Is coffee bad for lupus

Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect many parts of the body, including the joints, skin, kidneys, and heart. It is caused by the immune system attacking the body's own tissues.
One of the common symptoms of lupus is fatigue. Many people with lupus find it difficult to get through the day without feeling tired. This can make it difficult to work, go to school, or participate in other activities.
Coffee is a popular beverage that can help to improve energy levels. However, there is some concern that coffee may be bad for people with lupus. This is because coffee can contain caffeine, which is a stimulant. Caffeine can cause anxiety, insomnia, and other problems in people with lupus.
In this article, we will explore the evidence on whether coffee is bad for lupus. We will also provide tips on how to enjoy coffee without worsening your symptoms.
Is Coffee Bad for People with Lupus?
The relationship between coffee consumption and lupus is complex and not fully understood. While some studies suggest potential negative effects, others show no significant correlation or even potential benefits. It's crucial to remember that every individual with lupus is different, and what affects one person may not affect another. Individual responses to caffeine vary widely, and it's essential to pay attention to your own body's reaction.
Caffeine's Impact on Inflammation
Lupus is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation. Caffeine has been shown to have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects, depending on various factors such as dosage, individual sensitivity, and the type of inflammatory process involved. Some studies suggest that high caffeine intake might exacerbate inflammation in certain individuals, potentially worsening lupus symptoms. However, other research indicates that moderate caffeine consumption might have anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in relation to certain types of inflammation unrelated to lupus. More research is needed to clarify the specific effects of caffeine on lupus-related inflammation.
Caffeine and Lupus Medications
Caffeine can interact with some medications commonly prescribed for lupus. For example, it might affect the metabolism or effectiveness of certain drugs, potentially leading to either reduced efficacy or increased side effects. It's crucial to discuss your coffee consumption with your doctor or rheumatologist, especially if you are taking medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. They can help assess any potential interactions and advise on safe caffeine limits based on your individual circumstances and medication regimen.
The Role of Antioxidants
Coffee is a rich source of antioxidants, which are compounds that can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of lupus. Therefore, the antioxidant properties of coffee might offer some protective effects. However, the balance between potential benefits from antioxidants and potential negative effects from caffeine's influence on inflammation needs further investigation in the context of lupus.
Individual Tolerance and Symptoms
Individual responses to caffeine are highly variable. Some people with lupus may experience a worsening of their symptoms after consuming coffee, such as increased fatigue, joint pain, or skin rashes. Others might not notice any significant changes. It is essential to carefully monitor your own body's response to caffeine and adjust your intake accordingly. Keep a journal to track your coffee consumption and any associated symptoms to identify potential patterns.
Recommended Approach
The best approach is to consult your doctor or rheumatologist before making significant changes to your caffeine intake, especially if you have lupus. They can consider your individual health status, medication regimen, and any existing symptoms to determine if modifying your coffee consumption is necessary or beneficial. They might also recommend keeping a detailed diary to monitor your responses to different levels of caffeine intake.
| Factor | Potential Effect | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine Intake | May exacerbate inflammation in some; potential antioxidant benefits in others. | Individual variation; moderate consumption may be acceptable for some. |
| Medication Interactions | Caffeine can interact with certain lupus medications. | Discuss coffee consumption with your doctor. |
| Oxidative Stress | Coffee's antioxidants might counteract oxidative stress. | Balance between antioxidant and inflammatory effects needs further research. |
| Symptoms | Monitor your response to caffeine; keep a journal. | Adjust intake based on individual reactions. |
Is Coffee Bad for People with Lupus?
The relationship between coffee consumption and lupus is complex and not fully understood. While some studies suggest potential negative effects, others show no significant correlation or even potential benefits. It's crucial to remember that every individual with lupus is different, and what affects one person may not affect another. Individual responses to caffeine vary widely, and it's essential to pay attention to your own body's reaction.
Caffeine's Impact on Inflammation
Lupus is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation. Caffeine has been shown to have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects, depending on various factors such as dosage, individual sensitivity, and the type of inflammatory process involved. Some studies suggest that high caffeine intake might exacerbate inflammation in certain individuals, potentially worsening lupus symptoms. However, other research indicates that moderate caffeine consumption might have anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in relation to certain types of inflammation unrelated to lupus. More research is needed to clarify the specific effects of caffeine on lupus-related inflammation.
