Which fruit is best for the immune system

To maintain optimal health and well-being, a robust immune system is crucial. Fruits, nature's powerhouse of nutrients and antioxidants, can play a significant role in bolstering our body's defenses against disease and infection. In this article, we delve into the vast array of fruits to uncover which ones stand out as the most potent allies for boosting the immune system.
Which Fruit Reigns Supreme for Immune System Support?
There's no single "best" fruit for the immune system, as a variety of fruits offer different immune-boosting benefits. Optimal immune function relies on a balanced diet rich in various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, some fruits stand out due to their particularly high concentrations of key nutrients.
Citrus Fruits: Vitamin C Powerhouses
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes are renowned for their high Vitamin C content. Vitamin C is a crucial antioxidant that supports the production of white blood cells, which are vital for fighting off infections. It also helps in the repair of tissues and protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. While Vitamin C is water-soluble and excess is excreted, consistently consuming citrus fruits ensures a steady supply of this vital nutrient. It's important to remember that while Vitamin C is important, it doesn't magically prevent illness. A healthy diet and lifestyle are equally crucial.
Berries: Antioxidant All-Stars
Berries, including blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are packed with antioxidants like anthocyanins. These antioxidants combat inflammation and protect cells from damage, boosting the overall effectiveness of the immune system. Different berries offer various antioxidant profiles, making a mix of berries a particularly effective way to benefit from their collective power. Furthermore, some berries also provide a significant amount of vitamin C and fiber, contributing to overall gut health, a key component of a strong immune system.
Pineapple: Bromelain's Beneficial Effects
Pineapple contains bromelain, a powerful enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties. Bromelain can help reduce inflammation in the body, which plays a role in immune response. While further research is ongoing to fully understand its effects on the immune system, bromelain's ability to reduce inflammation could contribute to a healthier immune response. Remember that the amount of bromelain in pineapple depends on factors like ripeness and processing.
Papaya: Vitamin C and Immune-Boosting Enzymes
Papayas are another excellent source of vitamin C. They also contain papain, an enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties, similar to bromelain in pineapple. Papaya also offers a good supply of vitamin A, which supports the integrity of the mucous membranes (our body's first line of defense against infection) and further strengthens the immune system. The combination of Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and papain makes papaya a valuable addition to a healthy, immune-boosting diet.
Mangoes: A Rich Source of Vitamins and Antioxidants
Mangoes are rich in vitamin C, vitamin A, and various antioxidants. These nutrients work synergistically to enhance immune function. The abundance of vitamins and antioxidants in mangoes helps to protect against oxidative stress, a major contributor to inflammation and immune dysfunction. Incorporating mangoes into your diet offers a delightful and nutritious way to support your immune system.
| Fruit | Key Immune-Boosting Nutrients | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Citrus Fruits | Vitamin C | Supports white blood cell production, tissue repair, antioxidant protection |
| Berries | Anthocyanins (Antioxidants), Vitamin C | Combats inflammation, protects cells from damage |
| Pineapple | Bromelain | Reduces inflammation |
| Papaya | Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Papain | Supports mucous membranes, reduces inflammation |
| Mangoes | Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Antioxidants | Protects against oxidative stress |
https://youtube.com/watch?v=eating-for-a-healthy-immune-system
Which fruit gives the highest immunity?

There is no single fruit that definitively provides the "highest" immunity. Immunity is a complex system influenced by many factors including genetics, lifestyle, and overall diet. While certain fruits are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support immune function, attributing "highest immunity" to one fruit is inaccurate and misleading. A diverse diet rich in various fruits and vegetables is key to optimal immune health.
Which Nutrients Support Immunity?
Many fruits contain vital nutrients that contribute to a robust immune system. Vitamin C, found abundantly in citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, is crucial for the production and function of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Antioxidants, such as those present in berries, help combat oxidative stress that can weaken the immune system. Fiber, plentiful in many fruits, supports gut health, which plays a significant role in immune function. A balanced approach is paramount, focusing on consuming a range of fruits rich in different nutrients.
- Vitamin C: Crucial for white blood cell production.
