top contenders and delving into the scientific evidence behind their efficacy. From age-old remedies to innovative formulations, we will unveil the best drink to enhance your immune system and safeguard your overall well-being.
What's the Best Immune-Boosting Beverage?
There's no single "best" drink to magically boost your immune system. Your immune health depends on a variety of factors including a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, stress management, and regular exercise. However, certain beverages can contribute to a healthy immune system by providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Focusing on a variety of nutrient-rich drinks is key rather than relying on one "miracle" beverage.
1. The Power of Hydration: Water
Before even considering fancy juices or teas, remember that adequate hydration is crucial. Water is fundamental for all bodily functions, including immune responses. Dehydration can impair immune cell function and make you more susceptible to illness. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting based on your activity level and climate.
2. Vitamin C Powerhouse: Citrus Juices
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are rich in Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant known to support the immune system. Vitamin C helps in the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. However, it's important to note that excessive Vitamin C intake can cause digestive upset in some individuals. Freshly squeezed juice is preferable to processed options, as it retains more nutrients.
3. Herbal Tea Benefits: Chamomile and Ginger
Certain herbal teas offer potential immune-boosting benefits. Chamomile tea has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce stress, a factor that can negatively impact the immune system. Ginger tea possesses anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties, potentially easing symptoms of colds and flu. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is still ongoing and further research is needed.
4. Antioxidant Rich: Green Tea
Green tea is packed with antioxidants, particularly catechins, which have been linked to enhanced immune function. These antioxidants combat free radicals that can damage cells and weaken the immune system. Green tea also contains L-theanine, an amino acid that may promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
5. Nutrient-Packed: Bone Broth
Bone broth, made by simmering bones and connective tissue, is a rich source of collagen, amino acids, and minerals like gelatin and glycine, which may support gut health. A healthy gut is essential for a strong immune system as a significant portion of your immune system resides in your gut. The benefits of bone broth for immunity are still being studied.
| Beverage | Key Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Essential for all bodily functions, including immune responses. | Drink consistently throughout the day. |
| Citrus Juices | Rich in Vitamin C, supports white blood cell production. | Moderate intake, may cause digestive upset in some. |
| Chamomile Tea | Anti-inflammatory, may reduce stress. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
| Ginger Tea | Anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
| Green Tea | High in antioxidants, may enhance immune function. | Moderate caffeine intake. |
| Bone Broth | Supports gut health, rich in collagen and amino acids. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
What's the Best Immune-Boosting Beverage?
There's no single "best" drink to magically boost your immune system. Your immune health depends on a variety of factors including a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, stress management, and regular exercise. However, certain beverages can contribute to a healthy immune system by providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Focusing on a variety of nutrient-rich drinks is key rather than relying on one "miracle" beverage.
1. The Power of Hydration: Water
Before even considering fancy juices or teas, remember that adequate hydration is crucial. Water is fundamental for all bodily functions, including immune responses. Dehydration can impair immune cell function and make you more susceptible to illness. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting based on your activity level and climate.
2. Vitamin C Powerhouse: Citrus Juices
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are rich in Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant known to support the immune system. Vitamin C helps in the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. However, it's important to note that excessive Vitamin C intake can cause digestive upset in some individuals. Freshly squeezed juice is preferable to processed options, as it retains more nutrients.
3. Herbal Tea Benefits: Chamomile and Ginger
Certain herbal teas offer potential immune-boosting benefits. Chamomile tea has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce stress, a factor that can negatively impact the immune system. Ginger tea possesses anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties, potentially easing symptoms of colds and flu. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is still ongoing and further research is needed.
4. Antioxidant Rich: Green Tea
Green tea is packed with antioxidants, particularly catechins, which have been linked to enhanced immune function. These antioxidants combat free radicals that can damage cells and weaken the immune system. Green tea also contains L-theanine, an amino acid that may promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
5. Nutrient-Packed: Bone Broth
Bone broth, made by simmering bones and connective tissue, is a rich source of collagen, amino acids, and minerals like gelatin and glycine, which may support gut health. A healthy gut is essential for a strong immune system as a significant portion of your immune system resides in your gut. The benefits of bone broth for immunity are still being studied.
| Beverage | Key Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Essential for all bodily functions, including immune responses. | Drink consistently throughout the day. |
| Citrus Juices | Rich in Vitamin C, supports white blood cell production. | Moderate intake, may cause digestive upset in some. |
| Chamomile Tea | Anti-inflammatory, may reduce stress. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
| Ginger Tea | Anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
| Green Tea | High in antioxidants, may enhance immune function. | Moderate caffeine intake. |
| Bone Broth | Supports gut health, rich in collagen and amino acids. | More research needed to confirm immune benefits. |
What drinks can boost your immune system fast?