Caffeine and Lupus Medications
Caffeine can interact with some medications commonly prescribed for lupus. For example, it might affect the metabolism or effectiveness of certain drugs, potentially leading to either reduced efficacy or increased side effects. It's crucial to discuss your coffee consumption with your doctor or rheumatologist, especially if you are taking medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. They can help assess any potential interactions and advise on safe caffeine limits based on your individual circumstances and medication regimen.
The Role of Antioxidants
Coffee is a rich source of antioxidants, which are compounds that can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of lupus. Therefore, the antioxidant properties of coffee might offer some protective effects. However, the balance between potential benefits from antioxidants and potential negative effects from caffeine's influence on inflammation needs further investigation in the context of lupus.
Individual Tolerance and Symptoms
Individual responses to caffeine are highly variable. Some people with lupus may experience a worsening of their symptoms after consuming coffee, such as increased fatigue, joint pain, or skin rashes. Others might not notice any significant changes. It is essential to carefully monitor your own body's response to caffeine and adjust your intake accordingly. Keep a journal to track your coffee consumption and any associated symptoms to identify potential patterns.
Recommended Approach
The best approach is to consult your doctor or rheumatologist before making significant changes to your caffeine intake, especially if you have lupus. They can consider your individual health status, medication regimen, and any existing symptoms to determine if modifying your coffee consumption is necessary or beneficial. They might also recommend keeping a detailed diary to monitor your responses to different levels of caffeine intake.
| Factor | Potential Effect | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine Intake | May exacerbate inflammation in some; potential antioxidant benefits in others. | Individual variation; moderate consumption may be acceptable for some. |
| Medication Interactions | Caffeine can interact with certain lupus medications. | Discuss coffee consumption with your doctor. |
| Oxidative Stress | Coffee's antioxidants might counteract oxidative stress. | Balance between antioxidant and inflammatory effects needs further research. |
| Symptoms | Monitor your response to caffeine; keep a journal. | Adjust intake based on individual reactions. |
What foods trigger lupus flare-ups?
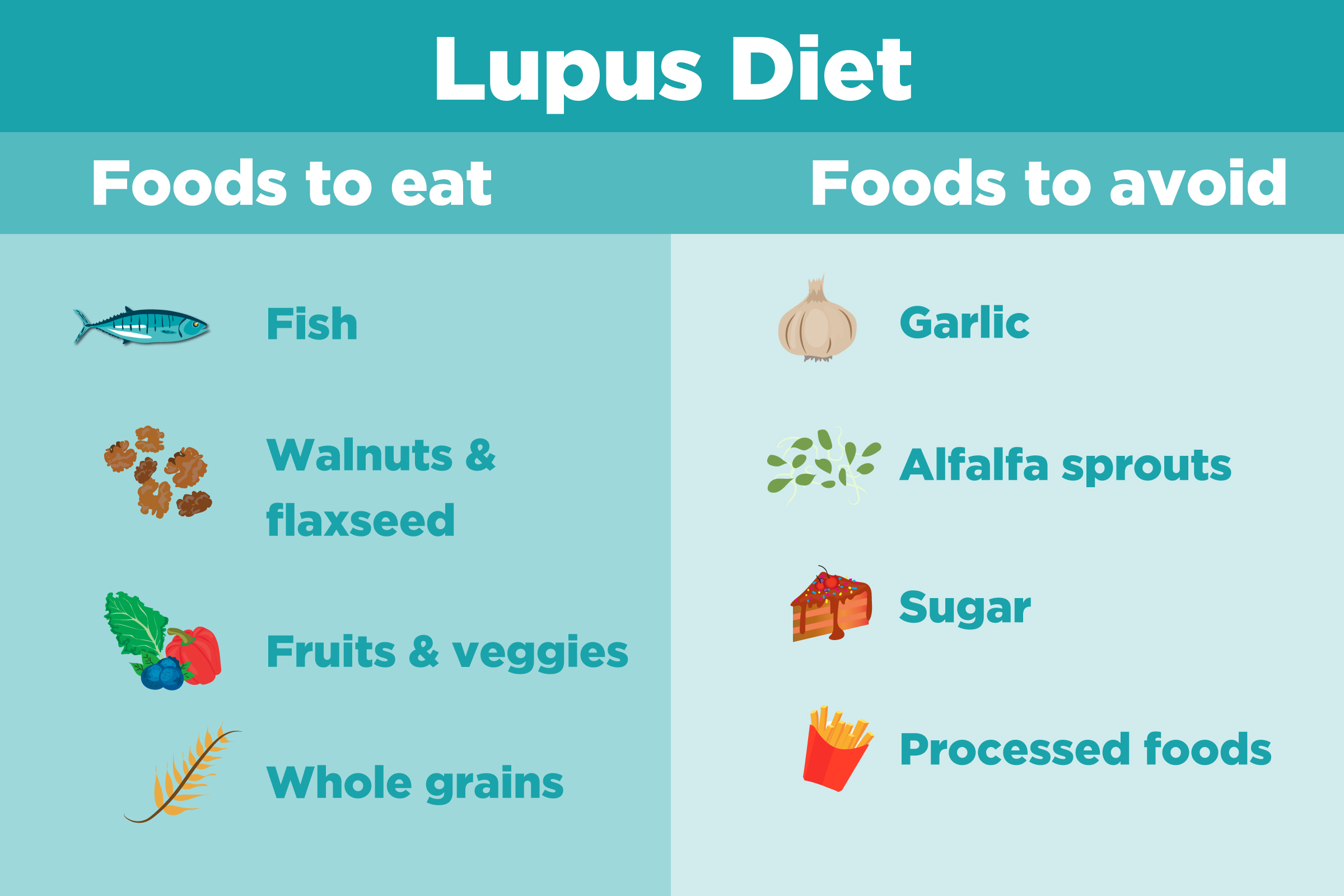
What Foods Trigger Lupus Flare-Ups?
There's no single definitive list of foods that trigger lupus flare-ups in every individual. The relationship between diet and lupus is complex and highly personalized. What might exacerbate symptoms in one person might have no effect on another. However, certain food groups and specific components are frequently associated with increased inflammation and are therefore suspected of potentially triggering or worsening lupus symptoms. These are often foods high in certain compounds that contribute to inflammation in the body. It's crucial to work closely with your doctor or a registered dietitian to identify any potential dietary triggers specific to your body and condition.