- Antioxidants: Protect against cell damage and inflammation.
- Fiber: Promotes a healthy gut microbiome essential for immunity.
The Role of Antioxidants in Immune Support
Antioxidants, found in high concentrations in many fruits, are potent defenders against free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells and weaken the immune system. Fruits like blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries are particularly rich in antioxidants. These compounds help protect immune cells and reduce inflammation, contributing to a healthier immune response. While not directly boosting immunity, they play a vital supporting role in maintaining a strong defense system.
- Blueberries: Rich in anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants.
- Cranberries: High in proanthocyanidins, beneficial for urinary tract health.
- Strawberries: Contain various antioxidants, including vitamin C.
The Importance of Vitamin C for Immunity
Vitamin C is a well-known immune-boosting nutrient. It's essential for the synthesis of collagen, a crucial component of connective tissue, and it plays a key role in the production and function of white blood cells. Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are excellent sources of vitamin C. However, it's vital to remember that obtaining vitamin C from various sources, including other fruits and vegetables, is more beneficial than relying solely on one fruit.
- Oranges: A classic source of readily available vitamin C.
- Grapefruits: Another good source of vitamin C and other antioxidants.
- Lemons: High in vitamin C and beneficial for hydration.
Beyond Vitamins: The Impact of Fiber on Immunity
The gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms living in your intestines, plays a substantial role in immune function. Fiber, found in many fruits, acts as prebiotic food for beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome helps to regulate inflammation and enhances the effectiveness of the immune system. Fruits rich in fiber, such as apples, pears, and bananas, contribute to a healthy gut, indirectly supporting immunity.
- Apples: A good source of pectin, a type of soluble fiber.
- Pears: Contain both soluble and insoluble fiber.
- Bananas: A good source of resistant starch, which acts as a prebiotic.
Considering Other Dietary Factors
While fruits contribute significantly to immune health, it is crucial to understand that immunity is not solely determined by fruit consumption. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is vital for optimal immune function. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and hydration are also essential components of a healthy immune system.
- Vegetables: Provide a range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Whole grains: Offer fiber and essential nutrients.
- Lean proteins: Support cell repair and growth.
