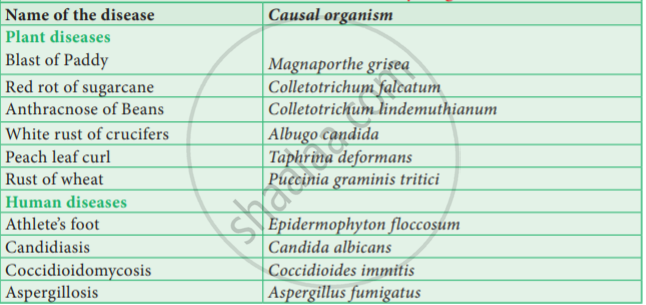
What are 10 diseases caused by fungi

Fungal infections are among the most common diseases affecting humans and can range in severity from mild skin irritation to life-threatening infections. These infections are caused by a diverse group of organisms known as fungi, which can be found in soil, water, and on plants or animals. They can also be present on the human body, where they typically cause no harm but can become pathogenic under certain conditions. In this article, we will explore 10 of the most common fungal infections and discuss their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
10 Diseases Caused by Fungi
1. Candidiasis
Candidiasis, also known as a yeast infection, is caused by Candida, a genus of yeasts. It commonly affects the mouth (thrush), vagina (vulvovaginitis), and skin. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the infection but can include redness, itching, pain, and white patches. Risk factors include weakened immune systems, antibiotic use, and diabetes.
2. Ringworm
Ringworm, despite its name, is a fungal infection, not caused by a worm. It's caused by dermatophytes, fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. It presents as a circular rash with a raised, scaly border. It can affect the skin, scalp (tinea capitis), groin (tinea cruris), and feet (athlete's foot or tinea pedis). Treatment typically involves antifungal creams or oral medications.
3. Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a lung infection caused by inhaling the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum, often found in bird and bat droppings. Most people experience mild or no symptoms, but severe cases can lead to pneumonia or disseminated disease, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems. Symptoms may include fever, cough, chest pain, and fatigue.
4. Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever)
Coccidioidomycosis, also known as Valley Fever, is caused by inhaling the spores of the fungi Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii. These fungi are found in soil in arid and semi-arid regions of the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central and South America. Symptoms range from mild flu-like illness to severe pneumonia or disseminated disease. Severe cases can be life-threatening.
5. Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is caused by the Aspergillus genus of fungi. These fungi are found everywhere in the environment. Most people inhale Aspergillus spores without experiencing any symptoms. However, individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing invasive aspergillosis, which can affect the lungs, sinuses, and other organs. Symptoms vary widely depending on the type and severity of infection.
6. Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is caused by the fungus Cryptococcus, commonly found in soil contaminated with bird droppings. It primarily affects the lungs and can spread to the brain, causing meningoencephalitis. Symptoms can range from mild respiratory symptoms to severe neurological problems. Individuals with weakened immune systems are at significantly increased risk.
7. Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a subcutaneous fungal infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii. It's usually acquired through inoculation of the skin, often through contact with plants, thorns, or soil. The infection typically presents as a nodular lesion at the site of inoculation, which may spread along lymphatic channels.
8. Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis, also known as South American blastomycosis, is a systemic fungal infection caused by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and Paracoccidioides lutzii. It is prevalent in Latin America and affects the lungs, skin, and mucous membranes. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the infection.
9. Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is a fungal infection caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis. This fungus is found in soil and decaying organic matter, primarily in eastern North America. Inhalation of fungal spores can lead to lung infection, which can disseminate to other parts of the body. Symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms to severe pneumonia and other systemic manifestations.