High-Processed Foods
Processed foods are often packed with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients that can fuel inflammation throughout the body. These processed foods often lack essential nutrients and fiber, further contributing to an imbalanced diet. For individuals with lupus, reducing inflammation is crucial for managing symptoms, and avoiding highly processed foods can be a beneficial step.
- Sugary drinks: Sodas, juices, and sweetened beverages.
- Processed meats: Sausages, bacon, hot dogs, and deli meats.
- Packaged snacks: Chips, cookies, and pastries.
Foods High in Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated and trans fats are known to contribute to systemic inflammation, potentially exacerbating lupus symptoms. These fats are found abundantly in fried foods, baked goods made with shortening or lard, and many processed foods. Minimizing your intake of these fats can be beneficial in managing your condition.
- Fried foods: French fries, fried chicken, and other deep-fried items.
- Baked goods with shortening or lard: Many commercially-produced pastries and cookies.
- Processed snacks containing partially hydrogenated oils.
Foods High in Omega-6 Fatty Acids
While omega-6 fatty acids are essential nutrients, an imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids can promote inflammation. Many processed foods, vegetable oils (like corn, soybean, and sunflower oil), and certain nuts and seeds are high in omega-6s. Maintaining a balance with omega-3s from sources like fatty fish is key. Excessive omega-6 intake might worsen lupus symptoms in some individuals.
- Vegetable oils: Corn oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil.
- Mayonnaise and salad dressings: Many contain high levels of omega-6 oils.
- Certain nuts and seeds: Although nutritious, moderation is key.
Gluten-Containing Foods
While not definitively linked to lupus flare-ups in all individuals, some individuals with lupus may find that gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, can trigger or exacerbate their symptoms. This is potentially due to increased intestinal permeability ("leaky gut") which is thought to be implicated in autoimmune diseases. A gluten-free diet may be beneficial for some lupus patients, though this should be undertaken under medical supervision. This is highly individualized.
- Wheat products: Bread, pasta, pastries.
- Barley: Found in some beers and soups.
- Rye: Often used in breads and cereals.
Nightshades
Nightshade vegetables, such as tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, and peppers, contain compounds called alkaloids that some people find inflammatory. Anecdotally, some lupus patients report an improvement in symptoms after eliminating nightshades from their diet. However, this effect is not consistently proven. This needs to be carefully assessed as part of an individualised dietary plan.
- Tomatoes: Fresh, canned, or processed.
- Potatoes (white and red): Especially fried or processed.
- Eggplant: In various dishes.