What foods boost your immune system?
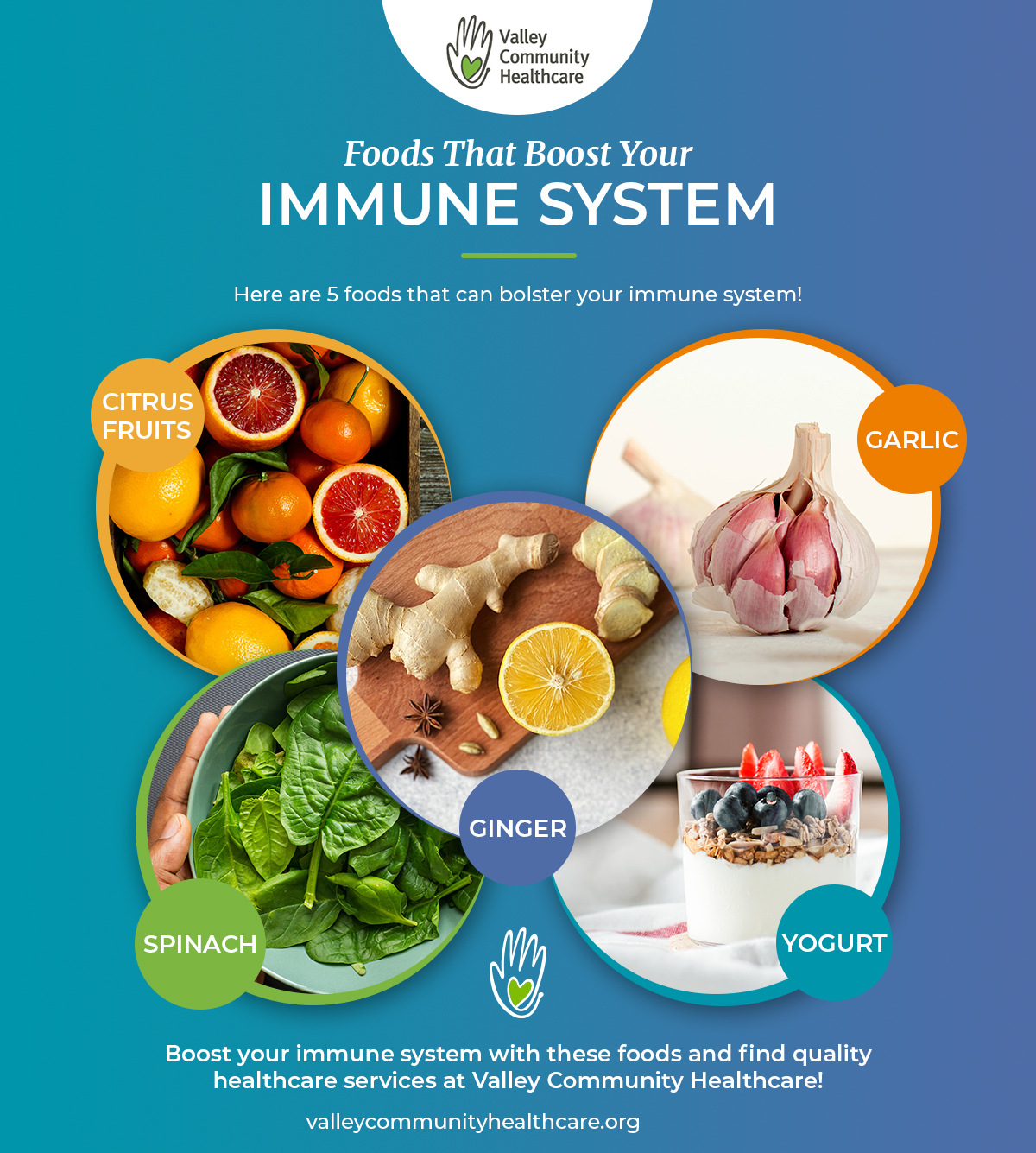
What Foods Boost Your Immune System?
A strong immune system is crucial for fighting off infections and maintaining overall health. While no single food magically grants immunity, incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into your diet can significantly support your body's natural defenses. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to various immune functions, from cell production to antibody creation. A balanced approach focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is key.
Fruits and Vegetables Rich in Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant vital for immune function. It's crucial for the production and function of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. A deficiency in Vitamin C can impair immune responses, making you more susceptible to illness. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your daily diet ensures you get a sufficient intake of Vitamin C.
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons): Excellent sources of Vitamin C.
- Bell peppers (especially red): Contain even more Vitamin C than citrus fruits.
- Dark leafy greens (kale, spinach): Provide Vitamin C along with other important nutrients.
Foods High in Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune regulation. It helps regulate the activity of immune cells, reducing the risk of infections. While sunlight is a primary source, many people are deficient, so dietary sources are important. Supplementing with Vitamin D might be necessary depending on your location and lifestyle, but consult a doctor before starting any supplement regimen.
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel): Naturally rich in Vitamin D.
- Egg yolks: Contain a moderate amount of Vitamin D.
- Fortified foods (milk, cereals): Check labels for added Vitamin D.
Foods Packed with Zinc
Zinc is a mineral essential for immune cell function. It's involved in various immune processes, including cell growth, wound healing, and antibody production. Zinc deficiency weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. Ensure your diet contains adequate amounts of zinc for optimal immune health.
- Oysters: Exceptionally high in zinc.
- Red meat: A good source of zinc.
- Legumes (beans, lentils): Contain a decent amount of zinc.
Probiotic-Rich Foods
Probiotics are live microorganisms, mainly bacteria, that benefit your gut health. A healthy gut is crucial for a strong immune system as a large part of your immune system resides in your gut. Probiotics aid in maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria, thus supporting immune function.
- Yogurt (especially those with live and active cultures).
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink similar to yogurt.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage rich in probiotics.