10. Zygomycosis
Zygomycosis, also known as mucormycosis, is a rare but serious fungal infection caused by fungi in the order Mucorales. These fungi are ubiquitous in the environment, but infections are typically seen in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions like diabetes or cancer. Infection can affect various organs, including the lungs, sinuses, brain, and skin. It is a medical emergency requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
| Disease | Causative Fungus | Common Symptoms | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Candidiasis | Candida spp. | Rash, itching, white patches | Weakened immune system, antibiotic use |
| Ringworm | Dermatophytes | Circular rash, itching | Warm, moist environments |
| Histoplasmosis | Histoplasma capsulatum | Fever, cough, chest pain | Exposure to bird/bat droppings |
| Coccidioidomycosis | Coccidioides spp. | Flu-like symptoms, pneumonia | Exposure to soil in endemic areas |
| Aspergillosis | Aspergillus spp. | Cough, fever, lung lesions | Weakened immune system |
| Cryptococcosis | Cryptococcus spp. | Lung infection, meningitis | Weakened immune system, exposure to bird droppings |
| Sporotrichosis | Sporothrix schenckii | Nodular lesions | Contact with plants, thorns |
| Paracoccidioidomycosis | Paracoccidioides spp. | Lung infection, skin lesions | Residence in endemic areas (Latin America) |
| Blastomycosis | Blastomyces dermatitidis | Lung infection, skin lesions | Exposure to soil in endemic areas (Eastern North America) |
| Zygomycosis | Mucorales | Sinusitis, lung infection, brain involvement | Weakened immune system, diabetes |
What are 10 fungal diseases?

10 Fungal Diseases
Here are 10 fungal diseases, along with descriptions:
- Candidiasis (Thrush): Caused by Candida yeast, it commonly affects the mouth, throat, vagina, and skin. Symptoms can include white patches, redness, itching, and pain.
- Ringworm: A common skin infection caused by several types of fungi. It presents as a circular, itchy rash. Different types affect different areas of the body (e.g., scalp, body, groin).
- Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis): A fungal infection of the feet, characterized by itching, scaling, and cracking of the skin between the toes.
- Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris): A fungal infection affecting the groin area, producing a red, itchy rash. It thrives in warm, moist environments.
- Histoplasmosis: A respiratory illness caused by inhaling Histoplasma capsulatum spores found in bird and bat droppings. Symptoms range from mild flu-like illness to severe pneumonia.
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever): A fungal infection acquired by inhaling spores of Coccidioides fungi, found in the soil of arid and semi-arid regions of the southwestern United States and parts of Central and South America. Symptoms can be mild or severe, and may include fever, cough, and chest pain.
- Aspergillosis: A group of diseases caused by Aspergillus fungi. Infection can affect the lungs (causing aspergillosis), sinuses, or other organs. Symptoms vary greatly depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Blastomycosis: A fungal infection caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, often affecting the lungs but potentially spreading to other organs. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may mimic other illnesses.
- Cryptococcosis: Primarily a lung infection caused by the fungus Cryptococcus, but can spread to the brain and other organs. It is particularly dangerous for individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Paracoccidioidomycosis: A systemic fungal infection primarily found in Latin America, caused by the fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and often affect the lungs and skin.
Fungal Infections of the Skin
Fungal infections commonly affect the skin, often presenting as itchy rashes. These infections thrive in warm, moist environments. Proper hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals are crucial in prevention.
- Ringworm
- Athlete's foot
- Jock itch
Systemic Fungal Infections
These fungal infections can spread throughout the body, impacting various organs. They are often more serious and require prompt medical attention. Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
- Histoplasmosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Aspergillosis
- Blastomycosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
Opportunistic Fungal Infections
Opportunistic fungal infections take advantage of a weakened immune system to cause disease. These infections are particularly dangerous for individuals with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those undergoing organ transplantation.
- Candidiasis
- Aspergillosis
- Cryptococcosis
Diagnosis and Treatment of Fungal Infections
Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, microscopic examination of samples, and sometimes more advanced testing. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, which can be topical or systemic depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Microscopic examination
- Culture testing
- Antifungal medications
Prevention of Fungal Infections
Several measures can be taken to prevent fungal infections. These include maintaining good hygiene, keeping skin dry, avoiding sharing personal items, and promptly treating any existing skin conditions.