What Drinks Can Boost Your Immune System Fast?
While no drink can instantly "boost" your immune system, certain beverages are rich in nutrients that support its function. It's crucial to remember that a healthy immune system relies on a holistic approach including balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management. However, incorporating these drinks into your diet can contribute to overall immune health.
Water: The Foundation of a Healthy Immune System
Water is essential for all bodily functions, including immune system activity. Dehydration can impair immune cell function and leave you more susceptible to illness. Staying properly hydrated ensures that your immune cells can effectively circulate and perform their duties.
- Supports nutrient transport: Water carries vital nutrients to immune cells.
- Aids in waste removal: Efficiently removes toxins and waste products that can weaken the immune system.
- Maintains optimal body temperature: Crucial for maintaining ideal conditions for immune function.
Green Tea: A Powerhouse of Antioxidants
Green tea is packed with antioxidants, particularly catechins like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). These antioxidants combat free radicals, which can damage cells and weaken the immune system. Furthermore, green tea contains L-theanine, an amino acid that promotes relaxation and may indirectly support immune function by reducing stress.
- Rich in antioxidants: Protects cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Contains L-theanine: Promotes relaxation and reduces stress, which can negatively affect immunity.
- May boost the activity of certain immune cells: Some studies suggest potential benefits on immune cell function.
Bone Broth: A Source of Nutrients for Gut Health
Bone broth is a nutrient-rich drink containing gelatin, collagen, and amino acids that support gut health. A healthy gut is crucial for a strong immune system as a significant portion of your immune cells reside in your gut. The minerals in bone broth also contribute to overall health and well-being.
- Supports gut health: A healthy gut is vital for a robust immune system.
- Provides essential amino acids: Building blocks for immune cell production.
- Rich in minerals: Contributes to overall health and immune function.
Citrus Juices: Vitamin C Boost
Citrus juices like orange, grapefruit, and lemon are excellent sources of Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant essential for immune function. Vitamin C helps to stimulate the production of white blood cells, which play a critical role in fighting off infections. However, it's important to consume these in moderation due to their sugar content.
- High in Vitamin C: Essential for white blood cell production.
- Powerful antioxidant: Protects cells from free radical damage.
- Supports collagen production: Important for wound healing and tissue repair.
Ginger Tea: Anti-inflammatory Properties
Ginger tea has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body, which can weaken the immune system. While it doesn't directly boost immune cells, reducing inflammation can indirectly support overall immune function and alleviate symptoms associated with illness.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Helps reduce inflammation that can hinder immune response.
- May reduce nausea and vomiting: Helpful in managing symptoms during illness.
- Contains antioxidants: Further contributes to cellular protection.
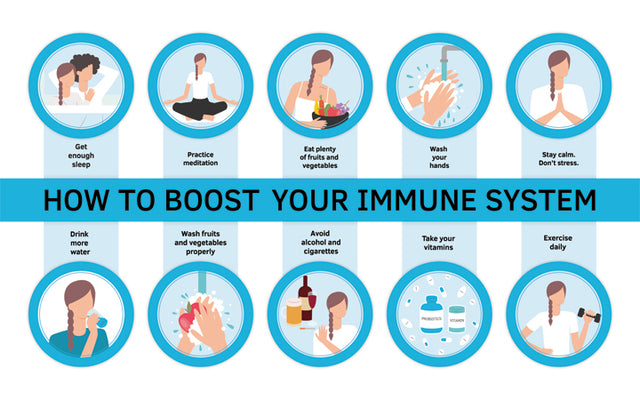
How can I boost my immune system fast?

How Can I Boost My Immune System Fast?
There's no magic bullet to instantly boost your immune system. Building a strong immune system is a long-term process involving consistent healthy habits. However, you can take steps to support your immune function and potentially reduce your susceptibility to illness. Remember that these strategies are supportive, not curative, and should not replace medical advice. If you are experiencing symptoms of illness, consult a doctor.
Prioritize Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for immune function. While you can't magically boost your immunity overnight, getting enough sleep consistently will significantly improve your overall health and resilience to illness. Sleep deprivation weakens your immune system, making you more vulnerable to infections. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up around the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to wind down before sleep. This could include a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool for optimal sleep conditions.
Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in immune function. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is key. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support your body's defense mechanisms. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated and unhealthy fats.
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables, aiming for a variety of colors to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
- Include sources of zinc (e.g., oysters, pumpkin seeds) and vitamin C (e.g., citrus fruits, berries), which are essential for immune cell function.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains for sustained energy and fiber, which supports gut health, crucial for immunity.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress significantly impacts your immune system. Stress hormones can suppress immune function, leaving you more susceptible to infections. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial for long-term immune health.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation.