Foods High in Beta-Carotene
Beta-carotene is a type of carotenoid that your body converts into Vitamin A, another crucial nutrient for immune function. Vitamin A plays a vital role in the maintenance of mucous membranes and skin, which are the body's first lines of defense against pathogens. A diverse diet rich in beta-carotene-rich foods strengthens these barriers, further protecting your immune system.
- Sweet potatoes: A great source of beta-carotene.
- Carrots: High in beta-carotene.
- Spinach: Contains a good amount of beta-carotene.
How can I boost my immune system asap?

There's no single magic bullet to instantly boost your immune system. However, you can take steps to support its function relatively quickly. It's crucial to understand that "boosting" your immune system isn't about making it stronger in the sense of creating superpowers, but rather optimizing its existing capabilities to function effectively. Rapid immune system support focuses on reducing stressors and providing the necessary building blocks for optimal function. Significant changes take time, but you can make a difference relatively quickly with the right approach.
Prioritize Sleep
Getting enough sleep is paramount for immune function. Sleep deprivation weakens your immune response, making you more susceptible to illness. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Consistency is key; try to go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Establish a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Create a dark, quiet, and cool sleeping environment.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed.
Hydrate Effectively
Dehydration significantly impacts immune function. Water is crucial for transporting immune cells throughout the body and flushing out toxins. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you're sweating or exercising. Avoid sugary drinks which can actually dehydrate you.
- Carry a reusable water bottle and sip on it regularly.
- Eat fruits and vegetables with high water content (e.g., watermelon, cucumber).
- Listen to your body; drink when you feel thirsty.
Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in immune function. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support immune cell production and activity. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats.
- Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Incorporate lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress weakens the immune system. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, yoga, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Even short bursts of stress-reducing activities can make a difference.
- Practice deep breathing exercises.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Prioritize activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Consider Supplements (With Caution)
While a balanced diet should provide most necessary nutrients, some supplements may offer additional support. However, always consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. Some commonly discussed supplements include Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Zinc, and Elderberry. These should be viewed as complementary, not replacement, to a healthy lifestyle.
- Choose reputable brands with third-party testing.
- Follow recommended dosage instructions carefully.
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications.
Is banana good for the immune system?

Bananas contain several nutrients that contribute to immune function, but they aren't a miracle cure. Their benefits are primarily due to their content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While they don't directly boost the immune system in a dramatic way, their contribution to overall health indirectly supports immune function. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables is much more impactful than relying on a single food. The immune system is complex and needs a range of nutrients for optimal performance; bananas contribute to this, but shouldn't be considered a primary immune booster.
Vitamins and Minerals in Bananas for Immune Support
Bananas are a good source of vitamin C and vitamin B6, both crucial for immune function. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage, while vitamin B6 is involved in the production of antibodies and other immune cells. Furthermore, bananas contain potassium, an essential electrolyte important for maintaining healthy cell function, including those of the immune system. They also provide small amounts of other minerals like magnesium and manganese.
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant, vital for white blood cell function.
- Vitamin B6: Essential for antibody production and immune cell development.
- Potassium: Important electrolyte crucial for cell function and immune system processes.
Antioxidants in Bananas and Immune Health
Bananas contain antioxidants, including dopamine, which helps protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation. Reducing oxidative stress through antioxidants, as found in bananas, can support a healthy immune response. However, it's important to note that antioxidants are just one piece of the puzzle; a variety of other nutrients and lifestyle factors also play a critical role in overall immune health.
- Dopamine: Acts as an antioxidant, combatting free radicals.
- Other antioxidants: Contribute to reducing oxidative stress, supporting a healthy immune response.
- Importance of Dietary Variety: A diverse range of antioxidants from different fruits and vegetables is most beneficial.
Fiber's Role in Immune System Function
Bananas are a decent source of dietary fiber. Fiber promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which is increasingly recognized as an essential component of a robust immune system. A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is vital for proper immune regulation. The fiber in bananas helps feed beneficial bacteria in the gut, contributing to a healthy gut environment. However, it is crucial to remember that fiber alone is insufficient for optimal immune health; it needs to be part of a holistic approach.