- Good hygiene
- Keep skin dry
- Avoid sharing personal items
- Prompt treatment of skin conditions
What are 3 illnesses fungi can cause?

Ringworm
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but by a fungus. It's a common and highly contagious infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. The infection presents as a red, itchy, circular rash that may be scaly. It's easily spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or through contaminated objects like towels and clothing. Treatment usually involves antifungal creams, lotions, or oral medications. Proper hygiene practices are crucial in preventing its spread.
- Contagious through direct contact or contaminated objects.
- Characterized by a red, itchy, circular rash.
- Treatable with antifungal medications.
Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete's foot is another common fungal infection, specifically affecting the feet. The fungus thrives in warm, moist environments like shoes and socks. Symptoms include itching, burning, scaling, and cracking of the skin between the toes or on the soles of the feet. The infection can spread to other areas of the body if not treated promptly. Good foot hygiene, including keeping the feet clean and dry, is vital in prevention. Various antifungal creams, powders, and sprays are effective treatments.
- Affects the feet, thriving in warm, moist conditions.
- Symptoms include itching, burning, scaling, and cracking.
- Treatment involves antifungal creams, powders, and sprays.
Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
Candidiasis is caused by the Candida fungus, a type of yeast naturally present on the skin, in the mouth, and in the digestive tract. However, an overgrowth of Candida can lead to infection. This can manifest as thrush (oral candidiasis) causing white patches in the mouth, vaginal candidiasis (yeast infection) causing itching, burning, and discharge, or other forms affecting the skin or nails. Risk factors include weakened immune systems, antibiotic use, and diabetes. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, either topical or oral.
- Caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast.
- Can manifest in various locations, including the mouth, vagina, and skin.
- Treated with antifungal medications, depending on the location and severity.
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a lung infection caused by inhaling the spores of the Histoplasma capsulatum fungus. This fungus is found in soil contaminated with bird or bat droppings. Most people who inhale the spores don't get sick, but those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing a more serious illness. Symptoms can range from mild flu-like illness to severe pneumonia. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests and chest X-rays. Treatment often includes antifungal medications.
- Lung infection caused by inhaling fungal spores.
- Risk is higher for those with weakened immune systems.
- Symptoms can range from mild to severe, requiring antifungal treatment.
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a group of diseases caused by Aspergillus fungi, which are found everywhere in the environment. Most people breathe in Aspergillus spores without any problems, but in individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, the spores can cause infection. This can range from allergic reactions to serious lung infections. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection and may involve antifungal medications.
- Group of diseases caused by Aspergillus fungi.
- Most commonly affects people with compromised immune systems.
- Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the infection.
What are the 5 harmful fungi?
What are 5 Harmful Fungi?
1. Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus of molds found worldwide in various environments, including soil, decaying organic matter, and indoor environments. Several Aspergillus species can cause diseases in humans, known as aspergillosis. These infections can range from relatively mild allergic reactions to severe, life-threatening invasive infections. The severity of the disease depends on the species of Aspergillus, the individual's immune status, and the site of infection.
- Aspergillosis can manifest as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), a hypersensitivity reaction affecting the lungs.
- Invasive aspergillosis is a serious condition, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, often requiring aggressive antifungal treatment.
- Some Aspergillus species produce aflatoxins, potent carcinogens found in contaminated food and feed.
2. Candida
Candida species, particularly Candida albicans, are common yeasts that are part of the normal human flora. However, under certain conditions, such as weakened immunity or antibiotic use, they can overgrow and cause candidiasis (also known as thrush). Candidiasis can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth, vagina, and bloodstream.
- Oral thrush, characterized by white patches on the tongue and mucous membranes, is a common form of candidiasis.
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis, or yeast infection, causes vaginal itching, burning, and discharge.
- Candidemia, a bloodstream infection, is a serious condition that can be life-threatening.