Is drinking coffee bad for autoimmune disease?

The relationship between coffee consumption and autoimmune diseases is complex and not fully understood. While some studies suggest potential negative impacts, others point to potential benefits, and many show no significant correlation. The effects likely vary greatly depending on the specific autoimmune disease, the individual's genetic predisposition, the amount of coffee consumed, and other lifestyle factors. There's no definitive answer as to whether coffee is universally harmful or beneficial for people with autoimmune diseases. More research is needed to establish clear guidelines.
Coffee's Impact on Inflammation
Inflammation plays a central role in many autoimmune diseases. Coffee contains various compounds, including antioxidants, that may influence inflammation. Some studies suggest that moderate coffee consumption might have anti-inflammatory effects, while excessive intake could potentially exacerbate inflammation. The impact on inflammation is highly individual and depends on factors like the type and amount of coffee, as well as the individual's overall health and genetic makeup.
- Antioxidant properties: Coffee is rich in antioxidants, which can combat oxidative stress and potentially reduce inflammation.
- Potential for increased inflammation: High coffee consumption might stimulate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in some individuals.
- Individual variation: The impact of coffee on inflammation varies greatly depending on genetic predisposition and other lifestyle factors.
Coffee and the Immune System
Coffee's influence on the immune system is another area of ongoing research. Some studies indicate that coffee consumption might modulate immune responses, potentially both positively and negatively depending on the dosage and the specific immune cell types involved. The complexity of the immune system makes it difficult to draw simple conclusions about coffee's overall effect. Moreover, the type of coffee (e.g., caffeinated vs. decaffeinated) may also play a role.
- Modulation of immune cells: Coffee can influence the activity of various immune cells, like lymphocytes and macrophages.
- Potential for immune suppression: In some cases, high coffee intake may suppress immune responses.
- Potential for immune stimulation: In other instances, coffee might enhance certain aspects of immune function.
Specific Autoimmune Diseases and Coffee
The effects of coffee can differ significantly depending on the specific autoimmune disease. For example, research on coffee and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has yielded mixed results, with some studies showing no correlation while others suggest a potential protective effect of moderate consumption. Research needs to be conducted on a disease-specific basis to determine the true impact of coffee. Generalizations about all autoimmune diseases are not necessarily accurate.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Studies on coffee and RA have yielded inconsistent results.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Research on the effect of coffee on Type 1 diabetes is limited.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The relationship between coffee consumption and MS remains largely unclear.
Individual Tolerance and Genetic Factors
Individual responses to coffee consumption vary widely due to genetic factors. Genetic variations influence how the body metabolizes caffeine and other compounds in coffee, which can affect the impact on the immune system and the degree of inflammation. This explains why some people with autoimmune diseases may tolerate coffee well, while others experience negative symptoms. Personal experimentation and careful monitoring are crucial.
- Caffeine metabolism: Genetic variations influence how quickly the body processes caffeine.
- Genetic predisposition to inflammation: Genetic factors can determine susceptibility to inflammation.
- Individual responses: There is substantial variation in individual reactions to coffee, even among those with similar autoimmune conditions.
The Role of Other Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors beyond coffee consumption also significantly influence autoimmune disease management. Diet, exercise, stress levels, and sleep quality all interact to influence inflammation and immune function. The effect of coffee on autoimmune diseases is likely intertwined with these other factors, making it difficult to isolate the impact of coffee alone. A holistic approach to health management is advisable.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support immune health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation, impacting autoimmune diseases.
What not to drink if you have lupus?

What Not to Drink if You Have Lupus
Alcohol
Alcohol can exacerbate several lupus symptoms. It's a known immune system depressant, potentially worsening inflammation and fatigue, two common lupus challenges. Excessive alcohol consumption can also interfere with medication effectiveness and contribute to liver problems, a concern for individuals already managing a chronic illness. Avoid excessive alcohol intake, and consider consulting your doctor about safe limits or complete abstinence.
- Increased inflammation: Alcohol can trigger or worsen inflammatory responses throughout the body.
- Medication interactions: Alcohol can negatively interact with many lupus medications, reducing their efficacy or increasing side effects.
- Liver stress: Lupus can already put a strain on the liver; alcohol adds further burden.
Caffeinated Beverages
While a moderate amount of caffeine might seem harmless, excessive caffeine consumption can trigger or worsen several lupus symptoms. Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase anxiety, heart palpitations, and insomnia, all of which are common issues for lupus patients. Reducing your caffeine intake can significantly improve sleep quality, reduce anxiety, and promote overall well-being.