- Engage in regular physical activity, which has been shown to reduce stress and boost immunity.
- Prioritize activities that you find enjoyable and relaxing, such as spending time in nature or pursuing hobbies.
Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for many bodily functions, including immune function. Dehydration can impair immune cell activity, making you more prone to illness. Make sure you're drinking enough water throughout the day.
- Carry a reusable water bottle and sip on it regularly.
- Eat fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as watermelon and cucumbers.
- Listen to your body’s thirst cues and drink water when you feel thirsty.
Maintain Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is a simple yet effective way to protect yourself from infections. Regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and covering your mouth when you cough or sneeze can significantly reduce your risk of getting sick.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places or before eating.
- Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Get vaccinated against preventable illnesses like the flu and COVID-19.
How can I boost my immune system ASAP?

How Can I Boost My Immune System ASAP?
There's no magic bullet to instantly boost your immune system, but you can take steps to support its function and improve its ability to fight off infections. Remember that a healthy immune system is a long-term project, not a quick fix. While some changes might show immediate effects, true immune enhancement takes time and consistent effort. Focusing on lifestyle changes is far more effective than relying on supplements or quick fixes that often lack scientific backing.
Prioritize Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for immune function. While you sleep, your body releases proteins called cytokines that help fight inflammation and infection. Sleep deprivation suppresses your immune response, making you more susceptible to illness. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up around the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to wind down before sleep. This could include a warm bath, reading, or listening to calming music.
- Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool for optimal sleep quality.
Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet
Your diet plays a vital role in supporting your immune system. Focus on consuming a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential for immune cell function. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated and unhealthy fats, as these can negatively impact your immune system.
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables, aiming for at least 5 servings a day.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains for sustained energy and better nutrient absorption.
- Include lean protein sources such as fish, chicken, beans, and lentils in your diet.
Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for many bodily functions, including immune system function. Dehydration can impair immune cell activity, making you more vulnerable to illness. Ensure you're drinking enough water throughout the day. The amount you need will vary depending on factors such as your activity level and climate, but aim to drink plenty of fluids.
- Carry a reusable water bottle and refill it frequently.
- Drink water before, during, and after physical activity.
- Listen to your body's thirst cues.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress weakens the immune system. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, is vital for immune support. Stress management techniques can help reduce the impact of stress hormones on your immune cells.
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Engage in regular physical activity, even a short walk can make a difference.
- Prioritize activities that bring you joy and help you relax.
Maintain Hygiene
Good hygiene practices are essential for preventing infections. Regular handwashing, avoiding touching your face, and practicing proper respiratory etiquette can significantly reduce your exposure to germs. These simple steps can greatly impact your chances of getting sick.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when you cough or sneeze.
Does drinking water boost your immune system?
The relationship between water intake and immune function is complex and not fully understood. While drinking enough water is crucial for overall health, it doesn't directly "boost" the immune system in the way that, say, a vaccine does. Instead, adequate hydration plays a vital supporting role in various bodily processes that are essential for a properly functioning immune system. Dehydration can impair immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections. This is because water is vital for several immune-related processes, such as the transportation of immune cells, the removal of waste products, and the proper functioning of lymphoid organs like the lymph nodes and spleen. Therefore, maintaining adequate hydration is important for optimal immune response, but it's not a stand-alone immune booster.
How Water Supports Immune Cell Function
Water is the primary solvent in the body, meaning it's the medium in which many biological processes occur. Immune cells, such as lymphocytes and phagocytes, rely on water to move through the bloodstream and lymph to reach sites of infection. Dehydration reduces blood volume, potentially hindering the efficient delivery of these cells to where they're needed. This can lead to a slower and less effective immune response. Proper hydration ensures efficient transportation of immune cells and other vital components, enabling a more robust immune defense.
- Facilitates efficient transport of immune cells: Water allows immune cells to travel swiftly throughout the body.
- Supports optimal blood volume: Adequate hydration ensures sufficient blood volume for effective immune cell delivery.
- Maintains lymphatic system function: The lymphatic system, crucial for immune function, relies on proper hydration.
Water's Role in Waste Removal
The immune system generates waste products during its operations, and water is essential for flushing these toxins out of the body. This occurs primarily through the kidneys and urinary system. If the body is dehydrated, these waste products can accumulate, potentially impacting the overall immune response. The build-up of metabolic wastes and toxins can interfere with the function of immune cells and organs. Efficient waste removal is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Kidney function: Water is needed to filter waste products from the blood.
- Flushing toxins: Water helps to remove harmful substances that can impair immune function.
- Maintaining optimal blood composition: Proper hydration helps to maintain a healthy balance of electrolytes and other substances crucial to immune function.