3. Cryptococcus
Cryptococcus is a fungus that can cause cryptococcosis, a fungal infection that primarily affects the lungs and central nervous system. Cryptococcus neoformans is the most common species causing disease in humans. Individuals with weakened immune systems, especially those with HIV/AIDS, are particularly susceptible.
- Cryptococcal meningitis is a serious complication of cryptococcosis, characterized by inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes.
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis can manifest as a cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications.
4. Histoplasma
Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus found in soil contaminated with bird or bat droppings. Inhalation of spores can lead to histoplasmosis, a lung infection. Most infections are asymptomatic or mild, but in immunocompromised individuals, it can develop into a severe systemic infection.
- Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis usually presents with flu-like symptoms.
- Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis can cause persistent lung damage and symptoms.
- Disseminated histoplasmosis affects multiple organs and is more common in immunocompromised individuals.
5. Pneumocystis
Pneumocystis jirovecii is a fungus that causes pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), a serious lung infection primarily affecting individuals with weakened immune systems, especially those with HIV/AIDS. PCP can cause severe respiratory distress and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- PCP is characterized by shortness of breath, cough, fever, and fatigue.
- Diagnosis typically involves chest X-ray and microscopic examination of respiratory samples.
- Treatment usually involves antifungals such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
What are the 5 diseases caused by fungi Class 8?
Ringworm
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but by a fungus. It's a common and highly contagious skin infection characterized by a circular, itchy rash. The rash can appear on various parts of the body, including the scalp, groin, and feet (athlete's foot is a type of ringworm). It thrives in warm, moist environments and spreads through direct contact or indirect contact with contaminated surfaces. Treatment usually involves antifungal creams, lotions, or oral medications.
- Highly contagious: Spreads easily through direct or indirect contact.
- Characterized by a circular rash: The rash is often red, scaly, and itchy.
- Various locations on the body: Can affect the scalp, groin, feet, and other areas.
Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection that commonly affects the feet. It thrives in warm, damp environments like shoes and socks. Symptoms include itching, burning, scaling, and cracking of the skin between the toes and on the soles of the feet. It's easily spread in public places like locker rooms and showers. Treatment typically involves antifungal creams or powders.
- Affects the feet: Commonly found between toes and on soles.
- Thrives in moist environments: Shoes and socks create ideal conditions.
- Easily spread in public places: Locker rooms and showers are high-risk areas.
Candidiasis (Thrush)
Candidiasis, or thrush, is a yeast infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans. It commonly affects the mouth (oral thrush), vagina (vaginal yeast infection), and skin. In the mouth, it presents as white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks. In the vagina, it causes itching, burning, and discharge. Skin infections can appear as red, itchy rashes. Risk factors include weakened immune systems, antibiotic use, and diabetes. Treatment usually involves antifungal medications.
- Yeast infection: Caused by the fungus Candida albicans.
- Affects mouth, vagina, and skin: Symptoms vary depending on the location.
- Risk factors include weakened immune systems: Individuals with compromised immunity are more susceptible.
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a lung infection caused by inhaling spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. These spores are commonly found in bird and bat droppings. Most people infected experience no symptoms, but some develop flu-like illness, including fever, cough, and chest pain. Severe cases can affect other organs. Treatment depends on the severity of the infection and may involve antifungal medications.
- Lung infection: Caused by inhaling spores from bird and bat droppings.
- Symptoms range from mild to severe: Most infections are asymptomatic.
- Treatment with antifungals: Severe cases may require medication.
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a group of diseases caused by Aspergillus fungi. These fungi are common in the environment and are usually harmless. However, in individuals with weakened immune systems, they can cause infections in the lungs (aspergilloma), sinuses, or other parts of the body (invasive aspergillosis). Symptoms vary widely depending on the type and severity of the infection. Treatment involves antifungal medications.
- Opportunistic infection: Primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Can affect lungs, sinuses, and other organs: The location of infection varies.