- Prebiotics: Bananas contain prebiotics that feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Gut Microbiome: A healthy gut microbiome is essential for immune regulation.
- Fiber's Impact: Fiber aids in maintaining a balanced gut ecosystem.
The Limitations of Bananas for Immune Support
While bananas offer some nutrients beneficial to immune function, they are not a substitute for a balanced diet or other crucial aspects of immune health. They lack certain essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A or zinc, that are also critical for immune system performance. Focusing solely on bananas for immune support would be neglecting other vital components of a healthy lifestyle.
- Not a complete immune booster: Bananas lack several nutrients critical for immune function.
- Holistic approach is necessary: Balanced diet, exercise, and stress management are crucial.
- Other nutrient sources are required: Various fruits, vegetables, and other foods offer a broader range of essential vitamins and minerals.
Overall Impact on Immune Health
Bananas can be considered a part of a healthy diet that supports overall well-being, which indirectly contributes to immune function. They provide some beneficial nutrients, but their contribution to immune health is modest compared to a diverse and balanced diet along with other lifestyle factors. Overreliance on a single food for immune support is not advised; a more comprehensive approach is essential for optimal health.
- Part of a healthy diet: Bananas contribute to overall well-being, indirectly supporting immune health.
- Modest contribution: Their impact on immune function is minor compared to a holistic approach.
- Comprehensive approach: Balanced nutrition, lifestyle choices, and adequate rest are crucial.
Which fruits are best for boosting the immune system?
Many fruits contribute to a strong immune system, but some stand out due to their high concentration of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are excellent sources of Vitamin C, a crucial nutrient for immune cell function. Vitamin C aids in the production of white blood cells, which are the body's primary defense against infection. Berries, including strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are packed with antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage. These antioxidants help to strengthen the immune response and reduce inflammation. Pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties that can support immune function. Mangoes are rich in Vitamin C and beta-carotene, a precursor to Vitamin A, which is also vital for maintaining healthy immune function. It’s important to remember that no single fruit provides all the necessary nutrients; a varied diet including a wide range of fruits and vegetables is crucial for optimal immune support.
Are there any fruits I should avoid if I have a weakened immune system?
While most fruits are beneficial for overall health, including immune function, some precautions should be taken, especially if you have a compromised immune system. Fruits that are unwashed or improperly stored can harbor harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Thoroughly washing all fruits before consumption is crucial. If you have specific health concerns or a weakened immune system, it's always recommended to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes. They can advise you on the specific fruits and amounts that are suitable for your particular situation. They can also guide you on how to safely prepare and handle fruits to minimize the risk of infections. Additionally, individuals with certain allergies should avoid fruits that trigger their allergic reactions. These reactions can compromise the immune system and exacerbate health problems.
How many servings of fruit should I eat daily to support my immune system?
The recommended daily intake of fruits varies depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health. However, general guidelines suggest that most adults should aim for at least two servings of fruit per day as part of a balanced diet. One serving is typically considered to be about one medium-sized fruit, such as an apple or banana, or half a cup of berries or sliced fruit. Eating a variety of fruits is important to obtain a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While increasing fruit intake can be beneficial for immune support, it’s crucial to remember that moderation is key. Excessive consumption of certain fruits can lead to unwanted side effects, such as digestive upset. A balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats provides a holistic approach to immune system strengthening. It is always best to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and health status.
Can I solely rely on fruit to boost my immune system?
While fruit plays a vital role in supporting a strong immune system due to its high concentration of essential nutrients, it's inaccurate to assume that fruit alone is sufficient for optimal immune function. A robust immune system relies on a combination of factors, including a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, adequate sleep, regular exercise, stress management, and hydration. Other essential nutrients, such as zinc, selenium, and Vitamin D, are crucial for immune function and aren’t primarily found in fruit. These can be obtained from other food sources, supplements (under medical guidance), and a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, while incorporating a variety of fruits into your diet is essential for immune support, it should be part of a broader holistic approach to health and well-being. Ignoring other crucial aspects of a healthy lifestyle can limit the effectiveness of even the most nutrient-rich fruit intake.
Deja una respuesta