- Sleep disruption: Caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns, worsening fatigue.
- Increased anxiety: Caffeine's stimulant properties can heighten feelings of anxiety and nervousness.
- Exacerbated heart palpitations: Caffeine can increase heart rate, potentially problematic for individuals with lupus-related cardiac issues.
Sugary Drinks
Sugary drinks, including sodas, juices, and sweetened teas, contribute to inflammation and weight gain, both detrimental to lupus management. High sugar intake is linked to increased oxidative stress, further compromising the immune system. Opting for water, unsweetened tea, or other healthy alternatives is crucial for better lupus management.
- Weight gain: Excess sugar contributes to weight gain, potentially impacting joint pain and overall health.
- Increased inflammation: Sugar consumption has been linked to increased systemic inflammation.
- Oxidative stress: High sugar levels can increase oxidative stress, harming cells and tissues.
Energy Drinks
Energy drinks often contain high levels of caffeine, sugar, and other stimulants, creating a perfect storm for lupus symptoms. The combined effects of these ingredients can exacerbate anxiety, insomnia, heart palpitations, and inflammation. Completely avoiding energy drinks is advisable for lupus patients.
- High caffeine content: Contributes to sleep problems, anxiety, and heart palpitations.
- High sugar content: Promotes inflammation and weight gain.
- Other stimulants: Can further stress the immune system and exacerbate symptoms.
Artificial Sweeteners
While marketed as healthier alternatives to sugar, some artificial sweeteners have been linked to potential negative health consequences, although research is still ongoing. Some individuals report experiencing worsened symptoms after consuming artificial sweeteners. Limiting or avoiding artificial sweeteners might be a prudent approach until more research clarifies their long-term effects on those with lupus.
- Uncertain long-term effects: Research on the long-term impact of artificial sweeteners is still limited.
- Individual sensitivities: Some lupus patients report experiencing worsened symptoms after consuming artificial sweeteners.
- Potential digestive issues: Some artificial sweeteners can contribute to digestive problems.
What is the enemy of lupus?

There isn't a single "enemy" of lupus in the sense of a cure or a specific substance that eliminates it. Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease with varied presentations and unpredictable behavior. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flares. Progress is being made in understanding its underlying mechanisms, leading to the development of more targeted therapies. However, a complete eradication remains elusive.
Effective Lupus Treatments: The Closest to an "Enemy"
While not an enemy in the traditional sense, effective treatments can significantly mitigate lupus's impact. These aim to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms like fatigue and joint pain, and prevent organ damage. Successful management is often considered the closest thing to defeating the disease for an individual. The specific treatment plan varies greatly depending on the individual's symptoms and the organs affected.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications suppress the overactive immune system, reducing inflammation. Examples include corticosteroids (like prednisone), methotrexate, and azathioprine.
- Biologics: These targeted therapies are designed to block specific components of the immune system involved in lupus. Examples include belimumab and rituximab.
- Antimalarials: These drugs, such as hydroxychloroquine, are often used to manage skin and joint symptoms.
Research and Understanding: The Path to a Future "Enemy"
Ongoing research is crucial in developing more effective treatments and potentially a cure for lupus. Scientists are exploring various avenues, including: investigating the genetic factors contributing to lupus, identifying specific immune pathways involved, and testing novel therapies. These efforts are paving the way toward a deeper understanding of the disease's mechanisms.
- Genetic studies: Identifying genes linked to lupus susceptibility helps in understanding the disease's predisposition.
- Immunological research: Investigating the specific immune cells and molecules involved in lupus pathogenesis is vital in designing targeted treatments.
- Development of new therapies: Testing novel drug candidates, such as gene therapies and immunomodulators, offers hope for future breakthroughs.
Lifestyle Modifications: Supporting the Body's Fight
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing lupus and improving quality of life. Although not a direct “enemy”, adopting healthy habits can help mitigate symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of flares. A holistic approach combining medical treatments with these modifications is often the most effective strategy.
- Stress management: Lupus flares can be exacerbated by stress, so techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can be beneficial.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can support the immune system and overall health.
- Regular exercise: Gentle exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve physical fitness and reduce fatigue, while avoiding overexertion.
Early Diagnosis and Monitoring: A Proactive Approach
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical in managing lupus effectively and preventing long-term complications. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, potentially preventing severe flares and organ damage. This proactive approach is essential for controlling the disease's progression.