- Treatment with antifungals: Essential for managing the infection.
What are some common fungal diseases affecting humans?
Fungi are ubiquitous organisms, and many species are capable of causing diseases in humans. These diseases, known as mycoses, vary widely in their severity and presentation. Some common examples include candidiasis (also known as thrush), which is caused by Candida species and often affects the mouth, throat, and vagina; ringworm (tinea), a group of skin infections caused by various dermatophyte fungi; and athlete's foot (tinea pedis), another dermatophyte infection commonly affecting the feet. Other notable fungal infections include histoplasmosis, a lung infection caused by inhaling Histoplasma capsulatum spores, often found in bird and bat droppings; coccidioidomycosis, a respiratory illness caused by inhaling Coccidioides spores found in arid soils of the southwestern United States; and cryptococcosis, an infection typically affecting the lungs and central nervous system, caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. The severity of these infections can vary widely depending on the individual's immune system, the specific fungus involved, and the location of the infection. Individuals with compromised immune systems are at significantly higher risk of developing severe fungal infections. Treatment options range from topical antifungals for superficial infections like ringworm to systemic antifungal medications for more serious invasive mycoses. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for successful management of fungal diseases.
How do fungal diseases spread?
The transmission of fungal diseases varies depending on the specific fungus. Many fungal infections are acquired through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or through contact with contaminated surfaces. For example, ringworm can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing towels or clothing. Spores, the reproductive units of fungi, play a crucial role in the spread of many fungal diseases. Inhaled spores are responsible for the development of systemic mycoses like histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis. These spores are often found in the environment, such as in soil, dust, or bird droppings. Some fungi are also transmitted through indirect contact, for instance, through contaminated surfaces or objects. Vectors, such as insects, can also play a role in the transmission of some fungal diseases, although this is less common than direct or indirect contact. Understanding the mode of transmission for a particular fungal infection is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces, and wearing protective equipment in high-risk environments. Furthermore, managing underlying health conditions that can compromise the immune system can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe fungal infections.
What are the symptoms of fungal infections?
The symptoms of fungal infections are highly variable and depend on several factors, including the type of fungus involved, the site of infection, and the individual's immune status. Superficial fungal infections, such as ringworm and athlete's foot, often manifest as itchy, scaly rashes, with lesions that may be circular or irregular in shape. Candidiasis can cause white patches in the mouth or vagina, along with burning, soreness, or itching. Systemic fungal infections, on the other hand, often present with more generalized symptoms, such as fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can mimic those of other illnesses, making diagnosis challenging. Some systemic mycoses can also lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis (inflammation of the brain and spinal cord) or disseminated disease, where the fungus spreads to multiple organs. It's important to note that some fungal infections may be asymptomatic, especially in individuals with healthy immune systems. If you suspect you may have a fungal infection, it's crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. A healthcare professional can perform necessary tests, such as skin scrapings, blood tests, or imaging studies, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of action.
How are fungal diseases treated?
The treatment of fungal diseases depends heavily on the type of fungus causing the infection and the severity and location of the infection. Superficial fungal infections, like ringworm and athlete's foot, are often treated with topical antifungal medications, such as creams, lotions, or powders. These medications work by interfering with the growth and reproduction of the fungus. For more serious or systemic fungal infections, oral or intravenous antifungal medications may be necessary. These medications can have potential side effects, and the choice of medication and the duration of treatment will be determined by a healthcare professional based on individual factors and the specific fungus. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove infected tissue. For individuals with compromised immune systems, treatment may be more challenging and prolonged. Supportive care, which includes managing symptoms and maintaining overall health, is an important aspect of treatment for all fungal infections. This may involve measures to improve nutrition, hydration, and rest. The prognosis for fungal infections varies depending on factors such as the type of fungus, the severity of the infection, and the individual's health status. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for improving the chances of a favorable outcome.
Deja una respuesta