The Impact of Dehydration on Immunity
Dehydration is detrimental to immune function. When the body is dehydrated, its ability to fight off infections is significantly compromised. This is because several immune processes are hindered by a lack of water. This can manifest in reduced immune cell activity, impaired lymphatic drainage, and a general decrease in the body's ability to combat pathogens. The severity of the impact depends on the degree and duration of dehydration.
- Reduced immune cell activity: Dehydration leads to less effective immune cell response.
- Impaired lymphatic drainage: Fluid balance is crucial for proper lymphatic function.
- Increased susceptibility to infections: A dehydrated body is more vulnerable to illness.
Hydration and Mucosal Immunity
The mucous membranes lining the respiratory and digestive tracts act as a first line of defense against pathogens. Adequate hydration helps to maintain the integrity and functionality of these mucous membranes. This is essential because a properly hydrated mucous membrane can effectively trap and remove pathogens before they can invade the body. Dehydration can lead to drier mucous membranes, which are less effective at preventing pathogen entry. Maintaining proper hydration is crucial for supporting the body's first line of defense.
- Mucous membrane integrity: Hydration maintains the moisture and thickness of mucus membranes.
- Effective pathogen trapping: Proper hydration improves the mucous membrane's ability to trap and remove pathogens.
- Reduced risk of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections: Hydration helps to prevent pathogens from penetrating mucous membranes.
Other Factors Affecting Immune Function
While adequate hydration is important, it's only one piece of the puzzle when it comes to immune health. Many other factors also significantly influence immune function, including nutrition, sleep, stress levels, and overall lifestyle choices. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, sufficient sleep, stress management techniques, and regular exercise all contribute to a robust and resilient immune system. Focusing solely on water intake while neglecting other crucial aspects of health may not yield optimal results.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet is crucial for optimal immune function.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep allows the immune system to repair and regenerate.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the immune system.
- Exercise: Moderate exercise boosts the immune system.
What is the single best drink to magically boost my immune system?
There's no single "magic bullet" drink that will instantly and dramatically boost your immune system. Claims suggesting otherwise are often misleading. Your immune system is a complex network, and its strength depends on many factors including nutrition, sleep, stress levels, and overall health. While certain beverages can contribute to a healthy immune system, they are not miracle cures. Focusing on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest is far more effective than relying on any one drink. Some drinks may contain components that support immune function, but their impact is marginal when considered in isolation. A holistic approach to wellness is crucial for robust immune health. Relying on a single drink to achieve a significant immune boost is unrealistic and potentially harmful if it replaces other crucial aspects of a healthy lifestyle.
Are there drinks that are particularly good for immune support?
Yes, several drinks contain nutrients that support immune function. Water, the most fundamental beverage, is crucial for overall health and plays a vital role in immune cell activity. Tea, especially green tea, is rich in antioxidants which can help protect cells from damage. Fruit and vegetable juices, especially those high in vitamin C (like orange juice) and other antioxidants, can provide immune-supporting nutrients. However, it's crucial to remember that these benefits are best achieved as part of a balanced diet. Juices are often high in sugar, so moderation is key. Bone broth is another option that provides gelatin and amino acids, which some believe support gut health, which in turn can impact immunity. The evidence on bone broth's immune benefits is still under research. Ultimately, the effectiveness of these drinks depends on your overall health and dietary habits. Don't consider these drinks as a replacement for a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Should I avoid certain drinks to support my immune system?
Yes, some drinks can negatively impact your immune system, particularly those high in sugar and alcohol. Excessive sugar intake can weaken the immune response, making you more susceptible to infections. Alcohol, even in moderate amounts, can suppress immune function. Sugary sodas, energy drinks, and excessive consumption of fruit juices (due to their sugar content) should be minimized. These beverages often offer minimal nutritional value and can contribute to inflammation and a weakened immune response. While an occasional treat is unlikely to cause significant harm, consistent consumption of these beverages can negatively impact your overall health and immune function. Prioritizing water, tea, and other nutrient-rich beverages is a much better strategy for immune support.
What is the best drink to have when I'm already sick?
When you're sick, the focus should be on hydration and comfort. Water remains the best choice as it helps your body replace fluids lost through fever and sweating. Herbal teas like chamomile or ginger tea can offer soothing properties to alleviate symptoms like nausea, sore throat, and coughing. Electrolyte drinks can help replace essential minerals lost during illness, particularly if you're experiencing vomiting or diarrhea. However, it is important to note that these drinks don't "cure" illness; they simply provide comfort and support your body's natural healing process. If symptoms are severe or persistent, it's crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Relying solely on drinks to treat illness is insufficient and could delay necessary medical attention.
Deja una respuesta