- Prompt medical attention: Seeking medical evaluation for any concerning symptoms is crucial for early detection.
- Regular check-ups: Consistent monitoring allows for early identification of flares and potential complications.
- Collaboration with healthcare team: Working closely with doctors, rheumatologists, and other specialists ensures comprehensive care and personalized treatment strategies.
Patient Advocacy and Support: Building a Community
Strong patient support networks can provide invaluable emotional, informational, and practical assistance to individuals living with lupus. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can foster a sense of community and shared understanding, which can significantly improve quality of life and resilience in managing the disease.
- Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Online communities: Online forums and social media groups offer opportunities for connection and information sharing.
- Advocacy organizations: Organizations dedicated to lupus research and patient support provide resources and advocate for improved treatment and care.
Does coffee worsen lupus symptoms?
The relationship between coffee consumption and lupus symptoms is complex and not fully understood. While there's no definitive scientific consensus stating that coffee directly worsens lupus, some individuals report experiencing exacerbated symptoms after consuming caffeine. This could be due to several factors. Firstly, caffeine is a stimulant that can increase inflammation, and lupus is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation. This means that for some people with lupus, the inflammatory response triggered by caffeine might lead to a flare-up of symptoms like joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes. However, it's crucial to note that this effect isn't universal. Many individuals with lupus can consume moderate amounts of coffee without experiencing negative consequences. Secondly, the impact of caffeine can be influenced by individual factors such as the severity of the lupus, the presence of other health conditions, and the person's overall sensitivity to caffeine. Finally, the type and amount of coffee consumed also matters. A large, highly caffeinated coffee might have a more significant effect than a small cup of decaf. Therefore, while coffee might trigger negative symptoms in some lupus patients, it's not inherently detrimental for everyone. Individual tolerance and careful monitoring of one's own response are key.
Can coffee interfere with lupus medications?
There's limited research directly exploring the interaction between coffee and specific lupus medications. However, caffeine's potential to affect the body's metabolism and absorption of certain drugs raises a concern. Caffeine is a known metabolic stimulant, potentially altering how the liver processes medications. This could lead to either a decreased or increased efficacy of the lupus treatment, or even increase the risk of side effects. For example, some medications used to treat lupus are known to be metabolized by the liver via specific enzymes. If caffeine interferes with these enzymes, it could affect the drug's effectiveness. Furthermore, caffeine can interact with other medications individuals with lupus may be taking for related symptoms such as corticosteroids or pain relievers. It's crucial to discuss your coffee consumption with your rheumatologist or prescribing physician, particularly if you are on multiple medications. They can assess the potential for interactions and advise on the appropriate level of caffeine intake, considering your specific medications and health status. Self-medication and disregarding professional advice can be harmful.
Is it better to avoid coffee entirely if I have lupus?
The decision of whether or not to avoid coffee completely with lupus is a personal one and should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. While some individuals with lupus may experience adverse reactions to coffee, others tolerate it without issue. There's no blanket recommendation to eliminate coffee entirely. A more practical approach involves careful self-monitoring. If you suspect coffee is worsening your symptoms, consider reducing your intake gradually and observing any changes. Keeping a symptom diary can help track potential links between coffee consumption and symptom flares. This diary can be valuable information to discuss with your doctor. Remember that the amount of coffee consumed matters; switching to decaf coffee or significantly reducing your caffeine intake might be a more suitable approach than complete abstinence, especially if you enjoy coffee and see no adverse effects from moderate consumption. Listen to your body and communicate your observations to your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Are there any alternatives to coffee for lupus patients?
If you find coffee negatively impacts your lupus symptoms, several caffeine-free alternatives can provide a similar morning ritual or energy boost. Herbal teas such as chamomile, ginger, or peppermint can be soothing and calming. These often contain antioxidants with potential anti-inflammatory properties that may even be beneficial for managing lupus symptoms (although this requires more research). Decaf coffee offers a compromise, allowing you to enjoy the taste and ritual of coffee without the high caffeine content. However, it's important to note that even decaf coffee can contain small amounts of caffeine. Other options include warm milk with a touch of honey or spices, fruit infused water, or even naturally sweetened juices (in moderation). Ultimately, finding the right alternative depends on individual preferences and tolerance. Experiment with different options to discover what works best for you, keeping in mind that moderation is generally advisable. Consult your doctor before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Deja una respuesta